Dynamic ultrasonography: An idea whose time has come
An ultrasound expert makes the case for using ultrasound-enhanced bimanual examination as a routine part of gynecologic care to assist in diagnosis and enhance patient care
Guidelines concerning pelvic ultrasound do not consider dynamic imaging
Until now, most imagers take a myriad of pictures, mostly still snapshots, to illustrate anatomy. Most imaging physicians then look at a series of such pictures and may never even hold the transducer. This is increasingly true in instances of remote teleradiology. Even for the minority of imagers who utilize video clips (VIDEOS 2A–2C), these are still representations of anatomy .
One need look no further than the guidelines that underpin the expectation of those who scan the female pelvis. The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) published a practice parameter for the performance of ultrasonography of the female pelvis, developed in collaboration with the American College of Radiology, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Society for Pediatric Radiology, and Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound. 3 Nowhere does this document mention anything other than what images to obtain, where to look, and how to measure. Nowhere is there any mention of dynamic imaging—the concept of using one’s other hand on the abdomen, eliciting pain with the vaginal probe, checking for mobility, asking the patient to bear down. The document lists indications for pelvic sonography that include but are not limited to 19 different indications, such as pelvic pain, evaluation of dysmenorrhea, evaluation for signs or symptoms of pelvic infection, and evaluation of incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse (TABLE). 3
Dynamic ultrasonography can aid in the diagnosis of certain conditions
Specifically, what can dynamic ultrasonography add to anatomic imaging? The main considerations are pain, adhesions, endometriosis, and pelvic organ prolapse.
Pelvic pain or tenderness
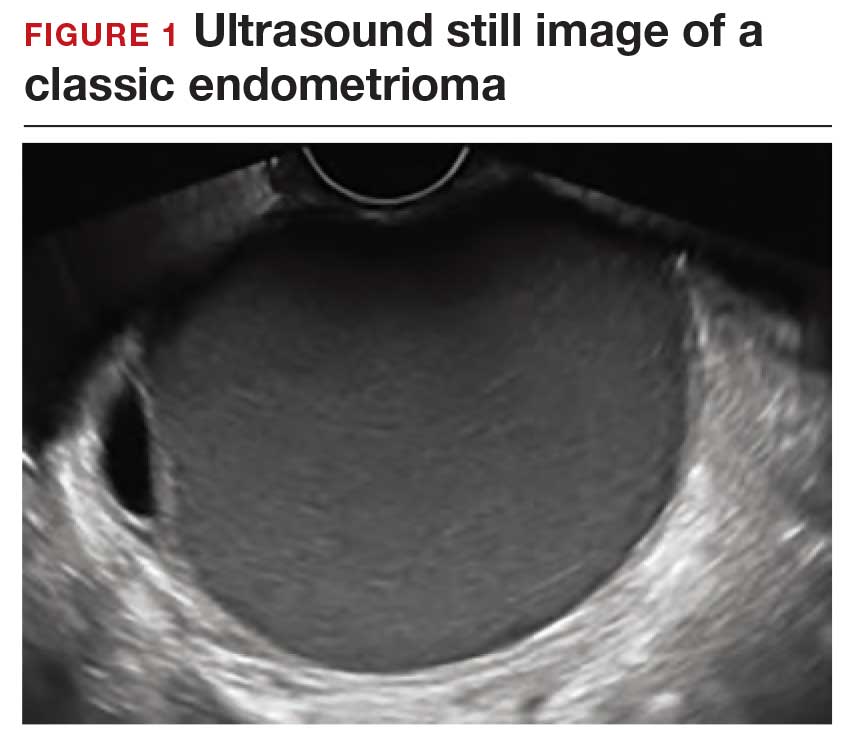
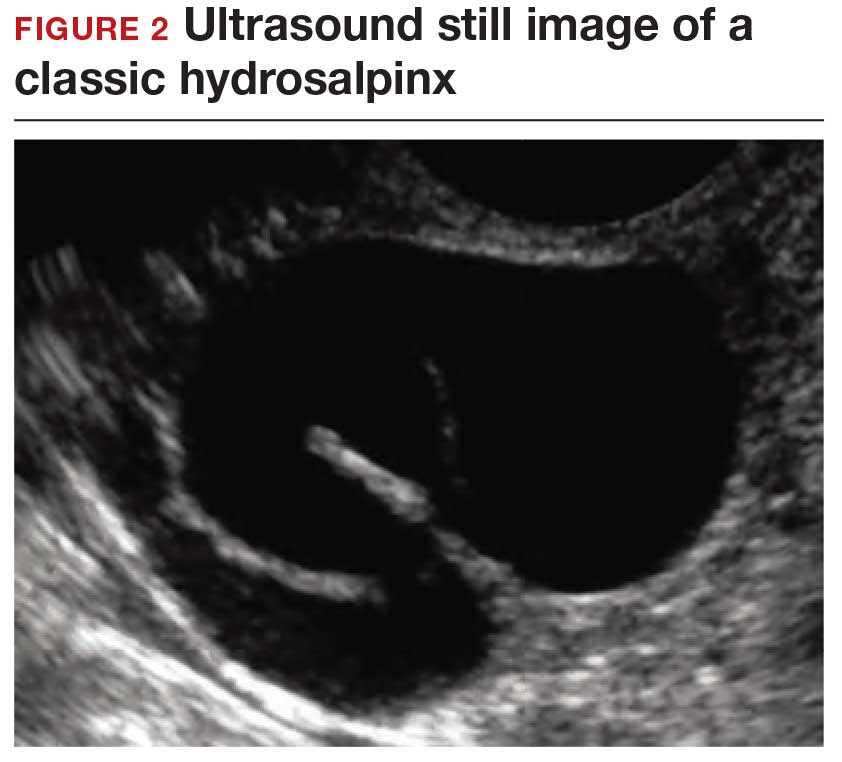
How can you evaluate a patient’s pelvic pain with an anatomic image? Perhaps pain can be corroborated if there is a classic ovarian endometrioma (FIGURE 1) (VIDEOS 3A, 3B) or classic hydrosalpinx (FIGURE 2) (VIDEOS 4A–4C). But can we evaluate pelvic pain with only an anatomic image? No, absolutely not. Evaluating pain requires dynamic assessment. As described above, in a dynamic ultrasound assessment, liberal use of the abdominal hand and the tip of the vaginal probe can elicit where the patient’s pain exists and whether the pain can be recreated.
Adhesions
Pelvic adhesions can be a significant source of pelvic pain and, also, sometimes infertility. The adhesions themselves may not be visible on anatomic imaging. This is where the concept of the sliding organ sign is paramount, a concept first described by Dr. Ilan Timor-Tritsch in his book Transvaginal Sonography . 4 He stated, “Diagnosis of pelvic adhesions becomes possible by the ‘sliding organ sign.’ The transducer tip is pointed at the uterus, ovaries or any pelvic finding, and a gentle push-pull movement of several centimeters is started. If no adhesions are present, the organs will move freely in the pelvis. This displacement of organs is perceived on the screen as a sliding movement.” 4 Thus, if structures are in fact adherent, they will move in tandem with each other as evidenced by this dynamic assessment. If they are not adherent, they will move slightly but independently of each other ( VIDEOS 5A–5G ).
Continue to: Endometriosis...







