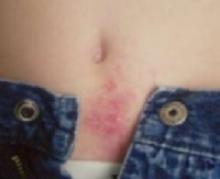
Itchy rash near the navel
Diagnosis: Blue jean button dermatitis
Contact dermatitis secondary to nickel allergy is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction to the nickel contained in many blue jean snaps and buttons (FIGURE 3). The rash is typical of contact dermatitis. Macular erythema, sometimes accompanied by papules or vesicles, is also common.
The border is usually ill-defined, and the lesion may become fissured and excoriated. Long-standing cases may become lichenified and scaly. Occasionally, secondary eruptions on flexor surfaces appear.
FIGURE 3
It all lines up
The child’s nickel allergy rash aligns with the snap and button of his blue jeans.
More common among women
Nickel allergy is relatively common; up to 20% of women and 4% of men are affected.1 This discrepancy is thought to be due to the ways in which individuals become sensitized to nickel.
Many women develop a nickel allergy after getting their ears pierced with nickel-containing studs, whereas men tend to be sensitized by an occupational exposure. Nickel allergy appears to be increasing, which may reflect the more common practice of body piercing in general.
How much nickel is too much?
Sensitized patients will react to a metal if more than 1 part in 10,000 is nickel. Metal objects can be tested for nickel content by using a cotton-tipped applicator to apply a few drops of dimethylglyoxime in ammonium hydroxide to the object. If greater than 1 part per 10,000 is nickel, the cotton will turn pink. Recently, Byer and Morrell found that 10% of blue jeans buttons, and more than 50% of belt buckles, test positive.2
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for a pruritic periumbilical rash in a child would include psoriasis, scabies, tinea corpus and pityriasis rosea.
Psoriatic lesions
The periumbilical area is a common location for psoriatic lesions. More often involved areas include the scalp and areas of trauma such as the knees, elbows, hands and feet. The lesions of psoriasis tend to have a sharp border and characteristically have silvery white scales associated with them. Psoriasis is often associated with nail abnormalities and arthritis.
Scabies
Scabies is a parasitic infestation with the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. Scabies causes an intensely pruritic rash that is classically worse in the finger and toe webs, along the belt line, the groin and axillary regions and, often, periumbilically.
The rash of scabies consists of linearly arranged papules and vesicles due to a hypersensitivity reaction to the mite’s eggs and feces which are left behind as it burrows through the skin. Excoriation often obscures the typical findings and may be extensive. Treatment of scabies with steroid creams often leads to diffuse erythema and crusting.3