Approach to dysphagia
Differentiating etiologies of esophageal dysphagia
The next step in diagnosing esophageal dysphagia is differentiating between structural, inflammatory, or dysmotility etiology (Figure 1).
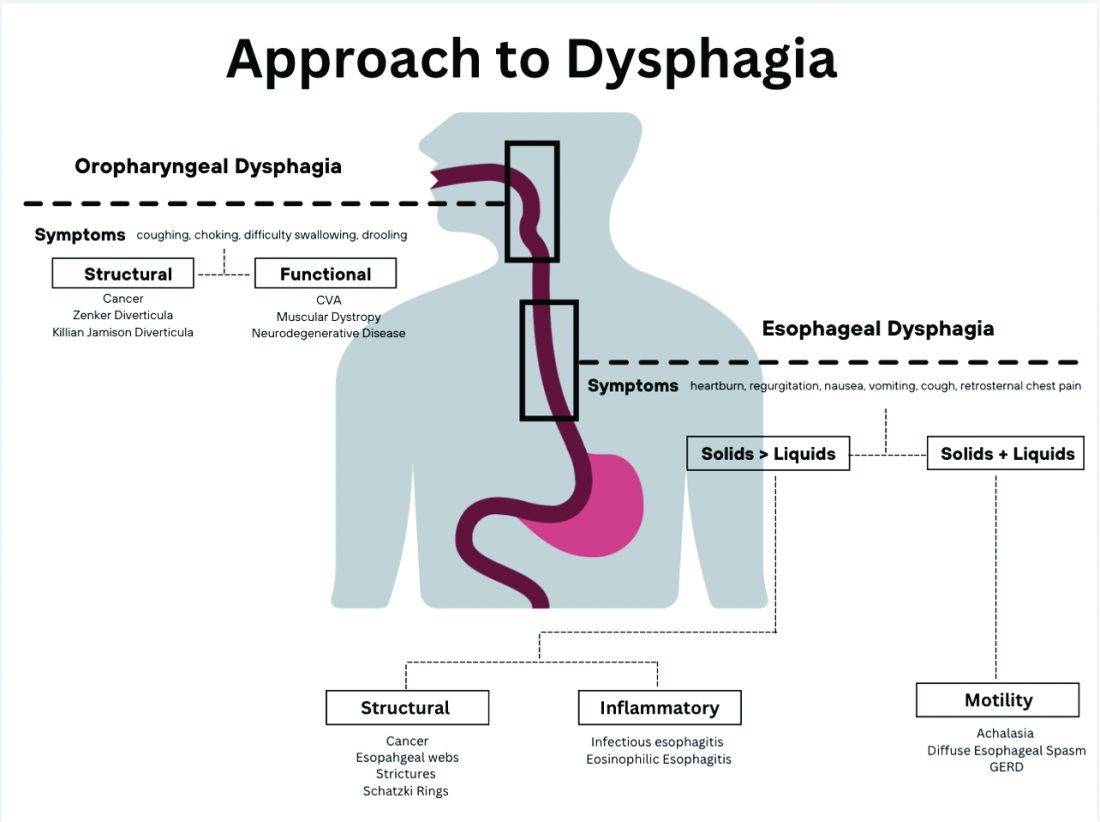
Patients with a structural cause typically have difficulty swallowing solids but are able to swallow liquids unless the disease progresses. Symptoms can rapidly worsen and lead to odynophagia, weight loss, and vomiting. In comparison, patients with motility disorders typically have difficulty swallowing both solids and liquids initially, and symptoms can be constant or intermittent.5
Prior to diagnostic studies, a 4-week trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is appropriate for patients with reflux symptoms who are younger than 50 with no alarm features concerning for malignancy.7,9 If symptoms persist after a PPI trial, then an upper endoscopy (EGD) is indicated. An EGD allows for visualization of structural etiologies, obtaining biopsies to rule out inflammatory etiologies, and the option to therapeutically treat reduced luminal diameter with dilatation.10 The most common structural and inflammatory etiologies noted on EGD include strictures, webs, carcinomas, Schatzki rings, and gastroesophageal reflux or eosinophilic esophagitis.4
If upper endoscopy is normal and clinical suspicion for an obstructive cause remains high, barium esophagram can be utilized as an adjunctive study. Previously, barium esophagram was the initial test to distinguish between structural and motility disorders. The benefits of endoscopy over barium esophagram as the first diagnostic study include higher diagnostic yield, higher sensitivity and specificity, and lower costs.7 However, barium studies may be more sensitive for lower esophageal rings or extrinsic esophageal compression.3
Evaluation of esophageal motility disorder
If a structural or inflammatory etiology of dysphagia is not identified, investigation for an esophageal motility disorder (EMD) is warranted. Examples of motility disorders include achalasia, ineffective esophageal motility, hypercontractility, spasticity, or esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO).10,11 High-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) remains the gold standard in diagnosis of EMD.12 An HRM catheter utilizes 36 sensors placed two centimeters apart and is placed in the esophagus to evaluate pressure and peristalsis between the upper and lower esophageal sphincters.13 In 2009, the Chicago Classification System was developed to provide a diagnostic algorithm that categorizes EMD based on HRM testing, with the most recent version (4.0) being published in 2020.12,14 Motility diagnoses are divided into two general classifications of disorders of body peristalsis and disorders of EGJ outflow. The most recent updates also include changes in swallow protocols, patient positioning, targeted symptoms, addition of impedance sensors, and consideration of supplemental testing when HRM is inconclusive based on the clinical context.12 There are some limitations of HRM to highlight. One of the main diagnostic values used with HRM is the integrated relaxation pressure (IRP). Despite standardization, IRP measurements vary based on the recorder and patient position. A minority of patients with achalasia may have IRP that does not approach the accepted cutoff and, therefore, the EGJ is not accurately assessed on HRM.15,16 In addition, some swallow protocols have lower sensitivity and specificity for certain motility disorders, and the test can result as inconclusive.14 In these scenarios, supplemental testing with timed barium esophagram or functional luminal imaging probe (EndoFLIP) is indicated.10,11
Over the past decade, EndoFLIP has emerged as a novel diagnostic tool in evaluating EMD. EndoFLIP is usually completed during an upper endoscopy and utilizes impedance planimetry to measure cross-sectional area and esophageal distensibility and evaluate contractile patterns.16 During the procedure, a small catheter with an inflatable balloon is inserted into the esophagus with the distal end in the stomach, traversing the esophagogastric junction (EGJ). The pressure transducer has electrodes every centimeter to allow for a three-dimensional construction of the esophagus and EGJ.17 EndoFLIP has been shown to accurately measure pyloric diameter, pressure, and distensibility at certain balloon volumes.18 In addition, FLIP is being used to further identify aspects of esophageal dysmotility in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, thought primarily to be an inflammatory disorder.19 However, limitations include minimal accessibility of EndoFLIP within clinical practice and a specific computer program needed to generate the topographic plots.20
When used in conjunction with HRM, EndoFLIP provides complementary data that can be used to better detect major motility disorders.15,20,21 Each study adds unique information about the different physiologic events comprising the esophageal response to distention. Overall, the benefits of EndoFLIP include expediting workup during index endoscopy, patient comfort with sedation, and real-time diagnostic data that supplement results obtained during HRM.10,16,20,2223
Of note, if the diagnostic evaluation for structural, inflammatory, and motility disorders are unrevealing, investigating for atypical reflux symptoms can be pursued for patients with persistent dysphagia. Studies investigating pH, or acidity in the esophagus, in relation to symptoms, can be conducted wirelessly via a capsule fixed to the mucosa or with a nasal catheter.3








