Pheochromocytoma: An Incidental Finding in an Asymptomatic Older Adult With Renal Oncocytoma
Case Presentation
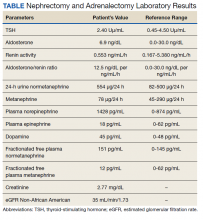
A 72-year-old male with a medical history of diabetes, hypertension, sensory neuropathy, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) status posttransurethral resection of the prostate, and chronic renal failure presented to establish care with the Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center. His medications included losartan 50 mg by mouth daily, diltiazem 180 mg extended-release by mouth daily, carvedilol 6.25 mg by mouth twice a day, and tamsulosin 0.4 mg by mouth daily. His presenting vitals were blood pressure (BP), 112/74 left arm sitting, pulse, 63/beats per min, and body mass index, 34. On physical examination, the patient was alert and oriented, and the chest was clear to auscultation without wheeze or rhonchi. On cardiac examination, heart rate and rhythm were regular; S1 and S2 were normal with no added murmurs, rubs or gallops, and no jugular venous distension. The abdomen was soft, nontender, with no palpable mass. His laboratory results showed sodium, 142 mmol/L; potassium, 5.3 mmol/L; chloride, 101 mmol/L; carbon dioxide, 24 mmol/L; albumin, 4.3 g/dL; creatinine, 1.89 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen, 29 mg/dL; estimated glomerular filtration rate non-African American, 35 mL/min/1.73; 24-h urine creatinine clearance, 105 mL/min; protein, 1306 mg/24 h (Table).
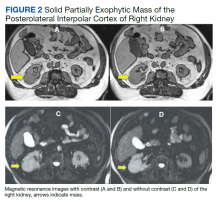
His renal ultrasound showed an exophytic isoechoic mass or complex cyst at the lateral aspect of the lower pole of the right kidney, measuring 45 mm in diameter. An MRI of the abdomen with and without contrast showed a solid partially exophytic mass of the posterolateral interpolar cortex of the right kidney, measuring 5.9 cm in the greatest dimension (Figure 2). No definite involvement of Gerota fascia was noted, a 1-cm metastasis to the right adrenal gland was present, renal veins were patent, and there was no upper retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy.
Treatment and Follow-up
The patient underwent right-hand-assisted lap-aroscopic radical nephrectomy and right adre-nalectomy without any complications. However, the surgical pathology report showed oncocytoma of the kidney (5.7 cm), pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland (1.4 cm), and papillary adenoma of the kidney (0.7 cm). Right kidney nephrectomy showed non-neoplastic renal parenchyma, diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Renal Pathology Society 2010 diabetic nephropathy class IIb), severe mesangial expansion, moderate interstitial fibrosis, moderate arteriosclerosis, and mild arteriolosclerosis.
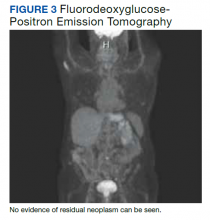
A fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan was significant for right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy and showed no significant evidence of residual neoplasm or local or distant metastases. A nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor and single positron emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan showed normal activity throughout the body and no evidence of abnormal activity (Figure 3).
Discussion
Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension. However, the real numbers are thought to be > 0.2 to 0.5%.1,2,4 Patients with pheochromocytoma should undergo surgical adrenal resection after appropriate medical preparation. Patients with pheochromocytoma who are not diagnosed preoperatively have increased surgical mortality rates due to fatal hypertensive crises, malignant arrhythmia, and multiorgan failure as a result of hypertensive crisis.15 Anesthetic drugs during surgery also can exacerbate the cardiotoxic effects of catecholamines. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are used in patients with pheochromocytoma.16
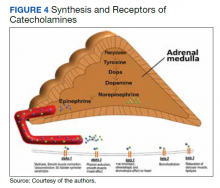
This case of pheochromocytoma illustrated no classic symptoms of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia, and the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. BP was well controlled with losartan, diltiazem, and a β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol). As the patient was not known to have pheochromocytoma, he did not undergo preoperative medical therapy. Figure 4 illustrates the receptors stimulate catecholamines, and the drugs blocking these receptors prevent hypertensive crisis during surgery. However, the surgery was without potential complications (ie, hypertensive crisis, malignant arrhythmia, or multiorgan failure). The patient was diagnosed incidentally on histopathology after right radical nephrectomy and adrenalectomy due to solid partially exophytic right renal mass (5.9 cm) with right adrenal metastasis. About 10% of patients are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Sometimes, the symptoms may be ignored because of the episodic nature. Other possible reasons can be small, nonfunctional tumors or the use of antihypertensive medications suppressing the symptoms.7
The adrenal mass that was initially thought to be a metastasis of right kidney mass was later confirmed as pheochromocytoma. One possible explanation for uneventful surgery could be the use of β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol), α-1 adrenergic blocker (tamsulosin) along with nondihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (diltiazem) as part of the patient’s antihypertensive and BPH medication regimen. Another possible explanation could be silent or episodically secreting pheochromocytoma with a small functional portion.