VHA Practice Guideline Recommendations for Diffuse Gliomas
New Diffuse Glioma Classification
Since the issuance of the previous edition of the WHO classification of CNS tumors in 2007, several sentinel discoveries have been made that have advanced our understanding of the underlying biology of primary CNS neoplasms. Since a detailed review of these findings is beyond the scope and purpose of this manuscript and salient reviews on the topic can be found elsewhere, we will focus on the molecular findings that have been incorporated into the recently revised WHO classification.10 The importance of providing such information for proper patient management is illustrated by the recent acknowledgement by the American Academy of Neurology that molecular testing of brain tumors is a specific area in which there is a need for quality improvement.11 Therefore, it is critical that these underlying molecular abnormalities are identified to allow for proper classification and treatment of diffuse gliomas in the veteran population.
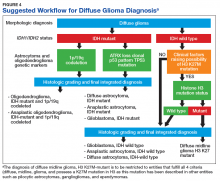
As noted previously, based on VA cancer registry data, diffuse gliomas are the most commonly encountered primary CNS cancers in the veteran population. Several of the aforementioned seminal discoveries have been incorporated into the updated classification of diffuse gliomas. While the recently updated WHO classification allows for the assignment of “not otherwise specified (NOS)” diagnostic designation, this category must be limited to cases where there is insufficient data to allow for a more precise classification due to sample limitations and not simply due to a failure of VA pathology laboratories to pursue the appropriate diagnostic testing.
Figure 4 presents the recommended diagnostic workflow for the workup of diffuse gliomas. As illustrated in the above cases, a variety of different methodologies, including immunohistochemical, FISH, loss of heterozygosity analysis, traditional and NGS may be applied when elucidating the status of molecular events at critical diagnostic branch points.