Implementation of a Pharmacist-Managed Transitions of Care Tool
Purpose: To improve, expand, and sustain a pharmacist-based transitions of care (TOC) program and to assess interventions targeting veterans at high risk for adverse outcomes.
Methods: A TOC program was developed and piloted at the Richard L. Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center (RLRVAMC). Following success of the pilot project, targeted interventions were identified to improve and expand the program. Patients deemed high risk for readmission by an acute care pharmacist were identified and referred for continued postdischarge follow-up. The study population included patients discharged to the community with primary care established within the RLRVAMC system. Eligible patients were entered into a TOC database by the referring acute care pharmacist. A pharmacist in the primary care clinic reviewed then contacted the patient within 1 week of discharge. Appropriate documentation of each visit was completed in the electronic health record. Data collection included background information, time to follow-up, medication discrepancies, pharmacist interventions, emergency department visits, and hospital readmissions.
Results: A total of 139 patients were included, of which 99 patients were reached for pharmacist follow-up. There were 43 medication-related discrepancies among all patients. The most common discrepancy was taking the wrong dose of a prescribed medication. Additional counseling was provided to 75% of patients. The subset of patients who were reached by a pharmacist had decreased index (5.1% vs 15.0%; P = .049) and all-cause readmissions (8.1% vs 27.5%; P = .03) at 30 days compared with those who did not received pharmacist follow-up, respectively.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that implementation and expansion of a pharmacist-based TOC process is effective in communicating high-risk patients and intervening on medication-related issues postdischarge.
Data Collection
A retrospective chart review was completed on patients entered into the tool. Data were collected and kept in a secured Microsoft Excel workbook. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using either a χ2 for nominal data or Student t test for continuous data. The primary outcomes were analyzed using a χ2 test. All statistical tests were analyzed using MiniTab 19 Statistical Software.
Results
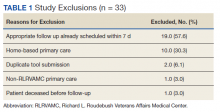
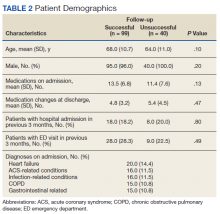
Pharmacists added 172 patients into the TOC tool; 139 patients met inclusion criteria. Of those excluded, most were because the PACT pharmacist did not attempt to contact the patient since they already had a primary care visit scheduled postdischarge (Table 1). Of the 139 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 99 were successfully contacted by a PACT pharmacist. Most patients were aged in their 60s, male, and white. Both groups had a similar quantity of outpatient medications on admission and medication changes made at discharge. Additionally, both groups had a similar number of patients with hospitalizations and/or ED visits in the 3 months before hospital admission that resulted in TOC tool referral (Table 2).
Hospital Readmission
Hospital 30-day readmission rates for patients who were successfully followed by pharmacy compared with those who were not were 5.1% vs 15.0% (P = .049) for index readmissions and 8.1% vs 27.5% (P = .03) for all-cause readmissions. No statistically significant difference existed between those patients with follow-up compared with those without follow-up for either index (10.1% vs 12.5%, respectively; P = .68) or for all-cause ED visit rates (15.2% vs 20.0%, respectively; P = .49).
Patient Encounters
The average time to follow-up was 8.8 days, which was above the predetermined goal of contact within 7 days. Additionally, this was a decline from the initial pilot study, which had an average time to reach of 4.7 days. All patients reached by a pharmacist received medication reconciliation, with ≥ 28% of patients having ≥ 1 discrepancy. There were 43 discrepancies among all patients. Of the discrepancies, 25 were reported as errors performed by the patient, and 18 were from an error during the discharge process. The discrepancies that resulted from patient error were primarily patients who took the wrong dose of prescribed medications. Other patient discrepancies included taking medications not as scheduled, omitting medications (both intentionally and mistakenly), continuing to take medications that had been discontinued by a health care provider and improper administration technique. Examples of provider errors that occurred during the discharge process included not ordering medications for patient to pick up at discharge, not discontinuing a medication from the patient’s profile, and failure to renew expired prescriptions.
Additional counseling was provided to 75% of patients: The most common reason for counseling was T2DM, hypertension, and dyslipidemia management. PACT pharmacists changed medication regimens for 27.3% of patients for improved control of chronic diseases or relief of medication AEs.
At the end of each visit, patients were assessed to determine whether they could benefit from additional pharmacy follow-up. Thirty-seven patients were added to the pharmacist schedules for disease management appointments. The most common conditions for these appointments were T2DM, hypertension, tobacco cessation, and hyperlipidemia. Among the 37 patients who had pharmacy follow-up, there were 137 additional pharmacy appointments within the study period.