Therapy-resistant major depression The attraction of magnetism: How effective—and safe—is rTMS?
Despite early mixed results, magnetic stimulation of the prefrontal cortex is showing potential in major depression and other psychiatric disorders.
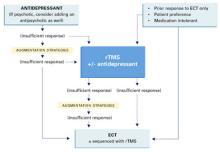
Solid lines represent current standards of practice. Dotted lines represent hypothetical roles for rTMS.
Source: Adapted and reprinted with permission from Dowd et al. Is repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation an alternative to ECTfor the treatment of depression? Contemp Psychiatry 2002;1:1-10.
POTENTIAL ROLE FOR rTMS
Today’s standard treatment of major depressive episodes begins with an antidepressant (plus an antipsychotic, if necessary) and proceeds to augmentation strategies if response is insufficient. rTMS may one day become an augmentation or monotherapy option for patients who do not respond sufficiently to standard treatments (Figure).
ECT treatment may be initiated if a patient has had a prior good response to ECT, is intolerant to medication, or prefers ECT. In that case, rTMS may be used as an alternate initial treatment or with ECT. Thus, rTMS may be used:
- to augment antidepressants
- as an alternative to antidepressants or ECT
- or sequentially with ECT.
Before that can happen, however, optimal treatment parameters need to be clarified by larger, well-designed, controlled studies comparing rTMS to a valid sham treatment, antidepressants, and ECT.
Related resources
- International Society for Transcranial Stimulation. www.ists.unibe.ch/
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Research Clinic at Yale-New Haven Psychiatric Hospital.
Disclosure
The authors report that they have no proprietary interest in the technology discussed in this article.