Long-acting injectable antipsychotics: What to do about missed doses
Use a stepwise approach based on the unique properties of the specific medication.
Aripiprazole long-acting injection is administered every 4 weeks. If a patient misses an injection, first determine how many consecutive doses he or she has received.33 If the patient has missed the second or third injection, and it has been <5 weeks since the last dose, give the next injection as soon as possible. If it has been >5 weeks, give the next injection as soon as possible, plus oral aripiprazole supplementation for 2 weeks (Figure 7).
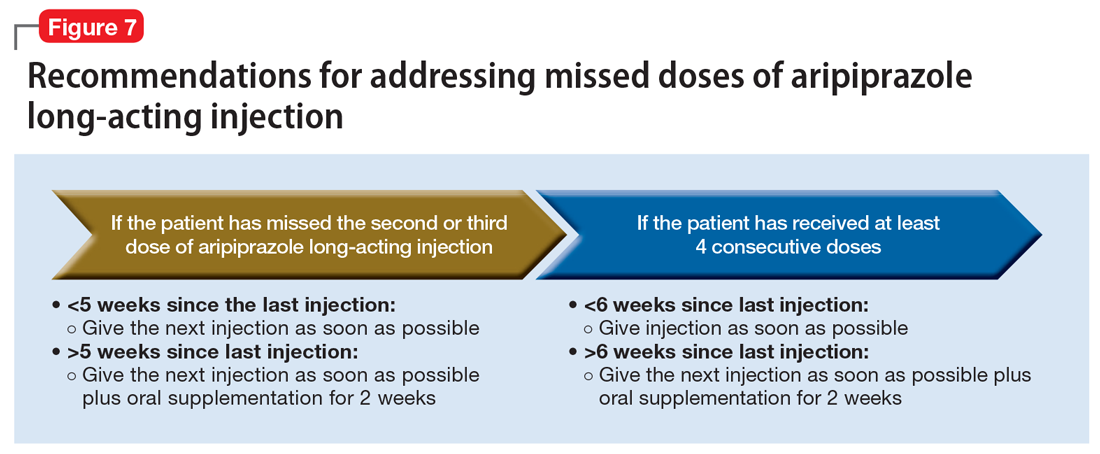
If the patient has received ≥4 consecutive doses and misses a dose and it has been <6 weeks since the last dose, administer an injection as soon as possible. If it has been >6 weeks since the last dose, give the next injection as soon as possible, plus with oral aripiprazole supplementation for 2 weeks.
Aripiprazole lauroxil long-acting injection. Depending on the dose, aripiprazole lauroxil can be administered monthly, every 6 weeks, or every 2 months. Aripiprazole lauroxil can be administered 14 days before or after the scheduled dose.34
The guidance for addressing missed or delayed doses of aripiprazole lauroxil differs depending on the dose the patient is stabilized on, and how long it has been since the last injection. Figure 8 summarizes how missed injections should be managed. When oral aripiprazole supplementation is needed, the following doses should be used:
- 10 mg/d if stabilized on 441 mg every month
- 15 mg/d if stabilized on 662 mg every month, 882 mg every 6 weeks, or 1,064 mg every 2 months
- 20 mg/d if stabilized on 882 mg every month.34

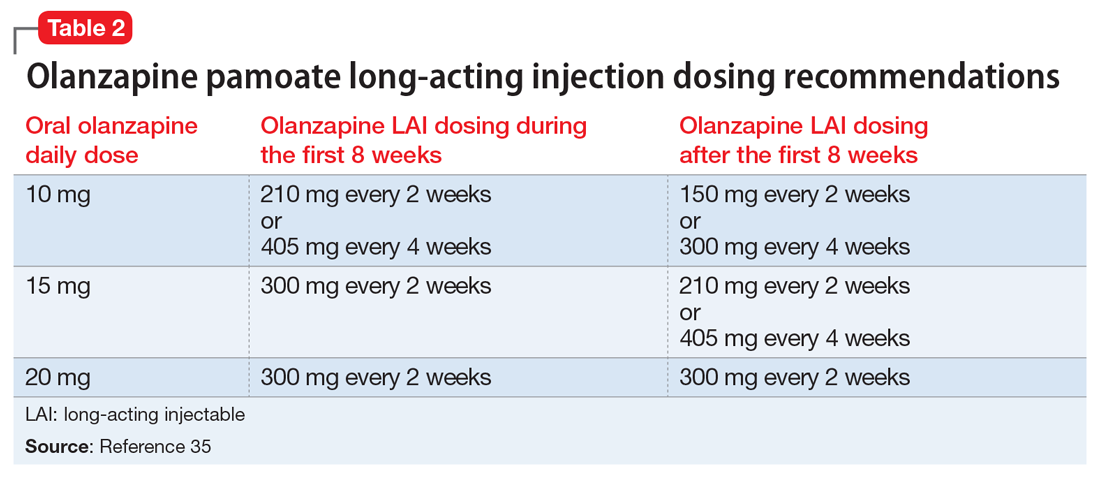
Olanzapine pamoate long-acting injection is a unique LAIA because it requires prescribers and patients to participate in a risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) program due the risk of post-injection delirium/sedation syndrome. It is administered every 2 to 4 weeks, with loading doses given for the first 2 months of treatment (Table 235). After 2 months, the patient can proceed to the maintenance dosing regimen.
Continue to: Currently, there is no concrete guidance...






