Screening High-Risk Women Veterans for Breast Cancer
Background: Within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), breast cancer prevalence has more than tripled from 1995 to 2012. Women veterans may be at an increased breast cancer risk based on service-related exposures and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Methods: Women veterans aged ≥ 35 years with no personal history of breast cancer were enrolled at 2 urban VA medical centers. We surveyed women veterans for 5-year and lifetime risks of invasive breast cancer using the Gail Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (BCRAT). Data regarding demographics, PTSD status, eligibility for chemoprevention, and genetic counseling were also collected. Descriptive statistics were used to determine results.
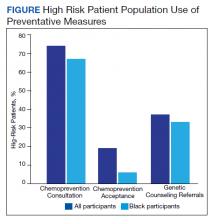
Results: A total of 99 women veterans participated, of which 60% were Black. In total, 35% were high risk with a 5-year BCRAT > 1.66%. Breast biopsies had been performed in 22% of our entire population; 57% had a family history positive for breast cancer. Comparatively, in our high-risk Black population, 33% had breast biopsies and 94% had a family history. High-risk patients were referred for chemoprevention; 5 accepted and 13 were referred for genetic counseling. PTSD was present in 31% of the high-risk subgroup.
Conclusions: A high percentage of Black patients participated in this pilot study, which also showed an above average rate of PTSD among women veterans who are at high risk for developing breast cancer. Historically, breast cancer rates among Black women are lower than those found in the general population. High participation among Black women veterans in this pilot study uncovered the potential for further study of this population, which is otherwise underrepresented in research. Limitations included a small sample size, exclusively urban population, and self-selection for screening. Future directions include the evaluation of genetic and molecular mutations in high risk Black women veterans, possibly even a role for PTSD epigenetic changes.
Discussion
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women.52 The number of women with breast cancer in the VHA has more than tripled from 1995 to 2012.1 The lifetime risk of developing breast cancer in the general population is about 13%.50 This rate can be affected by risk factors including age, hormone exposure, family history, radiation exposure, and lifestyle factors, such as weight and alcohol use.6,52-56 In the United States, invasive breast cancer affects 1 in 8 women.50,52,57
Our screened population showed nearly 3 times as many women veterans were at an increased risk for breast cancer when compared with historical averages in US women. This difference may be based on a high rate of prior breast biopsies or positive family history, although a provocative study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database showed military women to have higher rates of breast cancer as well.9 Historically, Blacks are vastly understudied in clinical research with only 5% representation on a national level.5,58 The urban locations of both pilot sites (Washington, DC and Bronx, NY) allowed for the inclusion of minority patients in our study. We found that the rates of breast cancer in Black women veterans to be higher than seen nationally, possibly prompting further screening initiatives for this understudied population.
Our pilot study’s chemoprevention utilization (19%) was double the < 10% seen in the national population.33-35 The presence of a knowledgeable breast health practitioner to recruit study participants and offer personalized counseling to women veterans is a likely factor in overcoming barriers to chemopreventive acceptance. These participants may have been motivated to seek care for their high-risk status given a strong family history and prior breast biopsies.
Interestingly, a 3-fold higher PTSD rate was seen in this pilot population (29%) when compared with PTSD rates in the general female population (7-10%) and still one-third higher than the general population of women veterans (20%).45-47 Mental health, anxiety, and PTSD have been barriers to patients who sought treatment and have been implicated in poor adherence to medical advice.48,49 Cancer screening can induce anxiety in patients, and it may be amplified in patients with PTSD. It was remarkable that although adherence with screening recommendations is decreased when PTSD is present, our patient population demonstrated a higher rate of screening adherence.
Women who are seen at the VA often use multiple clinical specialties, and their EMR can be accessed across VA medical centers nationwide. Therefore, identifying women veterans who meet screening criteria is easily attainable within the VA.
When comparing high-risk with average risk women, the lifestyle results (BMI, smoking history, exercise and consumption of fruits, vegetables and alcohol) were essentially the same. Lifestyle factors were similar to national population rates and were unlikely to impact risk levels.
Limitations
Study limitations included a high number of self-referrals and the large percentage of patients with a family history of breast cancer, making them more likely to seek screening. The higher-than-average risk of breast cancer may be driven by a high rate of breast biopsies and a strong family history. Lifestyle metrics could not be accurately compared to other national assessments of lifestyle factors due to the difference in data points that we used or the format of our questions.