A worsening abdominal rash
The confluence of 2 treatments (one appropriate, one not) led to a challenge in diagnosing this worsening rash.
Nummular eczema can be differentiated from tinea corporis by potassium hydroxide (KOH) examination. Nummular eczema is characterized by a negative KOH exam and response to topical corticosteroids.4
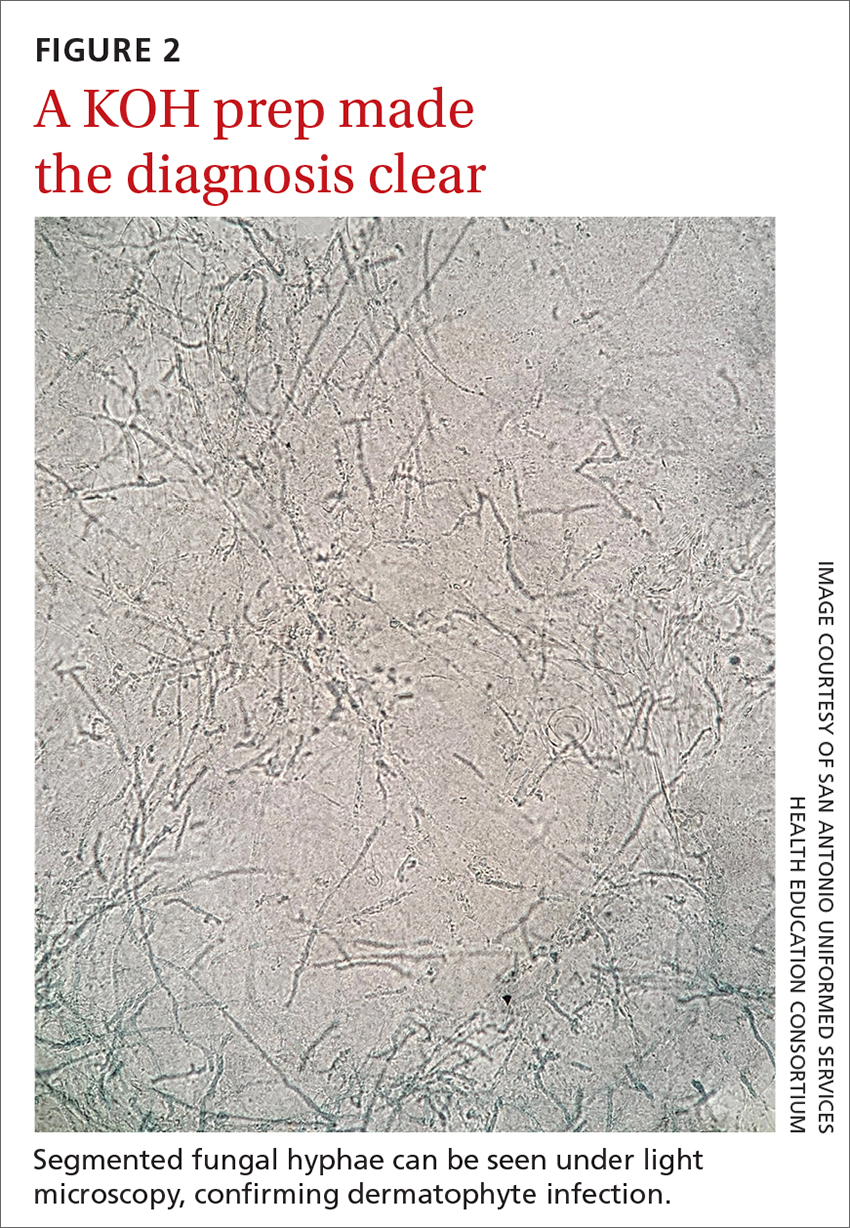
Performing a KOH examination, using the skin scrapings from the active border of a plaque, is useful on any lesion with potential fungal etiology. If the cause is indeed a dermatophyte infection, segmented fungal hyphae will be seen under light microscopy (FIGURE 2).1 If a KOH examination is not feasible, a skin scraping can be performed with a surgical scalpel blade and collected in a sterile urine cup for stain and culture at a qualified laboratory.
Topical and oral antifungal medications combat dermatophyte fungi
Treatments for cutaneous infections caused by dermatophyte fungi, such as tinea corporis, include topical and oral antifungals. The choice of agent depends on the extent of the disease.
Limited, localized disease can be treated topically with allylamines (terbinafine, naftifine) or imidazoles (clotrimazole). Other topical agents, such as butenafine, ciclopirox, and tolnaftate, also may be used.
Extensive disease, or tinea infection of vellus hairs, may require treatment with oral antifungal medications, such as the azoles (itraconazole, fluconazole), allylamines (terbinafine), or griseofulvin. Systemic therapy with oral antifungals has been associated with liver damage; therefore, oral therapy should not be used in patients with liver disease and liver enzymes should be monitored when appropriate.5 Nystatin is not effective in treating dermatophyte fungal infections.1
One complication of the inappropriate use of steroids on a dermatophyte infection is an increased risk of the fungus extending from the superficial skin into the hair follicles in the dermis, resulting in a condition known as Majocchi granuloma. Follicular infection is more severe and requires oral antifungal medication, such as terbinafine, itraconazole, fluconazole, or griseofulvin.1
Our patient was treated with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 4 weeks, due to the possibility of follicular infection. After the completion of 4 weeks of therapy, the patient’s cutaneous symptoms had resolved.






