The Current State of Advanced Practice Provider Fellowships in Hospital Medicine: A Survey of Program Directors
BACKGROUND: Postgraduate training for advanced practice providers (APPs) is a growing field in hospital medicine. As hospital programs continue to benefit from highly trained physician assistants (PAs) and nurse practitioners (NPs), fellowship programs have become more prevalent. However, little is known about the number of active programs or how they prepare trainees.
OBJECTIVES: To describe the existing APP fellowships in hospital medicine, with a focus on program characteristics, rationale, curricula, and learner assessment. METHODS: An electronic survey was distributed by e-mail to hospital medicine program directors in May 2018. The survey consisted of 25 multiple choice and short answer questions. Descriptive statistics were calculated utilizing Stata 13 for data analysis.
RESULTS: Of the 11 fellowships identified, 10 (91%) of directors responded to the survey. Eighty percent of programs accept both NPs and PAs and 80% are between 12 and 13 months long. All programs cite “training and retaining” as the main driver for their creation and 90% were founded in institutions with existing physician residencies. Ninety percent of program curricula are informed by Society of Hospital Medicine resources. Despite these similarities, there was wide variation in both curricular content and APP fellow assessment.
CONCLUSION: APP fellowships in hospital medicine are quickly growing as a means to train and retain nonphysician hospitalists. While most programs accept similar types of applicants and share a common rationale for program development, there is little standardization in terms of curriculum or assessment. Further research may be valuable to characterize the best practices to guide the future of these fellowships.
© 2019 Society of Hospital Medicine
The survey tool was developed and validated internally in the AAMC Survey Development style18 and was influenced by prior validated surveys of postgraduate medical fellowships.10,
A web-based survey format (Qualtrics) was used to distribute the questionnaire e-mail to the PDs. Follow up e-mail reminders were sent to all nonresponders to encourage full participation. Survey completion was voluntary; no financial incentives or gifts were offered. IRB approval was obtained at Johns Hopkins Bayview (IRB number 00181629). Descriptive statistics (proportions, means, and ranges as appropriate) were calculated for all variables. Stata 13 (StataCorp. 2013. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13. College Station, Texas. StataCorp LP) was used for data analysis.
RESULTS
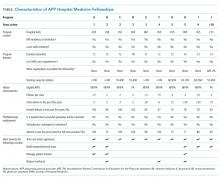
In total, 11 fellowships were identified using our multimethod approach. We found four (36%) programs by utilizing existing online databases, two (18%) through the SHM questionnaire and HMX forum, three (27%) through internet searches, and the remaining two (18%) were referred to us by the other PDs who were surveyed. Of the programs surveyed, 10 were adult programs and one was a pediatric program. Surveys were sent to the PDs of the 11 fellowships, and all but one of them (10/11, 91%) responded. Respondent programs were given alphabetical designations A through J (Table).
Fellowship and Individual Characteristics
Most programs have been in existence for five years or fewer. Eighty percent of the programs are about one year in duration; two outlier programs have fellowship lengths of six months and 18 months. The main hospital where training occurs has a mean of 496 beds (range 213 to 900). Ninety percent of the hospitals also have physician residency training programs. Sixty percent of programs enroll two to four fellows per year while 40% enroll five or more. The salary range paid by the programs is $55,000 to >$70,000, and half the programs pay more than $65,000.
The majority of fellows accepted into APP fellowships in hospital medicine are women. Eighty percent of fellows are 26-30 years old, and 90% of fellows have been out of NP or PA school for one year or less. Both NP and PA applicants are accepted in 80% of fellowships.
Program Rationales
All programs reported that training and retaining applicants is the main driver for developing their fellowship, and 50% of them offer financial incentives for retention upon successful completion of the program. Forty percent of PDs stated that there is an implicit or explicit understanding that successful completion of the fellowship would result in further employment. Over the last five years, 89% (range: 71%-100%) of graduates were asked to remain for a full-time position after program completion.