Overuse of Hematocrit Testing After Elective General Surgery at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Objective: To evaluate the clinical usefulness and costs of routine postoperative hematocrit testing after elective general surgery.
Methods: We reviewed charts of all patients who had elective general surgery at New Mexico Veterans Affairs Health Care System, Albuquerque hospital from 2011 through 2014. Demographic data and patient characteristics (eg, comorbidities, smoking/drinking history), estimated blood loss (EBL), pre- and postoperative hematocrit levels, and signs and symptoms of anemia were compared in patients who did or did not receive a blood transfusion within 72 hours of the operation.
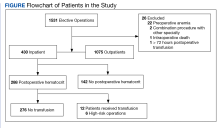
Results: Of 1531 patients who had an elective general surgery between 2011 and 2014, ≥ 1 postoperative hematocrit levels were measured in 288 individuals. There were 1312 postoperative hematocrit measurements before discharge (mean, 8.7; range, 1-44). There were 12 transfusions (0.8%) for patients without moderate to severe pre-existing anemia (hematocrit < 30%). Five of 12 transfused patients received intraoperative transfusions and 7 patients were transfused within 72 hours postoperation. No patients were transfused preoperatively. Of 12 patients receiving transfusion, 11 had EBL > 199 mL and/or signs of anemia. Risk factors for postoperative transfusion included lower preoperative hematocrit, increased EBL, and having either abdominoperineal resection or a total proctocolectomy.
Conclusions: Routine postoperative hematocrit measurements after elective general surgery at US Department of Veterans Affairs medical centers are of negligible clinical value and should be reconsidered. Clinical judgment, laboratory-documented pre-existing anemia, a high-risk operation, or symptoms of anemia should prompt monitoring of patient postoperative hematocrit testing. This strategy could have eliminated 206 initial hematocrit checks over the 4 years of the study.
Methods
This retrospective case-control study conducted at the New Mexico VA Health Care System (NMVAHCS) in Albuquerque compared data for patients who received transfusion within 72 hours of elective surgeries vs patients who did not. Patients who underwent elective general surgery from January 2011 through December 2014 were included. An elective general surgery was defined as surgery performed following an outpatient preoperative anesthesia evaluation ≥ 30 days prior to operation. Patients who underwent emergency operations, and those with baseline anemia (preoperative hematocrit < 30%), and those transfused > 72 hours after their operation were excluded. The NMVAHCSInstitutional Review Board approved this study (No. 15-H184).
A detailed record review was conducted to collect data on demographics and other preoperative risk factors, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), race and ethnicity, cardiac and pulmonary comorbidities, tobacco use, alcohol intake, diabetes, American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification, metabolic equivalent of task, hematologic conditions, and renal disease.
For each procedure, we recorded the type of elective general surgery performed, the diagnosis/indication, pre- and postoperative hemoglobin/hematocrit, intraoperative EBL, length of operation, surgical wound class, length of hospital stay (LOS), intensive care unit (ICU) status, number of hematocrit tests, cardiovascular risk of operation (defined by anesthesia assessment), presence or absence of malignancy, preoperative platelet count, albumin level, preoperative prothrombin time/activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), international normalized ratio (INR), hemoglobin A1c, and incidence of transfusion. Signs and symptoms of anemia were recorded as present if the postoperative vital signs suggested low intravascular volume (pulse > 120 beats/minute, systolic blood pressure < 90 mm Hg, or vasoactive medication requirement [per anesthesia postoperative note]) or if the patient reported or exhibited symptoms of dizziness or fatigue or evidence of clinically apparent bleeding (ie, hematoma formation). Laboratory charges for hematocrit tests and CBC at the NMAVAHCS were used to assess cost.11
To stratify the transfusion risk, patients were distributed among 3 groups based on the following criteria: discharged home the same day as surgery; admitted but did not have postoperative hematocrit testing; and admitted and had postoperative hematocrit testing. We also stratified operations into low or high risk based on the risk for postoperative transfusion (Figure). Recognizing that the American College of Chest Physicians guidelines for perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy places bowel resection in a high-risk category, we designated a surgery as high risk when ≥ 2 patients in the transfusion group had that type of surgery over the 4 years of the study.12 Otherwise, the operations were deemed low risk.
Statistical Analysis
Numeric analysis used t tests and Binary and categorical variables used Fisher exact tests. P value ≤ .05 was considered statistically significant. SAS software was used for all statistical analyses.