Whom to screen for anxiety and depression: Updated USPSTF recommendations
New guidance is offered concerning anxiety in children, adolescents, and adults. Advantages of particular screening tests are reviewed.
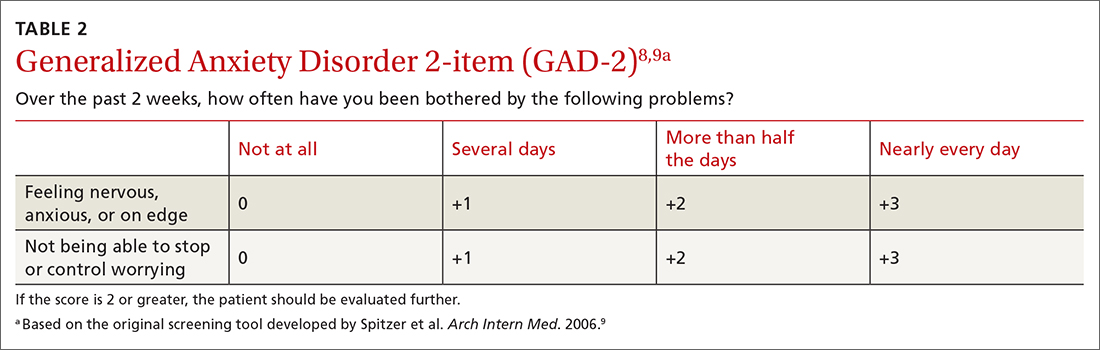
The sensitivity and specificity of each test depends on the cutoff used. With the GAD-2, a cutoff of 2 or more resulted in a sensitivity of 94% and a specificity of 68% for detecting generalized anxiety.7 A cutoff of 3 or more resulted in a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity of 86%.7 The GAD-7, using 10 as a cutoff, achieves a sensitivity of 79% and a specificity of 89%.7 Given the similar performance of the 2 options, the GAD-2 (TABLE 28,9) is probably preferable for use in primary care because of its ease of administration.
The tests evaluated by the USPSTF for anxiety screening in children and adolescents ≥ 8 years of age included the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) and the Patient Health Questionnaire–Adolescent (PHQ-A).3 These tools ask more questions than the adult screening tools do: 41 for the SCARED and 13 for the PHQ-A. The sensitivity of SCARED for generalized anxiety disorder was 64% and the specificity was 63%.10 The sensitivity of the PHQ-A was 50% and the specificity was 98%.10
Various versions of all of these screening tools can be easily located on the internet. Search for them using the acronyms.
Screening for major depression
The depression screening tests the USPSTF examined were various versions of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ), the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) in older adults, and the EPDS in postpartum and pregnant persons.7
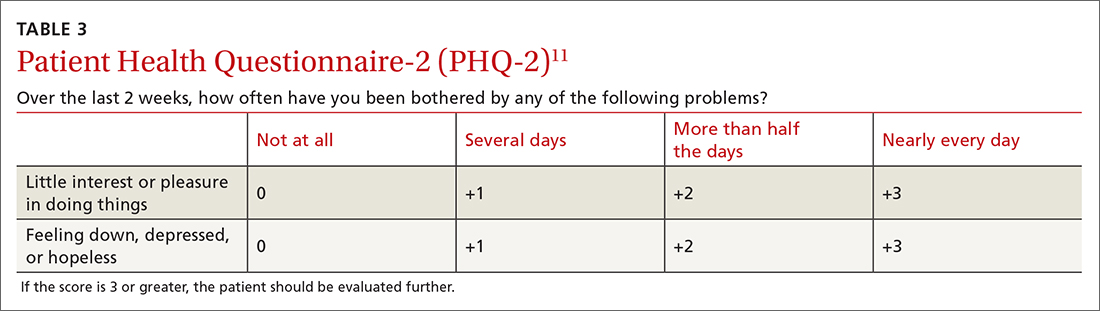
A 2-question version of the PHQ was found to have a sensitivity of 91% with a specificity of 67%. The 9-question PHQ was found to have a similar sensitivity (88%) but better specificity (85%).7 TABLE 311 lists the 2 questions in the PHQ-2 and explains how to score the results.
Continue to: The most commonly...






