Getting hypertension under control in the youngest of patients
After confirmation of the diagnosis, follow up with recommendations for lifestyle adjustment and, in certain clinical situations, pursue medical therapy.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Measure the blood pressure (BP) of all children 3 years and older annually; those who have a specific comorbid condition (eg, obesity, diabetes, renal disease, or an aortic-arch abnormality) or who are taking medication known to elevate BP should have their BP checked at every health care visit. C
› Encourage lifestyle modification as the initial treatment for elevated BP or hypertension in children. A
› Utilize pharmacotherapy for (1) children with stage 1 hypertension who have failed to meet BP goals after 3 to 6 months of lifestyle modification and (2) children with stage 2 hypertension who do not have a modifiable risk factor, such as obesity. C
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
When an initial reading is elevated, whether by oscillometric or auscultatory measurement, 2 more auscultatory BP measurements should be taken during the same visit; these measurements are averaged to determine the BP category.18
TABLE 16 defines BP categories based on age, sex, and height. We recommend using the free resource MD Calc (www.mdcalc.com/aap-pediatric-hypertension-guidelines) to assist in calculating the BP category.
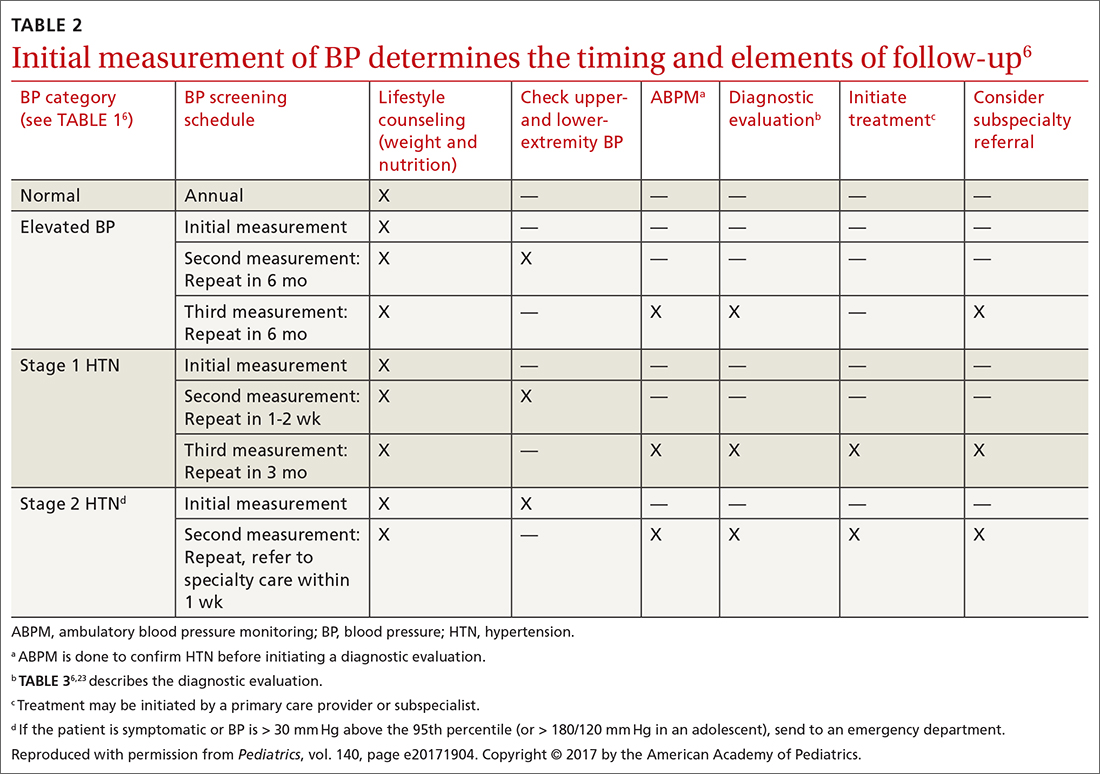
TABLE 26 describes the timing of follow-up based on the initial BP reading and diagnosis.
Ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM) is a validated device that measures BP every 20 to 30 minutes throughout the day and night. ABPM should be performed initially in all patients with persistently elevated BP and routinely in children and adolescents with a high-risk comorbidity (TABLE 26). Note: Insurance coverage of ABPM is limited.
ABPM is also used to diagnose so-called white-coat hypertension, defined as BP ≥ 95th percentile for age, sex, and height in the clinic setting but < 95th percentile during ABPM. This phenomenon can be challenging to diagnose.
Continue to: Home monitoring






