Racial Disparities, Germline Testing, and Improved Overall Survival in Prostate Cancer





Michael M. Goodman, MD
Associate Professor, Department of Hematology and Oncology
Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist
Winston-Salem, North Carolina;
VA Hematology/Oncology Physician and Program Manager
Director, Salisbury VA Infusion Center
Salisbury, North Carolina
Dr. Goodman has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.





The incidence of prostate cancer (PCa) has been rising1; this increase is particularly evident in more aggressive, advanced stages of PCa. Metastatic castration-resistant PCa has a median overall survival (OS) of up to about 2 years and is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men in the United States.2
Black men face a significantly higher risk for PCa compared with White men.1 Researchers have identified variations in the genomic profiles of metastatic PCa cells among US veterans that are potentially linked to race and ethnicity. Study findings represent a significant advancement in understanding genomic alterations in metastatic prostate cancer.1 This is especially noteworthy for Black men, who have been historically underrepresented in precision oncology research.3
A qualitative study of veterans with advanced PCa explored decision-making regarding germline testing. Several veterans with service-connected disability benefits declined testing, fearing it might jeopardize their benefits.4,5 Consequently, language in the veterans benefits manual was updated, clarifying that genetic results cannot disqualify service-connected benefits and emphasizing the importance of clear communication during counseling.4
Significant improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone sensitive PCa were observed in patients diagnosed between 2000 and 2019 in SEER and VHA databases. The gains were notable in patients younger than 70 years, likely driven by the increased adoption of combination therapies.6
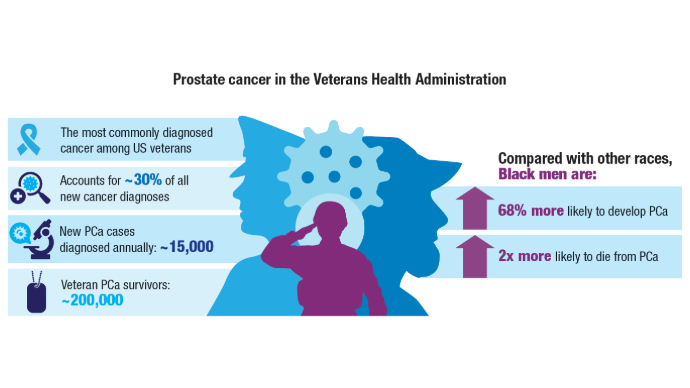 Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9
Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9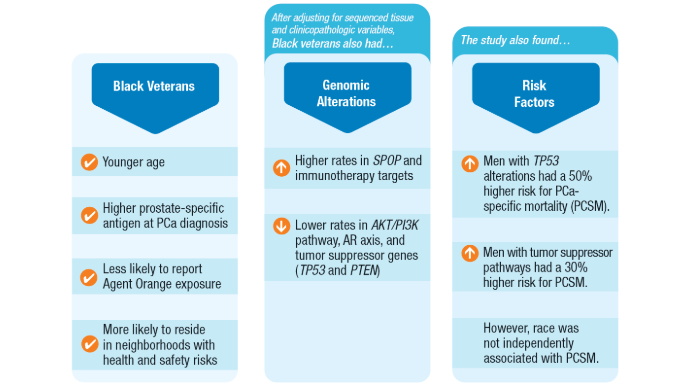 Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Associations among genomic alterations, race, and PCSM were studied in 5015 veterans with PCa (1784 Black and 3231 White veterans). Findings highlight the need for genetic testing to guide personalized treatments, using SPOP alterations to identify therapy targets and linkingTP53to higher mortality risk.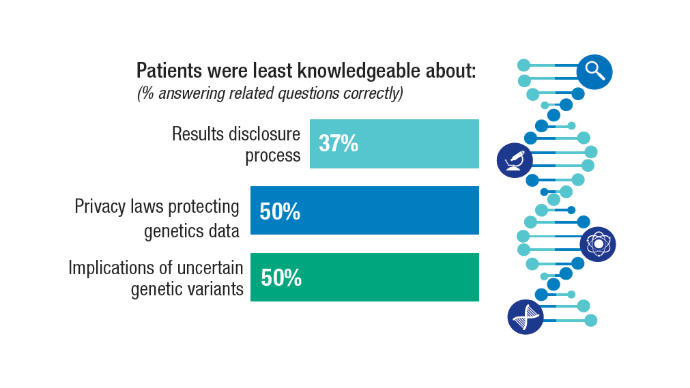 Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Misconceptions regarding service-connected benefits pose a major barrier to germline testing for veterans with advanced PCa. In December 2023, the Veterans Benefits Administration clarified that genetic test results do not affect previously granted service connected benefits. Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
