Dermoscopy in family medicine: A primer
Dermoscopy allows you to see deeper into the skin than with the naked eye. Here’s how you can make use of it to spot malignant conditions sooner.
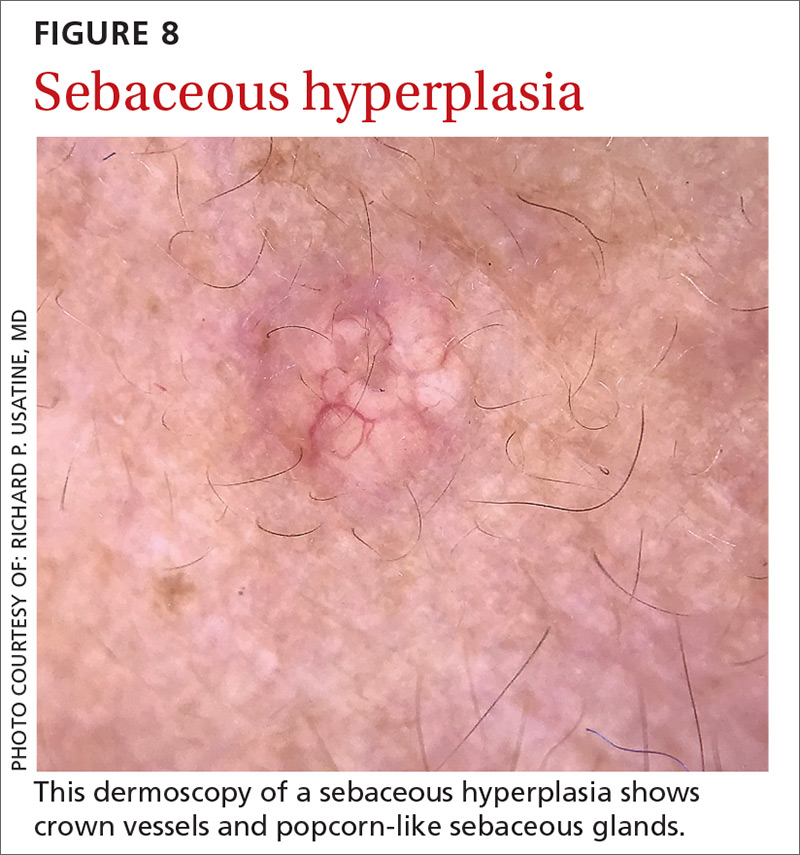
Sebaceous hyperplasia is the overgrowth of sebaceous glands. It can mimic BCC on the face. Sebaceous hyperplasia presents with multiple vessels in a crown-like arrangement that do not cross the center of the lesion. The sebaceous glands resemble popcorn (FIGURE 8).
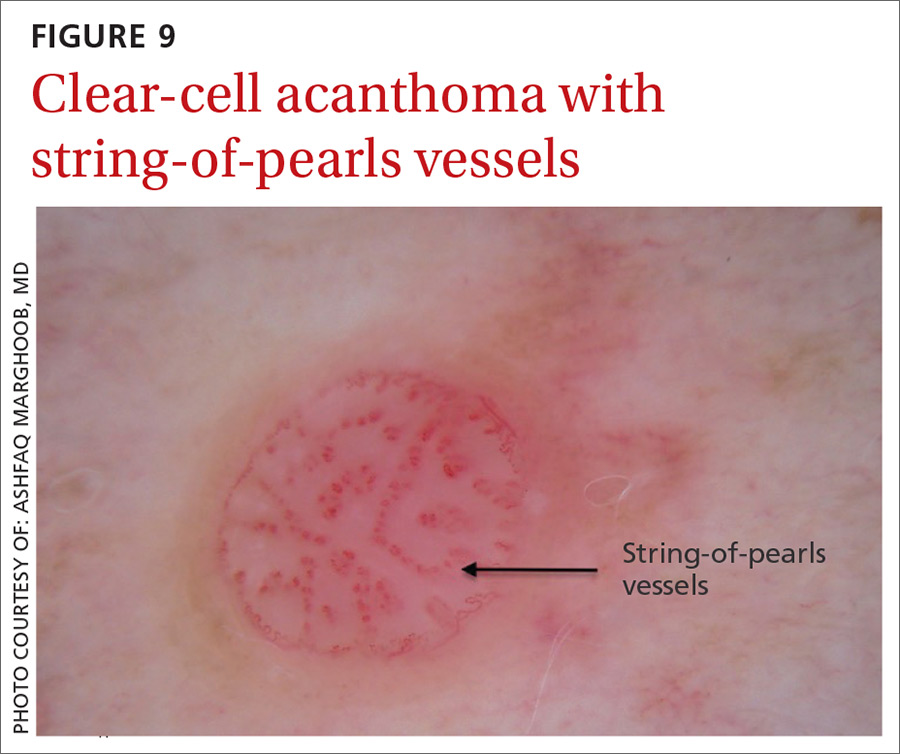
Clear-cell acanthoma is a benign erythematous epidermal tumor usually found on the leg with a string-of-pearls pattern. This pattern is vascular so the pearls are red in color (FIGURE 9).
