Impact of an Oral Antineoplastic Renewal Clinic on Medication Possession Ratio and Cost-Savings
Purpose: The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of a pharmacis t-driven oral antineoplastic (OAN) renewal clinic on medication adherence and cost savings.
Methods: This was a preimplementation and postimplementation retrospective cohort evaluation within a single US Department of Veterans Affairs health care system following implementation of a pharmacist-managed OAN refill clinic. The primary outcome was medication adherence defined as the median medication possession ratio (MPR) before and after implementation of the clinic. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients who were adherent from pre- to postimplementation and estimated cost-savings of this clinic. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they had received at least 2 prescriptions of the most commonly prescribed oral antineoplastic agents at the institution between September 1, 2013 and January 31, 2015.
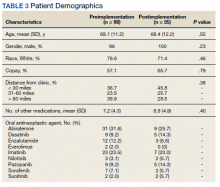
Results: Of preimplementation patients, 96 of 99 (96.9%) were male and all patients (n = 35) in the postimplementation group were male. The mean age of the preimplementation group was 69.2 years while the postimplementation group was 68.4 years. Median MPR in the preimplementation group was 0.94, compared with 1.06 in the postimplementation group ( P < .001). Thirty-six (36.7%) patients in the preimplementation group were considered nonadherent to their OAN regimen compared with zero patients in the postimplementation group. Estimated total cost savings was $36,335 in the postimplementation period.
Conclusions: Implementation of a pharmacist-driven OAN renewal clinic was associated with a 12% increase in median MPR while saving an estimated $36,335 during the 5-month postimplementation period.
Results
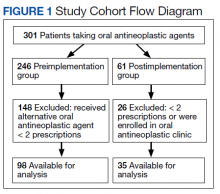
In the preimplementation period, 246 patients received an OAN and 61 patients received an OAN in the postimplementation period (Figure 1). Of the 246 patients in the preimplementation period, 98 were eligible and included in the preimplementation group. Similarly, of the 61 patients in the postimplementation period, 35 patients met inclusion criteria for the postimplementation group. The study population was predominantly male with an average age of approximately 70 years in both groups (Table 3). More than 70% of the population in each group was White. No statistically significant differences between groups were identified. The most commonly prescribed OAN in the preimplementation group were abiraterone, imatinib, and enzalutamide (Table 3). In the postimplementation group, the most commonly prescribed agents were abiraterone, imatinib, pazopanib, and dasatinib. No significant differences were observed in prescribing of individual agents between the pre- and postimplementation groups or other characteristics that may affect adherence including patient copay status, number of concomitant medications, and driving distance from the RLRVAMC.
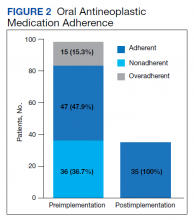
Thirty-six (36.7%) patients in the preimplementation group were considered nonadherent (MPR < 0.9) and 18 (18.4%) had an MPR < 0.8. Fifteen (15.3%) patients in the preimplementation clinic were considered overadherent (MPR > 1.1). Forty-seven (47.9%) patients in the preimplementation group were considered adherent (MPR 0.9 - 1.1) while all 35 (100%) patients in the postimplementation group were considered adherent (MPR 0.9 - 1.1). No non- or overadherent patients were identified in the postimplementation group (Figure 2). The median MPR for all patients in the preimplementation group was 0.94 compared with 1.06 (P < .001) in the postimplementation group.
Thirty-five (35.7%) patients had therapy discontinued or held in the preimplementation group compared with 2 (5.7%) patients in the postimplementation group (P < .001). Reasons for discontinuation in the preimplementation group included disease progression (n = 27), death (n = 3), lost to follow up (n = 2), and intolerability of therapy (n = 3). Both patients that discontinued therapy in the postimplementation group did so due to disease progression. Of the 35 patients who had their OAN discontinued or held in the preimplementation group, 14 patients had excess supply on hand at time of discontinuation. The estimated value of the unused medication was $37,890. Nine (25%) of the 35 patients who discontinued therapy had a dosage reduction during the course of therapy and the additional supply was not included in the cost estimate. Similarly, 1 of the 2 patients in the postimplementation group had their OAN discontinued during study. The cost of oversupply of medication at the time of therapy discontinuation was estimated at $1,555. No patients in the postimplementation group had dose reductions. After implementation of the OAN renewal clinic, the total cost savings between pre ($37,890) and postimplementation ($1,555) groups was $36,355.
Discussion
OANs are widely used therapies, with more than 25 million doses administered per year in the United States alone.12 The use of these agents will continue to grow as more targeted agents become available and patients request more convenient treatment options. The role for hematology/oncology clinical pharmacy services must adapt to this increased usage of OANs, including increasing pharmacist involvement in medication education, adherence and tolerability assessments, and proactive drug interaction monitoring.However, additional research is needed to determine optimal management strategies.