Recognition of skin cancer patterns
Squamous cell carcinoma
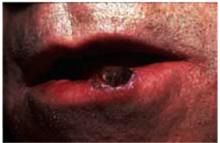
The next most common type of skin cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. These cancers are most often found on the lips, ears, and scalp. Figure 5 shows a squamous cell carcinoma on the lower lip. The lower lip catches more ultraviolet rays from the sun than the upper lip, and therefore is the more prevalent site for this carcinoma.
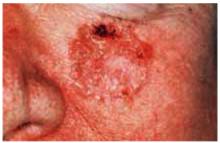
Figure 6 shows a squamous cell carcinoma on the face in an area of sun exposure. This carcinoma looks very much like the superficial basal cell carcinoma in Figure 3, except that the squamous cell carcinoma has one area of crusting. The only way to make a definitive diagnosis is to perform biopsy and get a pathologic reading.
FIGURE 5
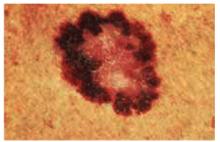
There are many different types of melanomas. Figure 7 shows one version of the most common melanoma, the superficial spreading melanoma. The dark pigmentation around the outside of this melanoma is where the lesion is superficially spreading away from the center (which has lost its pigmentation). This lesion meets all of the ABCDE criteria for malignant melanoma.
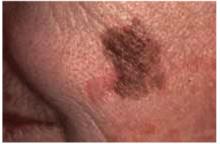
Figure 8 shows a melanoma arising in a lentigo maligna on the face of an older patient. It is not necessary to know the type of melanoma before the biopsy, but you should recognize that the lesion may be melanoma and perform a full-thickness biopsy. What may have started off as a simple age spot in this patient has become a malignant melanoma (see page 214).
Figure 9 shows a very thick and deadly nodular melanoma. One can recognize a nodular melanoma by the increased thickness and its darker pigmentation.
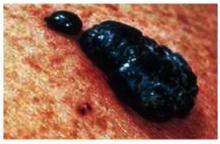
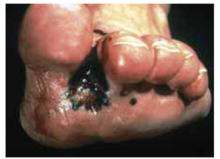
Figure 10 shows an uncommon type of melanoma but one of the deadliest—the acrallentiginous melanoma. This melanoma is often not detected until it has metastasized. Any pigmented lesion on the hands, feet, or under the fingernails that looks like melanoma should be biopsied early before it gets to this deadly stage.
FIGURE 7