There is a crucial need for ongoing clear, patient centered precision oncology communication, providing further education and reassurance to empower veterans to make informed decisions about germline testing.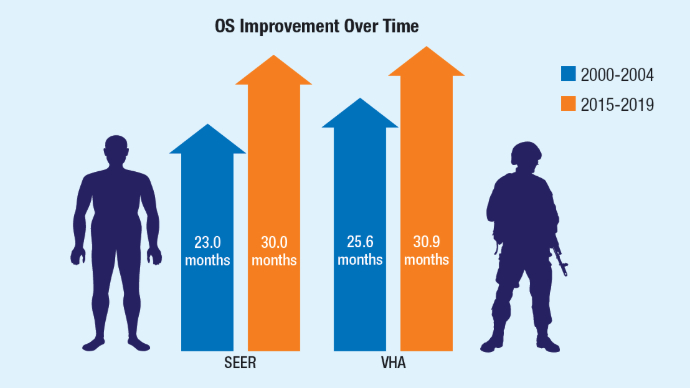 OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019.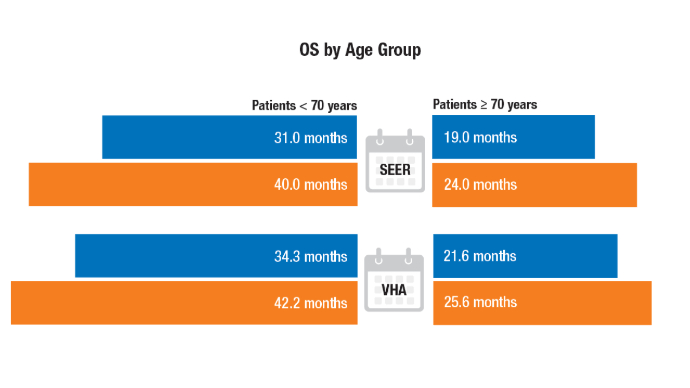 OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019. Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9
Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9 Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Associations among genomic alterations, race, and PCSM were studied in 5015 veterans with PCa (1784 Black and 3231 White veterans). Findings highlight the need for genetic testing to guide personalized treatments, using SPOP alterations to identify therapy targets and linkingTP53to higher mortality risk. Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Misconceptions regarding service-connected benefits pose a major barrier to germline testing for veterans with advanced PCa. In December 2023, the Veterans Benefits Administration clarified that genetic test results do not affect previously granted service connected benefits. Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
There is a crucial need for ongoing clear, patient centered precision oncology communication, providing further education and reassurance to empower veterans to make informed decisions about germline testing. OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019. OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019. Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9
Prostate Cancer Burden1-3,7-9 Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Race and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Prostate Cancer3
Associations among genomic alterations, race, and PCSM were studied in 5015 veterans with PCa (1784 Black and 3231 White veterans). Findings highlight the need for genetic testing to guide personalized treatments, using SPOP alterations to identify therapy targets and linkingTP53to higher mortality risk. Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Misconceptions regarding service-connected benefits pose a major barrier to germline testing for veterans with advanced PCa. In December 2023, the Veterans Benefits Administration clarified that genetic test results do not affect previously granted service connected benefits. Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
Veterans’ Knowledge of Germline Testing4,5
There is a crucial need for ongoing clear, patient centered precision oncology communication, providing further education and reassurance to empower veterans to make informed decisions about germline testing. OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019. OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
OS Improvement in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive PCa6
A large cross-sectional study found notable improvements in median OS for de novo metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in SEER and VHA patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2019.
Click here to view more from Cancer Data Trends 2025.
,false