Transition to Tenecteplase From t-PA for Acute Ischemic Stroke at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
Background: Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) has been the standard IV thrombolytic drug used in acute ischemic stroke treatment since 1995. Tenecteplase has been available for use in acute myocardial infarction and has been endorsed by the American Heart Association stroke guidelines as an alternative to t-PA.
Observations: A systematic process to safely transition from t-PA to tenecteplase for acute ischemic stroke was undertaken at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center. The process to implement tenecteplase required extensive training and education for staff physicians, nurses, pharmacists, radiologists, trainees, and the rapid response team. There are a variety of benefits and implementation challenges to consider when transitioning thrombolytic therapy for institutional use in acute ischemic stroke.
Conclusions: Evidence supports the transition from t-PA to tenecteplase for acute ischemic stroke. Successful transition required months of preparation involving multidisciplinary meetings that included neurology, nursing, pharmacy, radiology, rapid response teams, critical care, and emergency medicine. Safeguards must be implemented to avoid dosing errors that can lead to life-threatening adverse events
All inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined to be the same for tenecteplase as they were for t-PA with the notable exception that the WAKE-UP trial protocol would not be supported until further evidence became available.9 The results of the WAKE-UP trial had previously been used at WRNMMC to justify administration of t-PA in patients who awoke with symptoms of acute ischemic stroke, the last known well was unclear or > 4.5 hours, and for whom a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain could be obtained rapidly. Based on the WAKE-UP trial, if the MRI scan of the brain in these patients demonstrated restricted diffusion without fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) signal changes (diffusion-weighted [DWI]-FLAIR mismatch sign), this indicated that the stroke had likely occurred recently, and it was safe to administer t-PA. This allowed for administration of t-PA outside the standard treatment window of 4.5 hours from last known well, especially in the cases of patients who awoke with symptoms.
Since safety data are not yet available for the use of tenecteplase in this fashion, the WAKE-UP trial protocol was not used as an inclusion criterion. The informed consent form was modified, and the following scenarios were outlined: (1) If the patient or surrogate is immediately available to consent, paper consent will be documented with the additional note that tenecteplase is being used off-label; and (2) If the patient cannot consent and a surrogate is not immediately available, the medicine will be used emergently as long as the neurology resident and attending physicians agree.15
Risk mitigation was considered carefully. The stroke box described above is stocked and maintained by the pharmacy as we have transitioned to using designated pharmacists for the storage and preparation of tenecteplase. We highly recommend the use of designated pharmacists or emergency department pharmacists in this manner to avoid dosing errors.7,16 Since the current pharmacy-provided tenecteplase bottle contains twice the maximum dose indicated for ischemic stroke, only a 5 mL syringe is included in the stroke box to ensure a maximum dose of 25 mg is drawn up after reconstitution. Dosing card charts were made like existing dosing card charts for t-PA to quickly calculate the 0.25 mg/kg dose. In training, the difference in dosing in ischemic stroke was emphasized. Finally, pharmacy has taken responsibility for dosing the medication during stroke codes.
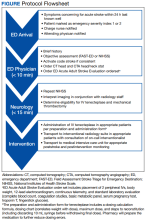
Any medical personnel at WRNMMC can initiate a stroke code by sending a page to the neurology consult service (Figure).
TRANSITION AND RESULTS
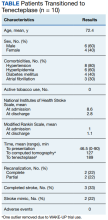
From November 2020 to December 2021, 10 patients have been treated in total at WRNMMC (Table).
CONCLUSIONS
The available evidence supports the transition from t-PA to tenecteplase for acute ischemic stroke. The successful transition required months of preparation involving multidisciplinary meetings between neurology, nursing, pharmacy, radiology, rapid response teams, critical care, and emergency medicine departments. Safeguards must be implemented to avoid a tenecteplase dosing error that can lead to potentially life-threatening adverse effects. The results at WRNMMC thus far are promising for safety and efficacy. Several process improvements are planned: a hospital-wide overhead page will accompany the direct page to neurology; other team members, including radiology and pharmacy, will be included on the acute stroke alert; and a stroke-specific paging application will be implemented to better track real-time stroke metrics and improve flow. These measures mirror processes that are occurring in institutions that treat acute stroke patients.