Effectiveness of duloxetine in treatment of painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
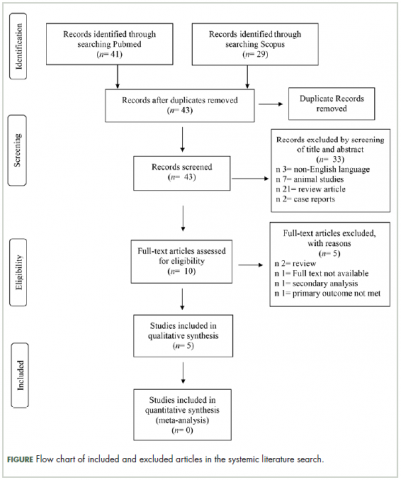
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a serious side effect that can be dose limiting and affect patient quality of life. To date, the therapeutic options for CIPN are limited. We performed a systematic literature search of the PubMed and Scopus databases to assess the effectiveness of duloxetine in the treatment of pain in patients with CIPN. The search included randomized controlled trials, nonrandomized controlled trials, retrospective studies, and single-arm studies of duloxetine in treatment of CIPN. A descriptive analysis of the studies was performed. The PubMed database online search identified 41 publications, and a second database search through Scopus identified 29 publications. A total of 10 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility, with 5 articles excluded. Altogether, the included studies reported 431 patients with painful CIPN. An improvement in pain scores was the primary and/or secondary endpoint in the included studies. Pain was assessed by 6 different scores. Comparator drugs were used in 4 studies in our review. The comparator drug was placebo in 1 study only, and the remaining 3 studies used other antineurotoxicity therapy. The chemotherapeutic agents used in the studies were the following: paclitaxel (52.9%), oxaliplatin (39.7%), R-CHOP (rituximab, doxorubicin, vincristine, and cyclophosphamide; 3.30%), combined bortezomib-dexamethasone (1.89%), FOLFOX (folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin; 1.18%), and other taxanes (0.94%). From the descriptive analyses, and from the available data of relatively small sample sized studies, it can be concluded that despite the above limitations, duloxetine remains a useful therapeutic option for pain in CIPN patients, regardless of the type of chemotherapeutic agent used.
Accepted for publication November 20, 2018
Correspondence Wael Ibrahim, MD; dr.wael_ezzat@hotmail.com
Disclosures The authors report no disclosures/conflicts of interest.
©2018 Frontline Medical Communications
doi https://doi.org/10.12788/jcso.0436
Exclusion criteria
Studies in a non-English language, animal studies, studies whose full-text article was not available, and thesis and conference papers were not included.
Objective and study design
The objective of this systematic review was to systematically assess the effectiveness of duloxetine in the treatment of pain in patients with CIPN.
Information sources and search
Medical electronic databases. PubMed and Scopus, from inception to January 2018, were searched using the following search queries: (((duloxetine) AND chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy)) OR ((((chemotherapy) AND (neuropathic pain OR peripheral neuropathy))) AND duloxetine).
,Selection of studies. The authors selected eligible studies. The screening of search results was performed in the following 2 steps:
n Screen title and abstracts against the selection criteria. Articles that were unclear from their title or abstract were reviewed against the selection criteria through the full text.
n Retrieve and screen full-text articles of eligible abstracts for eligibility to systematic review.
Data extraction
Two authors extracted the following data independently: sample size, mean age, chemotherapeutic drug, duloxetine dosage, and outcomes for pain assessment using at least one score from VAS, BPI-SF, neuropathic pain score using the NCI-CTCAE v3.0 and v4.0, or FACT-Tax, and other secondary outcomes. The data was exported from the online forms as a Microsoft Excel sheet.
Statistical analysis
We calculated the mean age and associated standard deviations (SDs) for all patients by using the pooled mean and pooled SD equation, according to Cochrane handbook of systematic reviews of interventions 5.1.0 (updated March 2011).23 When data are expressed as median and interquartile range, we used Hozo and colleagues’ BMC Research Methodology equation to calculate or estimate the mean and SD.24
Data are expressed as means with SD (unless stated otherwise); statistical results were considered significant when the P-value was less than .05. Data analysis was performed using the SPSS Statistical Package, version 23 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY).
Synthesis of data and analysis
Because of heterogeneity and low sample size of studies, no statistically justified analyses could be performed on the provided data. Instead, a descriptive analysis of published studies was performed.
Summary measures
The search strings, the list of relevant reviews, the data coding, and the quality criteria that were used can be requested from the corresponding author.
Results
Selection of articles
The