2021 update on contraception
The FDA approved 3 new contraceptive methods this past year, but they are not new types of contraceptives. Do these products—a pill, a patch, and a vaginal gel—represent anything novel for patients? We review efficacy and safety data for all 3 methods to aid in physician counseling and selection of appropriate contraceptive methods based on clinical factors.
New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE
Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
The COC E4/drospirenone was evaluated in 2 parallel multinational studies. Here, we review the North American data that are more relevant for the US population; the European-Russian data also are published.15
Study examined 1 year’s use of E4/drospirenone
The US–Canadian trial conducted by Creinin and colleagues enrolled 1,864 participants aged 16 to 50 years to evaluate contraceptive efficacy, bleeding patterns, and adverse events with 1-year use (13 cycles) of E4/drospirenone. The primary efficacy group included 1,524 women aged 16 to 35. This study enrolled healthy, heterosexually active participants with a BMI ≤35 kg/m2 and regular menses from 70 sites in the United States and 7 sites in Canada. The dropout rate was 45%, comparable to that in other contraceptive studies. Participants used E4/drospirenone cyclically, taking 1 hormone-containing pill daily for 24 days followed by 4 days of placebo pills.
Contraceptive efficacious, no VTE observed
The researchers reported efficacy as a Pearl Index (PI) of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years in participants aged 16 to 35 and an overall 13-cycle life-table pregnancy rate of 2.06%. The PI did not differ among nonobese and obese participants in multivariable analysis. Most users experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding; only 13% to 18% reported absence of scheduled bleeding. Unscheduled bleeding was typically spotting (55.2%), and this decreased with treatment duration from 30% in cycle 1 to 15% to 20% in cycle 5 and on.
Overall, 28.9% of participants reported treatment-related adverse events (AEs), which most commonly were headache (5.0%), metrorrhagia (4.6%), and nausea (3.8%). Investigators reported a minimal change in mean (SD) BMI of 0.4 (1.7) kg/m2 from baseline after 1 year of E4/drospirenone use, and only 0.5% of participants discontinued use due to weight gain. The most common reasons for AE-related treatment discontinuation included metrorrhagia (0.9%), menorrhagia (0.8%), and vaginal hemorrhage (0.5%). Importantly, no cases of VTE occurred in this study of estetrol despite 23% of participants being obese, a known risk factor for VTE.
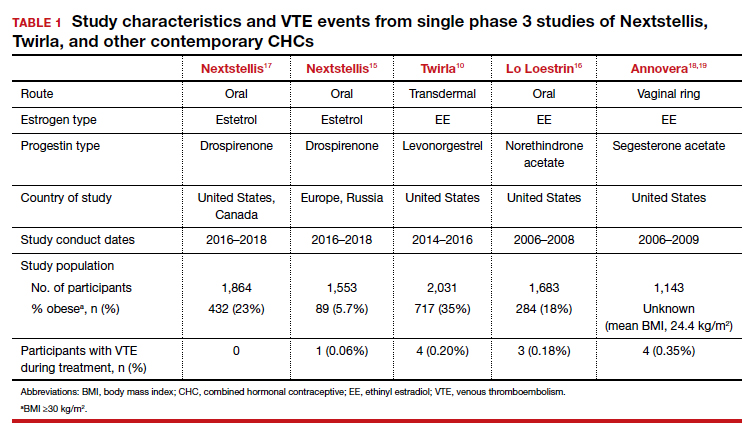
Nextstellis provides safe, effective contraception with a PI comparable to that of other available CHCs as well as a favorable bleeding profile in healthy users who are adherent to treatment. Importantly, contraceptive efficacy was maintained in obese users with a BMI up to 35 kg/m2. In contrast to EE or estradiol, E4 demonstrates a lower impact on the hepatic system, and preliminary findings suggest a lower VTE risk compared with other CHCs on the market. The European phase 3 trial of 1,553 participants also demonstrated a low rate of VTE, with only 1 case diagnosed.15 By contrast, similar phase 3 trials of available CHCs demonstrated more frequent VTE events despite low-dose EE formulations (TABLE 1).10,15-18 In general, most US phase 3 trials have 3 to 4 VTE events in the studied population, and the Nextstellis North American trial, of which 92% of participants were from the United States, had 0. However, confirmation of any potential lower VTE risk requires further analysis from large, population-based postmarketing studies.
Continue to: Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women...






