Safety Profile of Mutant EGFR-TK Inhibitors in Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Background: Despite the use of platinum-based chemotherapy, lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related death in the world. To overcome the rate of lung cancer–related death, scientists discovered advanced therapies, including mutant epidermal growth factor receptor–tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) inhibitors.
Observations: We conducted a meta-analysis to determine the safety profile of mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors in the management of advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Included in this study are 9 phase 3 randomized controlled trials designed to study the safety profile of mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors in patients with advanced NSCLC. The study showed that mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors have an incidence of adverse effects that is less reported when compared with platinum-based chemotherapy.
Conclusions: We recommend continuing using mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors in patients with advanced NSCLC especially in patients having mutant EGFR receptors. Adverse effects caused by mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors are significant but are usually tolerable and can be avoided by reducing the dosage of it with each cycle or by skipping or delaying the dose until patient is symptomatic.
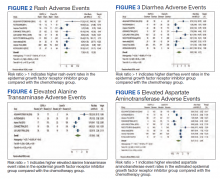
Elevated ALT levels developed in 27.9% of patients in the treatment group receiving mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors compared with 15.1% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 1.37 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming higher ALT levels in patients receiving EGFR-TK inhibitors for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 4).
Elevated AST levels occurred in 40.7% of patients in the mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors treatment group vs 12.8% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 1.77 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming elevated AST levels in patients receiving EGFR-TK inhibitors for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 5).
Stomatitis developed in 17.2% of patients in the treatment group receiving mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors compared with 7.9% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 1.53 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming higher stomatitis event rates in patients receiving EGFR-TK inhibitors for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 6).
Nausea occurred in 16.5% of patients in the mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors group vs 42.5% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 0.37 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming higher nausea rates in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy compared with treatment group for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 7).
Leucopenia developed in 9.7% of patients in the mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors group compared with 51.3% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 0.18 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming higher leucopenia incidence in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy compared with treatment group for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 8).
Fatigue was reported in 17% of patients in the mutant EGFR-TK inhibitors group compared with 29.5% of patients in the control group receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Overall RR of 0.59 and 95% CI was noted, which was statistically significant, confirming higher fatigue rates in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy compared with treatment group for their advanced NSCLC (Figure 9).