Proper Use and Compliance of Facial Masks During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Observational Study of Hospitals in New York City
Proper mask usage is a cornerstone of the prevention of COVID-19 transmission. Hospitals, in particular, are important settings for proper mask compliance due to the risk for viral exposure. Despite the presence of health care personnel and financial resources to ensure proper compliance, mask usage is variable in health care settings. The impact of mask compliance is particularly important in New York City (NYC) because of the burden of COVID-19 and at-risk demographics. We conducted a prospective observational study in 4 NYC hospitals assessing rates of proper mask compliance among adult patients entering the hospital. Six hundred unique individuals were observed for proper mask fit, exposure of the nose and mouth, and the presence of nontraditional face coverings in lieu of a mask at 4 NYC hospitals. Proper mask usage is a large health education gap that must be addressed by health care administrations and governmental agencies, as mask usage continues to be an effective form of COVID-19 prevention.
Practice Points
- Enormous financial and human resources have been utilized by health care systems to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in health care settings, including universal temperature checks, clinical symptom triage, and masking policies. Despite these mitigation practices, mask noncompliance continues to be a major problem in hospitals.
- Mask compliance among 600 individuals entering 4 New York City hospitals was observed to be 78%, despite months of policies for universal masking and the city’s high mortality rates during the first COVID-19 wave.
- Masks have been shown to reduce the spread of COVID-19, and proper mask compliance is an important issue that must be addressed by health care administrations and governmental agencies.
Mask usage was observed and classified into several categories: correctly fitting mask over the nose and mouth, no face mask, mask usage with nose exposed, mask usage with mouth exposed, mask usage with both nose and mouth exposed (ie, mask on the chin/neck area), loosely fitting mask, vented/valved mask, or other form of face covering (eg, bandana, scarf).
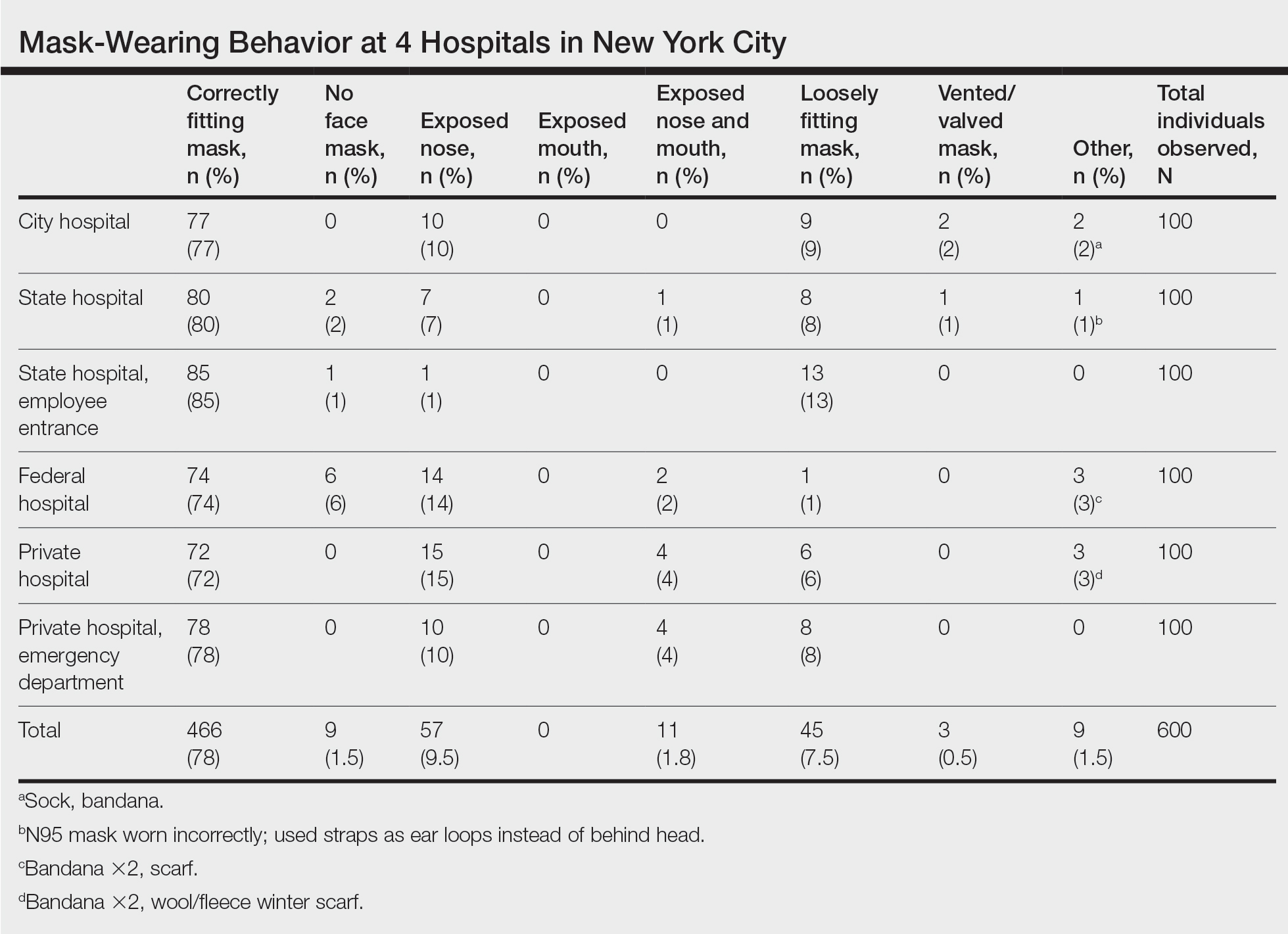
Results
