International Travelers Can Bring Home Unwelcome Rashes, Disease
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE ANNUAL MEETING OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF EMERGENCY PHYSICIANS
"Treatment is symptomatic, but in this case you can use NSAIDs because they have less of the thrombocytopenia that you see with dengue," she said. "There have been many case reports that chloroquine was effective, but there are no controlled studies of that."
Typhoid
Transmitted by ingestion of contaminated food or water, typhoid (enteric fever) has an incubation period of about 1-2 weeks. It produces fever, abdominal pain, and constipation more often than diarrhea. About 30% of cases will have a rash consisting of macular lesions called rose spots. Patients may also have leukopenia, mild thrombocytopenia, and moderately elevated alanine aminotransferase levels. Untreated patients may develop life-threatening complications such as gastrointestinal perforation, pneumonia, and myocarditis, typically in the third week of infection, Dr. Chin said.
"The diagnosis relies on isolation of Salmonella typhi from the patients, [using] either blood … or urine cultures," she said. "Stool is not often done, because they are constipated." Typhoid is typically treated with fluoroquinolones, but clinicians should be aware that multidrug resistance is now problematic in India (seen in 35% of isolates from there) and Vietnam (in 80%). "If your patient is coming back from a fluoroquinolone resistance area, you can consider ceftriaxone or azithromycin," she advised.
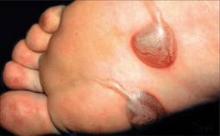
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
Travelers acquire cutaneous larva migrans, the infective (larval) stage of the dog or cat hookworm, through contact with contaminated soil or sand on tropical or subtropical beaches. Hence, this rash is more often seen on the feet or buttocks.
The infection begins with pruritic papules, which are followed by a serpiginous linear rash that migrates superficially several millimeters a day and hence is referred to as a creeping eruption. It usually lasts from weeks to months if not treated.
"Our [infectious disease] people think that these [organisms] die anyway, so they question treatment," Dr. Chin commented. If cutaneous larva migrans is treated, clinicians should use ivermectin or albendazole, she said.
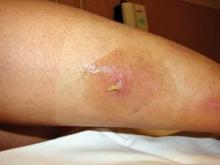
Botfly Infestation
Travelers acquire botfly infestation (cutaneous myiasis) when they are bitten by insects carrying eggs of the human botfly, which is widely distributed in Central and South America, Dr. Chin said. They seek medical care for enlarging bumps on and possibly a crawling sensation beneath their skin, in the absence of any psychiatric illness.
On examination, patients have raised papules resembling boils, with a central punctate air hole through which the growing botfly larva breathes. The larva can be surgically extracted, smothered with occlusive agents such as petroleum jelly to encourage emergence, removed with a venom extractor, or simply squeezed out of the lesion, she said.
Acute Schistosomiasis
The rash of acute schistosomiasis, also called Katayama fever, is pruritic and accompanied by flulike symptoms, lymphadenopathy, and eosinophilia, appearing after an incubation period of 2-8 weeks. Travelers acquire this parasitic infection through contact with fresh water harboring the organism's host, the snail, in endemic regions such as sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Southeast Asia, Dr. Chin said. It is treated with praziquantel. Some patients develop a schistosomal myelopathy that can lead to permanent neurologic damage, she noted.
Leptospirosis
The spirochete that causes leptospirosis is carried by and shed in the urine of livestock, dogs, rodents, and wild animals, and is thus found in water or soil, according to Dr. Chin. The incubation period is 7-12 days. "Patients may have a biphasic illness," she noted. "Fever, headaches, myalgias, sometimes with conjunctivitis and a rash," initially. "And some people may develop a secondary systemic infection of jaundice and renal failure," known as Weil syndrome.
This infection is diagnosed with serology and treated with doxycycline or penicillin, she said.
Dr. Chin reported no conflicts of interest.