Gender and Patient Satisfaction in a Veterans Health Administration Outpatient Chemotherapy Unit
Background: Our objective was to explore whether differences in patient satisfaction based on gender exist at the Veterans Affairs Portland Health Care System (VAPHCS) outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit.
Methods: Veterans who received outpatient infusion treatments at the VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit from 2018 to 2020 were invited to take an anonymous survey. Response differences were analyzed using Fisher exact and Welch t tests. Male and female patient lists were first generated based on Computerized Patient Record System designation, then defined and results reported based on gender self-identification from survey responses.
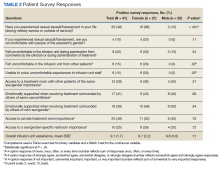
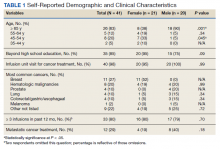
Results: The survey was conducted over a 2-week period during January and February of 2021. In total, 69 veterans were contacted: 21 (70%) of 30 female and 20 (51%) of 39 male veterans completed the survey. Most (62%) female patients were aged < 65 years, and 52% were treated for breast cancer. Most (90%) male patients were aged ≥ 65 years, and most commonly treated for prostate cancer (20%) or a hematologic malignancy (20%). Using our survey, patient satisfaction (SD) was 8.7 (2.2) on a 10-point scale among women, and 9.6 (0.6) among men (P = .11). History of sexual abuse or harassment was reported by 86% of women compared with 10% of men (P < .001). Women reported feeling uncomfortable around other patients in the infusion unit compared with men (29% vs 0%; P = .02) and discomfort in relaying uncomfortable feelings to a clinician (29% vs 0%; P = .02).
Conclusions: Gender seems to be related to how veterans with cancer perceive their ambulatory cancer care. This may be due to the combination of a high history of sexual abuse and/or harassment among women who represent a minority of the total infusion unit population, the majority of whom receive treatment for a primarily gender-specific breast malignancy. Analysis was limited by the small sample size of women, many with advanced malignancy.
Male and female patient lists were first generated based on CPRS categorization. We identified all female veterans treated in the ambulatory infusion unit during the study period. Male patients were then chosen at random, recording the most recent names for each year until a matched number per year compared with the female cohort was reached. Patients were recorded only once even though they had multiple infusion unit visits. Patients were excluded who were deceased, on hospice care, lost to follow-up, could not be reached by phone, refused to take the survey, had undeliverable email addresses, or lacked internet or email access.
After filing the appropriate request through the VAPHCS Institutional Review Board committee in January 2021, patient records were reviewed for demographics data, contact information, and infusion treatment history. The survey was then conducted over a 2-week period during January and February 2021. Each patient was invited by phone to complete a 25-question anonymous online survey. The survey questions were created from patient-relayed experiences, then modeled into survey questions in a format similar to other patient satisfaction questionnaires described in cancer care and gender differences.2,13,14 The survey included self-identification of gender and was multiple choice for all except 2 questions, which allowed an open-ended response (Appendix). Only 1 answer per question was permitted. Only 1 survey link was sent to each veteran who gave permission for the survey. To protect anonymity for the small patient population, we excluded those identifying as gender nonbinary or transgender.
Statistical Analysis
Patient, disease, and treatment features are separated by male and female cohorts to reflect information from the EHR (Table 1). Survey percentages were calculated to reflect the affirmative response of the question asked (Table 2). Questions with answer options of not important, minimally important, important, or very important were calculated to reflect the sum of any importance in both cohorts. Questions with answer options of never, once, often, or every time were calculated to reflect any occurrence (sum of once, often, or every time) in both patient groups. Questions with answer options of strongly agree, somewhat agree, somewhat disagree, and strongly disagree were calculated to reflect any agreement (somewhat agree and strongly agree summed together) for both groups. Comparisons between cohorts were then conducted using a Fisher exact test. A Welch t test was used to calculate the significance of the continuous variable and overall ranking of the infusion unit experience between groups.
Results
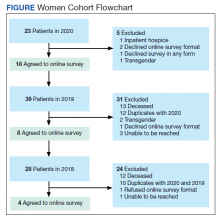
In 2020, 414 individual patients were treated at the VAPAHCS outpatient infusion unit. Of these, 23 (5.6%) were female, and 18 agreed to take the survey. After deceased and duplicate names from 2020 were removed, another 14 eligible 2019 female patients were invited and 6 agreed to participate; 6 eligible 2018 female patients were invited and 4 agreed to take the survey (Figure). Thirty female veterans were sent a survey link and 21 (70%) responses were collected. Twenty-one male 2020 patients were contacted and 18 agreed to take the survey. After removing duplicate names and deceased individuals, 17 of 21 eligible 2019 male patients and 4 of 6 eligible 2018 patients agreed to take the survey. Five additional male veterans declined the online-based survey method. In total, 39 male veterans were reached who agreed to have the survey link emailed, and 20 (51%) total responses were collected.
Most respondents answered all questions in the survey. The most frequently skipped questions included 3 questions that were contingent on a yes answer to a prior question, and 2 openended questions asking for a write-in response. Percentages for female and male respondents were adjusted for number of responses when applicable.
Thirteen (62%) female patients were aged < 65 years, while 18 (90%) of male patients were aged ≥ 65 years. Education beyond high school was reported in 20 female and 15 male respondents. Almost all treatment administered in the infusion unit was for cancer-directed treatment, with only 1 reporting a noncancer treatment (IV iron). The most common malignancy among female patients was breast cancer (n = 11, 52%); for male patients prostate cancer (n = 4, 20%) and hematologic malignancy (n = 4, 20%) were most common. Four (19%) female and 8 (40%) male respondents reported having a metastatic diagnosis. Overall patient satisfaction ranked high with an average score of 9.1 on a 10-point scale. The mean (SD) satisfaction score for female respondents was 1 point lower than that for men: 8.7 (2.2) vs 9.6 (0.6) in men (P = .11).
Eighteen (86%) women reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment compared with 2 (10%) men (P < .001). The sexual abuse assailant was a different gender for 17 of 18 female respondents and of the same gender for both male respondents. Of those with sexual abuse history, 4 women reported feeling uncomfortable around their assailant’s gender vs no men (P = .11), but this difference was not statistically significant. Six women (29%) and 2 (10%) men reported feeling uncomfortable during clinical examinations from comments made by the clinician or during treatment administration (P = .24). Six (29%) women and no men reported that they “felt uncomfortable in the infusion unit by other patients” (P = .02). Six (29%) women and no men reported feeling unable to “voice uncomfortable experiences” to the infusion unit clinician (P = .02).