Multimodal Pain Management With Adductor Canal Block Decreases Opioid Consumption Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
Background: Ease of access to opioids in the perioperative period is a risk factor for subsequent opioid misuse. The purpose of this study was to quantify a decrease in opioid consumption following implementation of a new analgesic protocol after total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed analyzing patients who underwent TKA at a US Department of Veterans Affairs medical center. Patients were divided into 2 groups by multimodal analgesic regimen: Analgesia with intraoperative general anesthesia, a patient-controlled analgesia pump, and oral opioids (control group) or analgesia with intraoperative spinal anesthesia, a multimodal medication regimen, and an adductor canal block (protocol group).
Results: A total of 533 TKAs were included. The mean (SD) IV morphine equivalent dose (MED) requirement was 178.2 (98.0) for the control and 12.0 (24.6) for the protocol group ( P < .001). Total mean (SD) opioid MED requirement was 241.7 (120.1) for the control group and 74.8 (42.7) for the protocol group ( P < .001). The protocol group required only 6.7% of the IV opioids and the control group 30.9%. No difference in oral opioid requirements was found ( P = .85). The control group required more opioid refills at the first postoperative visit ( P < .001).
Conclusions: The described analgesic protocol resulted in significant decreases in IV and total opioid requirement, and lower rates of opioid prescriptions at the first postoperative visit. These findings demonstrate a decrease in opioid utilization with modern perioperative analgesia protocols and reinforce multiple recommendations to decrease opioid exposure and access.
In August 2014, a new analgesic protocol was adopted for TKA consisting of intraoperative spinal anesthesia (0.75% bupivacaine) with IV sedation (propofol), a postoperative multimodal analgesic regimen, an ACB performed in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU), and opioids as needed (protocol group). The ACB catheter was a 0.5% ropivo caine hydrochloride injection. It was attached to a local anesthetic fixed flow rate pump that administers 0.5% ropivacaine without epinephrine at 8 mL/h and was removed on POD 5 by the patient. The multimodal medication regimen included IV ketorolac 15 mg every 6 hours for 3 doses, gabapentin 300 mg every 8 hours, acetaminophen 975 mg every 8 hours, meloxicam 7.5 mg daily, tramadol 50 mg every 6 hours, oxycodone 5 mg 1 to 2 tabs every 4 hours as needed, and IV hydromorphone 0.5 mg every 4 hours as needed for breakthrough pain.
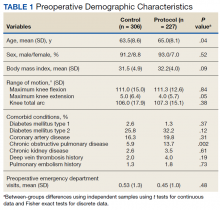
Preoperative demographic characteristics were collected (Table 1). Data on all IV and oral opioid requirements were collected for both groups, converted to morphine milligram equivalents (MME), and a total morphine equivalent dose (MED) was calculated.20,21
In April 2015, a separate protocol change occurred at the DVAMC with the goal of discharge on POD 1. To standardize outcomes before and after this change, data collection regarding opioid requirements was concluded at midnight on POD 1. If a patient was discharged before midnight on POD 1, opioid requirement through the time of discharge was collected. All surgeries were performed in the morning to early afternoon; however, specific surgical times were not collected. Patients were also evaluated by a physical therapist on POD 0, and maximal knee flexion and extension were measured on POD 1. Patients were discharged with prescriptions for oxycodone/acetaminophen and tramadol and were seen 3 weeks later for their first postoperative visit. Opioid refills at the first postoperative visit were recorded. All statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4 with significance set to α = 0.05. Between-groups differences in preoperative and perioperative characteristics as well as postoperative outcomes were analyzed using independent samples t tests for continuous variables and Fisher exact tests for dichotomous discrete variables. Where groups differed for a pre- or perioperative variable, linear mixed models analysis was used to determine whether IV, oral, and total MEDs were significantly affected by the interaction between the pre- or perioperative variable with analgesia group. For refills at the postoperative visit, the effects of pre- or perioperative differences were tested using χ2 tests. Effect sizes for outcome variables were estimated using Cohen d and probability of superiority (Δ) for continuous variables, and relative risk (RR) in the case of discrete variables.22
Results
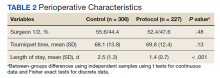
During the study period from June 1, 2011, through December 31, 2015, 533 eligible TKAs were performed, 306 in the control group and 227 in the protocol group. The groups had similar sex distribution; body mass index; knee range of motion; diagnoses of diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and chronic kidney disease; and history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (P ≥ .05). The protocol group was significantly older (P = .04) and had a significantly higher rate of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (P = .002). There were no significant differences between number of procedures performed by surgeon (P = .48) or total tourniquet time (P = .13) (Table 2). Mean (SD) length of stay was significantly greater in the control group compared with the protocol group (2.5 [1.3] vs 1.4 [0.7] days, P < .001).
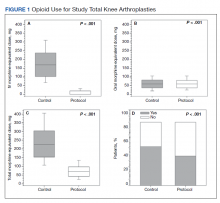
Figure 1 shows the distributions of each type of opioid used. Compared with the control group, the protocol group had a significantly lower mean (SD) IV opioid use: 178.2 (98.0) MED vs 12.0 (24.6) MED (P < .001; d = 2.19; Δ = 0.94) and mean (SD) total opioid use: 241.7 (120.1) MED vs 74.8 (42.7) MED (P < .001; d = 1.76; Δ = 0.89). Mean (SD) oral opioid use did not differ between groups (control, 63.6 [45.4] MED; protocol, 62.9 [31.4] MED; P = .85; d = 0.02; Δ = 0.51). A significantly lower percentage of patients in the protocol group received additional opioids at the 3-week follow-up when compared to the control group: 46.7% vs 61.3%, respectively (P < .001; RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.65-0.90).
There were no significant differences in postoperative mean (SD) maximum knee flexion (control, 67.2 [15.7]°; protocol, 67.8 [19.2]°; P = .72; d = 0.03; Δ = 0.51) or mean (SD) total flexion/extension arc (control, 66.2 [15.9]°; protocol, 67.9 [19.4]°; P = .32; d = 0.10; Δ = 0.53). Mean (SD) postoperative maximum knee extension was significantly higher in the protocol group compared with the control group (-0.1 [2.1]° vs 1.0 [3.7]°; P < .001; d = 0.35; Δ = 0.60). More patients in the protocol group (92.5%) were discharged to home compared with the control group (86.6%) (P = .02; RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.01-1.13).