Malignant nonmelanocytic lesions
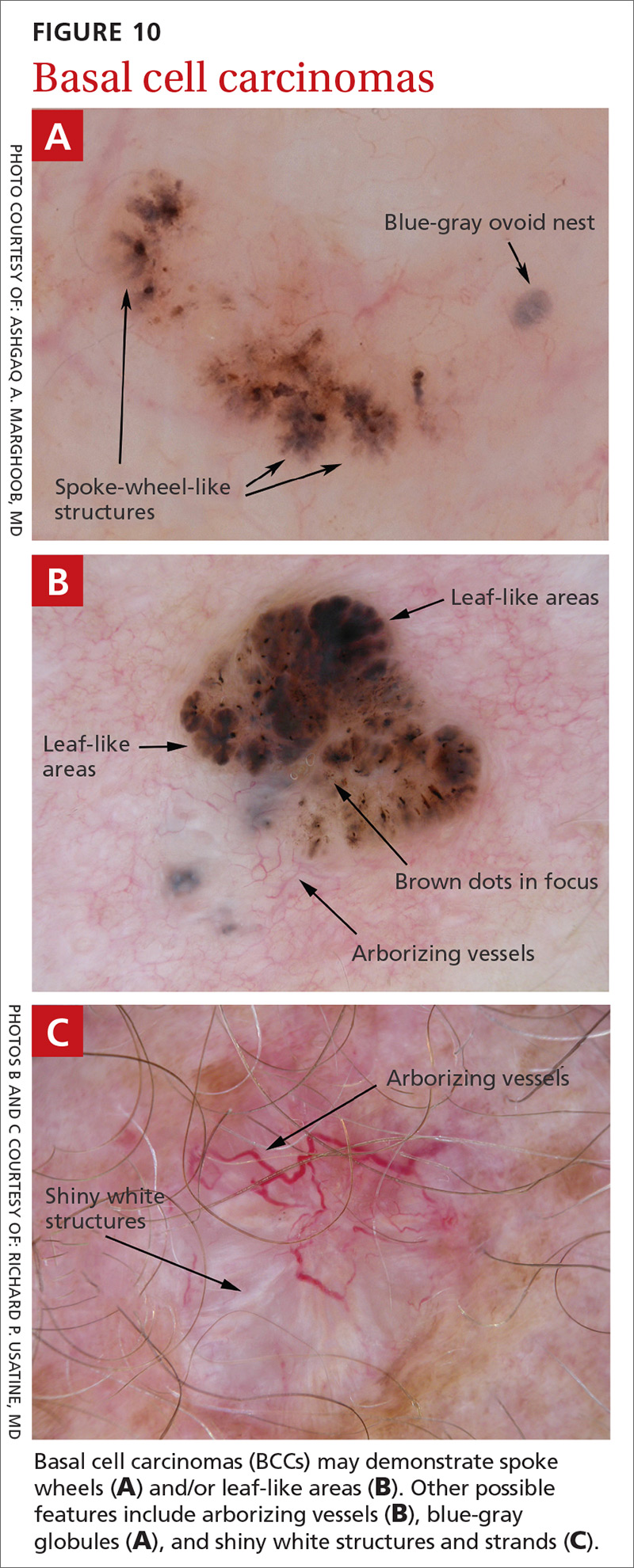
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. Features often include:
- spoke-wheel-like structures or concentric structures (FIGURE 10A)
- leaf-like areas (FIGURE 10B)
- arborizing vessels (FIGURE 10b and 10C)large blue-gray ovoid nest (FIGURE 10A)
- multiple blue-gray non-aggregated globules
- ulceration or multiple small erosions
- shiny white structures and strands (FIGURE 10C).
Additional dermoscopic clues include short, fine, superficial telangiectasias and multiple in-focus dots in a buck-shot scatter distribution.
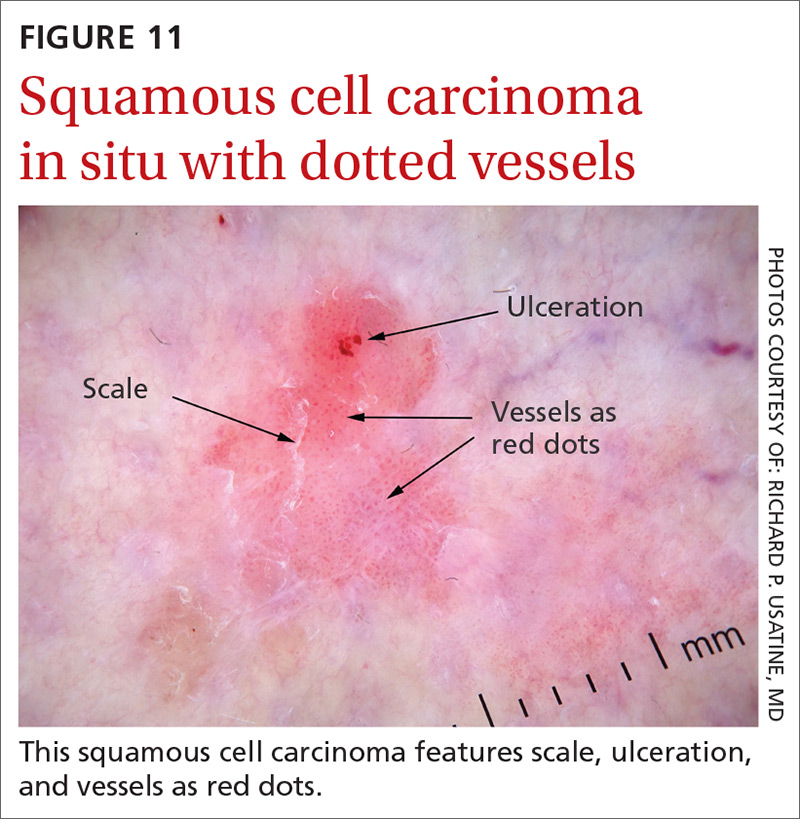
Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the skin are keratinizing malignant tumors. Each SCC generally has some of the following features (FIGURE 11):
- dotted and/or glomerular vessels, commonly distributed focally at the periphery. They can also be diffuse or aligned linearly within the lesion.
- scale (yellow or white)
- rosettes (seen with polarized light)
- white circles or keratin pearls
- brown circles
- ulcerations
- brown dots or globules arranged in a linear configuration.
Continue to: Step 2...






