The Role of High Reliability Organization Foundational Practices in Building a Culture of Safety
Background: High reliability organizations are designed to operate under complex conditions for extended periods by strengthening systems that help serious adverse events for patients. The US Department of Veterans Affairs formally began its enterprise-wide journey to high reliability in 2019. Four foundational practices were identified to advance a culture of safety across all Veterans Health Administration facilities. This article describes these practices, summarizes supporting evidence from the literature, and illustrates strong practices for improving safety.
Observations: A literature review was conducted from 2018 to March 2023 to identify recent evidence outlining the value of implementing the 4 foundational high reliability organization practices to improve patient safety. This evidence was used to create and implement formal processes for the foundational practices. For each foundational practice, a representative example of a strong practice within the Veterans Health Administration is provided.
Conclusions: Effective and sustained application of the foundational organization practices described can support a health care organization’s journey to high reliability. Collectively, the 4 foundational practices can be adopted and implemented by other organizations in the continued pursuit of high reliability in health care.
To support the implementation of HROs, the VHA paired HRO executive leader coaches with select medical center directors and their leadership teams. Executive leader coaches also support an organization’s HRO Lead and HRO Champion. The HRO Lead coordinates and facilitates the implementation of HRO principles and practices in pursuit of no harm across an organization. The HRO Champion supports the same as the HRO Lead, but typically has a different specialty background. For example, if the HRO Lead has an administrative background, the HRO Champion would have a clinical background.
Coaching focuses heavily on supporting site-specific implementation and sustainment of the 4 HRO foundational practices. The aim is to accelerate change, build enduring capacity, foster a safety culture, and accelerate HRO maturity. To measure change, HRO executive leader coaches track the progress of their aligned VA medical centers (VAMCs) using the Organizational Learning Tool (OLT). This tool was developed to provide information such as a facility summary and relationships between a medical center director, HRO Lead, HRO Champion, and the executive leader coach (Figure 1). The OLT also serves as a structured process to measure leader coaching performance against mutually agreed upon objectives that ultimately contribute to enterprise outcomes. It also collects data on the progress in implementing foundational practices, strong practices, needs and gaps, and more (Figure 2). Data collected from facilities supported by HRO executive leader coaches on whether foundational practices are in place are briefly described.
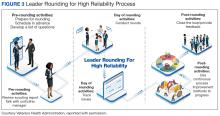
Leader Rounding
Leader rounding for high reliability ensures effective, bidirectional communication and collaboration among all disciplines to improve patient safety. It is an essential feature of a robust patient safety culture and an important method for demonstrating leadership engagement with high reliability.4,5 These rounds are conducted by organizational leadership (eg, executive teams, department/service chiefs, or unit managers) and frontline staff from different areas. They are specifically focused on high reliability, patient and staff safety, and improvement efforts. The aim is to learn about daily challenges that may contribute to patient harm.4
Leader rounding has been found to be highly effective at improving leadership visibility across the organization. It enhances interaction and open communication with frontline staff, fostering leader-staff collaboration and shared decision-making, as well as promoting leadership understanding of operational, clinical, nonclinical (eg, administrative, nutrition services, or facilities management), and patient/family experience issues.4 Collaboration among team members fosters the delivery of more effective and efficient care, increases staff satisfaction, and improves employee retention.6 Leader rounding for high reliability significantly contributes to the breakdown of power barriers by giving team members voice and agency, ultimately leading to deeper engagement.7
It is important that leader rounding for high reliability occurs as planned and when possible, scheduled in advance. This helps to avoid rounding at peak times when care activities are being performed.4,6 When scheduling conflicts arise, another leader should be sent to participate in rounds.4 Developing a list of questions in advance allows leadership to prepare messaging to share with staff as it relates to high reliability and patient safety (Table).4,6,8
Closing the loop improves bidirectional communication and is critical to leader rounding for high reliability. Closed-loop communication and following up on and/or closing out issues raised during rounding empowers the sharing of information, which is critical for advancing a culture of safety.4,8 Enhanced feedback is also associated with greater workforce engagement, staff feeling more connected to quality improvement activities, and lower rates of employee burnout.7 It is important to recognize that senior leaders are not responsible for resolving all issues. If a team or manager can resolve concerns that are raised, this should be encouraged and supported. Maintaining accountability at the lowest level of the organization promotes principles and practices of high reliability (Figure 3).4,8
The VA Bedford Healthcare System created and implemented a strong practice for leader rounding for high reliability. This phased implementation involved creating an evidence-based process, deciding on an appropriate cadence, developing a tracking tool, and measuring impact to determine the overall effectiveness of leader rounding for high reliability.4