Atypical knee pain
The patient found it hard to climb stairs—and to complete a particular task when getting dressed. Difficulty with that task provided a useful diagnostic clue.
A comprehensive exam can reveal a different origin of pain
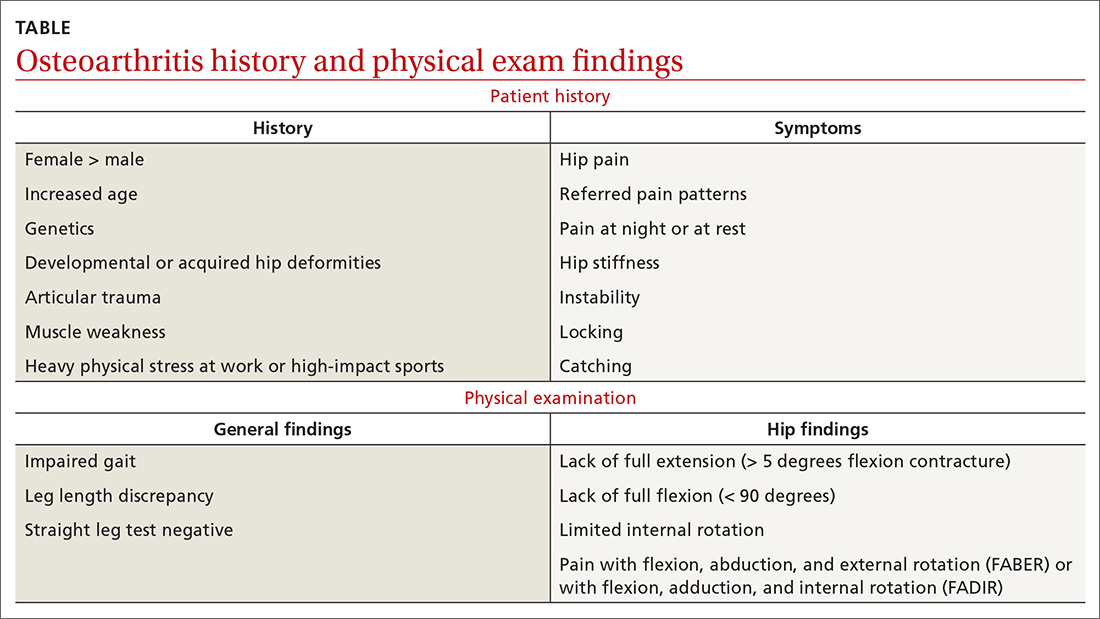
As with any musculoskeletal complaint, history and physical examination should include a focus on the joints proximal and distal to the purported joint of concern. When the hip is in consideration, historical inquiry should focus on degree and timeline of pain, stiffness, and traumatic history. Our patient reported difficulty donning socks, an excellent screening question to evaluate loss of range of motion in the hip. On physical examination, the FABER and FADIR maneuvers are quite specific to hip OA. A comprehensive list of history and physical examination findings can be found in the TABLE.
The differential includes a broad range of musculoskeletal diagnoses
The differential diagnosis for knee pain includes knee OA, spinopelvic pathology, infection, and rheumatologic disease.
Knee OA can be confirmed with knee radiographs, but one must also assess the joint above and below, as with all musculoskeletal complaints.
Spinopelvic pathology may be established with radiographs and a thorough nervous system exam.
Infection, such as septic arthritis or gout, can be diagnosed through radiographs, physical exam, and lab tests to evaluate white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein levels. High clinical suspicion may warrant a joint aspiration.
Continue to: Rheumatologic disease