An Overview of Pharmacotherapy Options for Alcohol Use Disorder
When compared with other pharmacotherapy options for AUD, naltrexone is less effective for abstinence and more effective for decreasing the time and frequency of heavy drinking days and average number of drinks consumed.29 A meta-analysis of 19 clinical trials found that naltrexone significantly reduced relapse rates in patients with AUD compared with those of placebo.30 This analysis also found that naltrexone reduced both the number of alcoholic beverages consumed and the risk of relapse to heavy drinking while increasing the total number of days of abstinence.30 The COMBINE study also found that patients receiving oral naltrexone in combination with medical treatment had a 28% reduced risk of having a heavy-drinking day.31
Dosing and Formulations
Naltrexone is available as a tablet or a long-acting injectable. The tablet is often dosed as 50 mg daily; although some studies suggest that daily doses up to 150 mg are safe and efficacious.21,25,32 The initial and maintenance dose for most patients is 50 mg daily.
Nonadherence to the oral formulation of naltrexone is a significant barrier to the treatment of AUD. The long-acting injectable formulation is an option for patients who may have difficulty with adhering to oral naltrexone. As with the oral formulation, the long-acting naltrexone injection significantly reduces drinking days and increases abstinence.33 It was also found to be superior to oral naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram in preventing discontinuation of AUD treatment.34 The long-acting injectable should be administered as an intramuscular gluteal injection at a dose of 380 mg monthly.35
Ideally, naltrexone should be initiated following the cessation of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. However, naltrexone can be safely administered in patients who are actively withdrawing from alcohol or in patients who continue to consume alcohol.25
Warnings, Precautions, and AEs
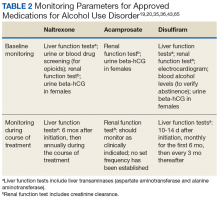
Naltrexone carries a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) boxed warning for reversible hepatotoxicity. The risk of hepatotoxicity is increased in patients who receive higher doses (100-300 mg daily).21 A safety study demonstrated that the administration of 50 mg daily or less is not associated with significant hepatotoxicity.21,31 It is contraindicated in patients with acute hepatitis or liver failure and should be avoided in patients with liver function tests > 5 times the upper limit of normal.
Since naltrexone is a µ-opioid receptor antagonist, it is contraindicated in patients who are actively taking opioids or patients who have used opioids within the past 7 days. Co-administration with an opioid can lead to precipitated opioid withdrawal.21 Therefore, opioids should not be administered within 7 to 10 days of initiating naltrexone and 2 to 3 days after discontinuation of oral naltrexone.21 For patients receiving the long-acting injectable form of naltrexone, opioids should be avoided at least 1 month after the injection.25
To ensure that a patient is opioid free, HCPs can perform a toxicology screening prior to the initiation of naltrexone. Some HCPs may also perform a naloxone challenge to test whether a patient is at risk for precipitated opioid withdrawal prior to prescribing naltrexone.
The adverse effects (AEs) of naltrexone are transient and include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, dizziness, and fatigue.19,35 Injection site reactions can be experienced with the long-acting naltrexone injection. Liver transaminases, such as the alanine aminotransferase and aspartate transaminase, should be monitored at baseline, 6 months after initiation, and annually during the course of treatment (Table 2).