We observed a consistent rate of mask compliance between 72% and 85%, with an average of 78% of the 600 individuals observed wearing correctly fitting masks across the 4 hospitals included in this study (Table). The employee entrance included in this study had the highest compliance rate of 85%. An overall low rate of complete mask noncompliance was observed, with only 9 individuals (1.5%) in the entire study not wearing any mask. The federal hospital had the highest rate of mask noncompliance. We also observed a low rate of nose and mouth exposure, with 1.8% of individuals wearing a mask with the nose and mouth exposed (ie, mask tucked under the chin). No individuals were observed with the mouth exposed but with the nose covered by a mask. Additionally, only 3 individuals (0.5%) wore a mask with a vent/valve. The most common way that masks were worn incorrectly was with the nose exposed, accounting for 9.5% of individuals observed. Overall, only 9 individuals (1.5%) wore a nontraditional face covering, with a bandana being the most commonly observed makeshift mask.
Signage regarding the requirement to wear masks and to social distance was universally instituted at all hospital entry points (both inside and outside the hospital) in this study. However, there were no illustrations demonstrating correct and incorrect forms of mask usage. All signage merely displayed a graphic of a facial mask noting the requirement to wear a mask prior to entering the building. Hospital staff also had face masks available for patients who failed to bring a mask or who wore an inappropriate mask (ie, vented/valved masks).
Comment
Mask Effectiveness—Masks reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2 by preventing both droplets and potentially virus-bearing aerosols.6,21,22 It has been demonstrated that well-fitted cotton homemade masks and medical masks provide the most effective method of reducing droplet dispersion. Loosely fitted masks as well as bandana-style facial coverings minimally reduce small aerosolized droplets, and an uncovered mouth and nose can disperse particles at a distance much greater than 6 feet.22
Mask Compliance—We report an overall high compliance rate with mask wearing among individuals visiting a hospital; however, compliance was still imperfect. Overall, 78% of observed individuals wore a correctly fitting mask when entering a hospital, even with hospital staff positioned at entry points to ensure proper mask usage. With all the resources available at health care centers, we anticipated a much higher compliance rate for correctly fitting masks at hospital entrances. We hypothesize that given only 78% of individuals showed proper mask compliance in a setting with enforcement by health care personnel, the mask compliance rate in the larger community is likely much lower. It is imperative to enforce continued mask compliance in medical centers and other public areas given notable vaccine noncompliance in certain parts of the country.






