An Interdisciplinary Approach to Educating Medical Students About Dementia Assessment and Treatment Planning
Background: Many general practitioners consider dementia care beyond their clinical domain and feel that dementia assessment and treatment should be addressed by specialists, such as geriatricians, geriatric psychiatrists, or neurologists. An urgent need exists to educate all medical trainees in dementia care, regardless of their specialization interests.
Observations: We developed a multicomponent, experiential, brief curriculum using team-based learning to expose senior medical students who rotated through the US Department of Veterans Affairs Memory Disorders Clinic at the Central Arkansas Veterans Healthcare System in Little Rock to an interdisciplinary assessment of dementia. The curriculum included didactics, clinical experience, and team-based learning. In pre- and postevaluation, students rated their perception of the role of interdisciplinary team members in assessing and managing dementia, their personal abilities to assess cognition, behavioral problems, caregiver burden, and their perception of the impact of behavioral problems on dementia care.
Conclusions: Dementia knowledge gaps were prevalent in this cohort of senior medical students. Providing interdisciplinary geriatric educational experience improved students perception of their ability to assess for dementia and their recognition of the roles of interdisciplinary team members. Plans are in place to continue and expand the program to other complex geriatric syndromes.
Systems learning was an important component integrated throughout the clinical experience. Examples include using video teleconferences to communicate findings among team members and electronic health records to seamlessly obtain and integrate data. Students learned how to create worksheets to graph laboratory data such as B12, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and rapid plasma regain levels. Student gained experience in using applications to retrieve neuroimaging data, results of sleep studies, and other data. Many patients had not received the results of their sleep study, and students had the responsibility to share these reports, including the number of apneic episodes. Students used the VA Computerized Patient Record System for reviewing patient records. One particularly useful tool was Joint Legacy Viewer, a remote access tool used to retrieve data on veterans from anywhere within the US. Students were also trained on medication and consult order menus in the system.
Team-Based
Learning The objectives of the team-based learning section were to teach students basic concepts of integrating the interdisciplinary assessment and formulating a treatment plan, to provide an opportunity to present their case in a group format, to discuss the differential diagnosis, management and treatment plan with a geriatrician in the team-based learning format, and to answer questions from other students. The instructors developed a set of prepared take-home points (Table 1). The team-based learning sessions were structured so that all take-home points were covered.
Evaluations
Evaluations were performed before and immediately after the clinical experience. In preevaluation, students reported the frequency of their participation in an interdisciplinary team assessment of any condition and specifically for dementia. In pre- and postevaluation, students rated their perception of the role of interdisciplinary team members in assessing and managing dementia, their personal abilities to assess cognition, behavioral problems, caregiver burden, and their perception of the impact of behavioral problems on dementia care. A Likert scale (poor = 1; fair = 2; good = 3; very good = 4; and excellent = 5) was employed (eApendices 1 and 2 can be found at doi:10.12788/fp.0052). The only demographic information collected was the student’s gender. Semistructured interviews were conducted to assess students’ current knowledge, experience, and needs. These interviews lasted about 20 minutes and collected information regarding the students’ knowledge about cognitive and behavioral problems in general and those occurring in dementia, their experience with screening, and any problems they encountered.
Statistical Analysis
Student baseline characteristics were assessed. Pre- and postassessments were analyzed with the McNemar test for paired data, and associations with experience were evaluated using χ2 tests. Ratings were dichotomized as very good/excellent vs poor/fair/ good because our educational goal was “very good” to “excellent” experience in dementia care and to avoid expected small cell counts. Two-sided P < .05 indicated statistical significance. Data were analyzed using SAS Enterprise Guide v5.1.
Results
One hundred fourth-year medical students participated, including 54 women. Thirtysix percent reported they had not previously attended an interdisciplinary team assessment for dementia, while 18% stated that they had attended only 1 interdisciplinary team assessment for dementia.
Before the education, students rated their dementia ability as poor. Only 2% (1 of 54), of those with 0 to 1 assessment experience rated their ability for assessing dementia with an interdisciplinary team format as very good/excellent compared with 20% (9/46) of those previously attending ≥ 2 assessments (P = .03); other ratings of ability were not associated with prior experience.
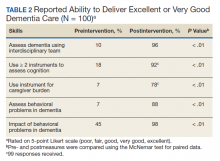
There was a significant change in the students’ self-efficacy ratings pre- to postassessment (P < .05) (Table 2). Only 10% rated their ability to assess for dementia as very good/excellent in before the intervention compared with 96% in postassessment (P < .01). Students’ perception of the impact of behavioral problems on dementia care improved significantly (45% to 98%, P < .01). Similarly, student’s perception of their ability to assess behavioral problems, caregiver burden, and cognition improved significantly from 7 to 88%; 7 to 78%, and 18 to 92%, respectively (P < .01). Students perception of the role of social worker, neuropsychologist, geriatrician, and geriatric psychiatrist also improved significantly for most measures from 81 to 98% (P = .02), 87 to 98% (P = .05), 94 to 99% (P = .06), and 88 to 100% (P = .01), respectively.
The semistructured interviews revealed that awareness of behavioral problems associated with dementia varied for different behavioral problems. Although many students showed familiarity with depression, agitation, and psychosis, they were not comfortable assessing them in a patient with dementia. These students were less aware of other behavioral problems such as disinhibition, apathy, and movement disorders. Deficits were noted in the skill of administering commonly used global cognitive screens, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE).15