Clinical Presentation of Subacute Combined Degeneration in a Patient With Chronic B12 Deficiency
Background: Subacute combined degeneration (SCD) is a rare complication of chronic vitamin B12 deficiency that presents with a variety of neurologic findings, including decreased sensation in the extremities, increased falls, and visual changes. Treatment of SCD involves prompt replacement of vitamin B12 and addressing the underlying conditions that cause the deficiency. Given the prevalence of B12 deficiency in the older adult population, clinicians should remain alert to its possibility in patients who present with progressive neuropathy.
Case Presentation: This report presents a case of a patient with progressive SCD secondary to chronic B12 deficiency despite monthly intramuscular B12 injections.
Conclusions: Appropriate B12 replacement is aggressive and involves intramuscularB12 1000 mcg every other day for 2 to 3 weeks, followed by additional IM administration every 2 months before transitioning to oral therapy. Failure to adequately replenish B12 can lead to progression or lack of resolution of SCD symptoms.
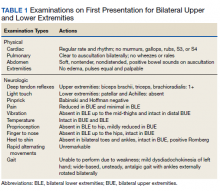
Ophthalmology suspected B12 deficiency. Notable findings included reduced deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) in the upper extremities and absent DTRs in the lower extremities, reduced sensation to light touch in all extremities, absent sensation to pinprick, vibration, and temperature in the lower extremities, positive Romberg sign, and a wide-based antalgic gait with the ankles externally rotated bilaterally (Table 1)
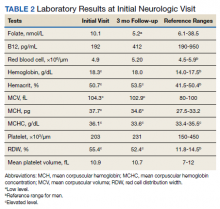
Previous cardiac evaluation failed to provide a diagnosis for syncopal episodes. MRI of the brain revealed nonspecific white matter changes consistent with chronic microvascular ischemic disease. Electromyography was limited due to pain but showed severe peripheral neuropathy. Laboratory results showed megalocytosis, low-normal serum B12 levels, and low serum folate levels (Table 2). The patient was diagnosed with polyneuropathy and was given intramuscular (IM) vitamin B12 1000 mcg once and a daily multivitamin (containing 25 mcg of B12). He was counseled on alcohol abstinence and medication adherence and was scheduled for follow-up in 3 months. He continued outpatient phlebotomy every 6 weeks for polycythemia.
At 3-month follow-up, the patient reported medication adherence, continued alcohol use, and worsening of symptoms. Falls, which now occurred 2 to 3 times weekly despite proper use of a walker, were described as sudden loss of bilateral lower extremity strength without loss of consciousness, palpitations, or other prodrome. Laboratory results showed minimal changes. Physical examination of the patient demonstrated similar deficits as on initial presentation. The patient received one additional B12 1000 mcg IM. Gabapentin was replaced with pregabalin 75 mg twice daily due to persistent uncontrolled pain and paresthesia. The patient was scheduled for a 3-month followup (6 months from initial visit) and repeat serology.
At 6-month follow-up, the patient showed continued progression of disease with significant difficulty using the walker, worsening falls, and wheelchair use required. Physical examination showed decreased sensation bilaterally up to the knees, absent bilateral patellar and Achilles reflexes, and unsteady gait. Laboratory results showed persistent subclinical B12 deficiency. MRI of the brain and spine showed high T2 signaling in a pattern highly specific for SCD. A formal diagnosis of SCD was made. The patient received an additional B12 1000 mcg IM once. Follow-up phone call with the patient 1 month later revealed no progression or improvement of symptoms.
Radiographic Findings
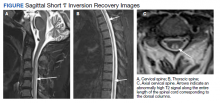
MRI of the cervical and thoracic spine demonstrated abnormal high T2 signal starting from C2 and extending along the course of the cervical and thoracic spinal cord (Figure). MRI in SCD classically shows symmetric, bilateral high T2 signal within the dorsal columns; on axial images, there is typically an inverted “V” sign.2,4 There can also be abnormal cerebral white matter change; however, MRI of the brain in this patient did not show any abnormalities.2 The imaging differential for this appearance includes other metabolic deficiencies/toxicities: copper deficiency; vitamin E deficiency; methotrexateinduced myelopathy, and infectious causes: HIV vacuolar myelopathy; and neurosyphilis (tabes dorsalis).4
Discussion
This case demonstrates the clinical and radiographic findings of SCD and underscores the need for high-intensity dosing of B12 replacement in patients with SCD to prevent progression of the disease and development of morbidities.
Symptoms of SCD may manifest even when the vitamin levels are in low-normal levels. Its presentation is often nonspecific, thus radiologic workup is beneficial to elucidate the clinical picture. We support the use of spinal MRI in patients with clinical suspicion of SCD to help rule out other causes of myelopathy. However, an MRI is not indicated in all patients with B12 deficiency, especially those without myelopathic symptoms. Additionally, follow-up spinal MRIs are useful in monitoring the progression or improvement of SCD after B12 replacement.2 It is important to note that the MRI findings in SCD are not specific to B12 deficiency; other causes may present with similar radiographic findings.4 Therefore, radiologic findings must be correlated with a patient’s clinical presentation.