Tackling Inflammatory and Infectious Nail Disorders in Children
Nail disorders are common in the pediatric population and affect quality of life. We review inflammatory conditions (ie, nail psoriasis, nail lichen planus [NLP], trachyonychia, nail lichen striatus, nail atopic dermatitis [AD]) as well as infectious conditions (ie, nail disease due to hand, foot, and mouth disease [HFMD] or Kawasaki disease, onychomycosis, acute paronychia). Inflammatory and infectious nail conditions may involve the skin or occur in isolation. By highlighting the distinctive features and clinical presentations of these infectious and inflammatory nail disorders in children, we aim to raise awareness among dermatologists to improve diagnosis and management.
Practice Points
- Nail plate pitting is the most common clinical sign of nail psoriasis in children.
- Nail changes are common in hand, foot, and mouth disease, with the most frequent being onychomadesis.
- Because onychomycosis may resemble other nail disorders, mycologic confirmation is recommended to avoid misdiagnosis.
- Many nail conditions in children self-resolve but recognizing these manifestations is important in providing anticipatory guidance to patients and caregivers.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
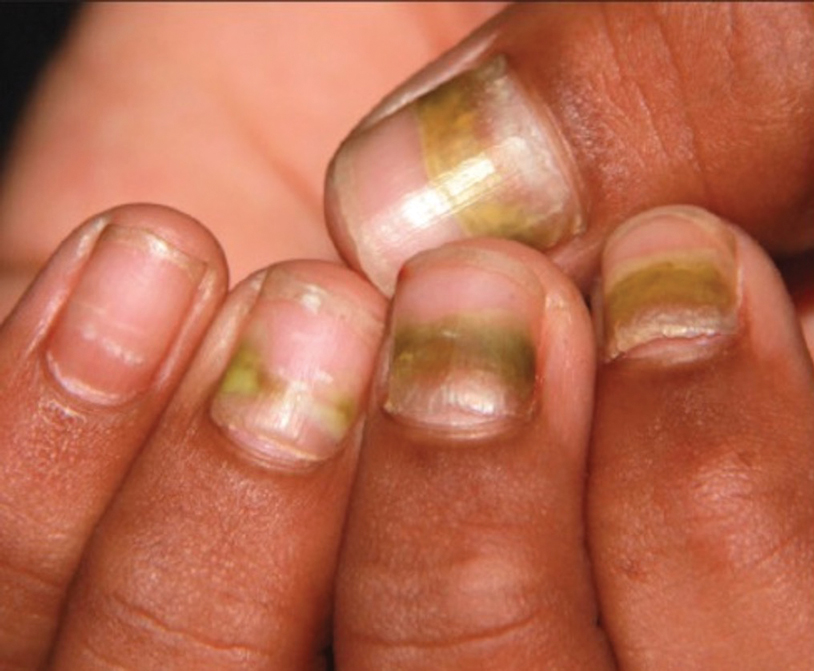
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.