Feasibility of Risk Stratification of Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Chest Pain Using HEART Score
Study design
We conducted a
We conducted our study to determine the importance of calculating the HEART score in each patient, which will help to correctly place them into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups for clinically important, irreversible adverse cardiac events and guide the clinical decision-making. Patients with low risk will avoid costly tests and hospital admissions, thus decreasing the cost of treatment and ensuring timely discharge from the ED. Patients with high risk will be treated immediately, to possibly prevent a life-threatening, ACS-related incident. Thus, the HEART score will serve as a quick and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and help clinicians to make accurate diagnostic and therapeutic choices in uncertain situations.
HEART score
The total number of points for History, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Age, Risk factors, and Troponin was noted as the HEART score (Table 1).
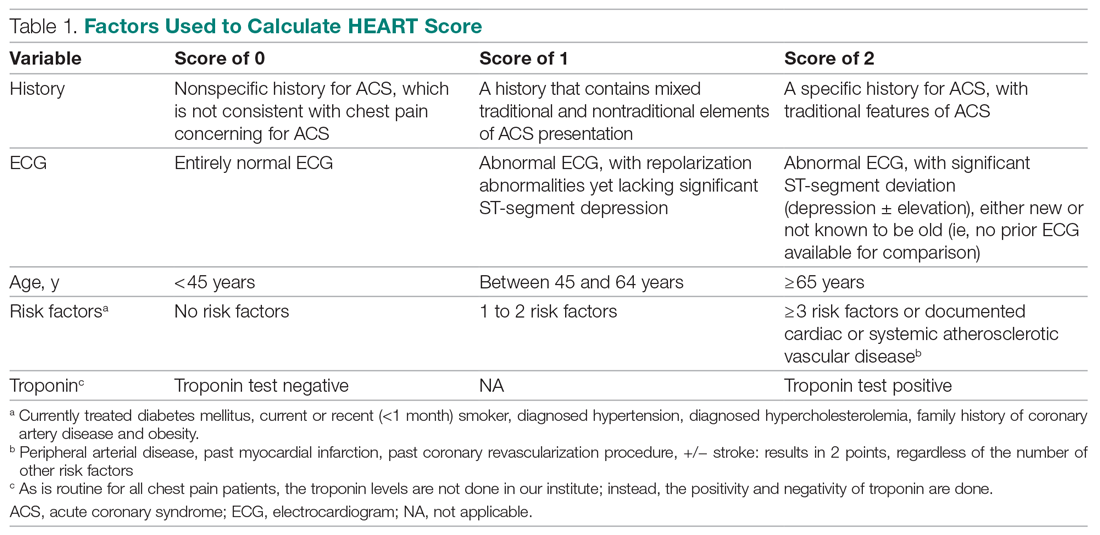
For this study, the patient’s history and ECGs were interpreted by internal medicine attending physicians in the ED. The ECG taken in the emergency room was reviewed and classified, and a copy of the admission ECG was added to the file. The recommendation for patients with a HEART score in a particular range was evaluated. Notably, those with a score of 3 or lower led to a recommendation of reassurance and early discharge. Those with a HEART score in the intermediate range (4-6) were admitted to the hospital for further clinical observation and testing, whereas a high HEART score (7-10) led to admission for intensive monitoring and early intervention. In the analysis of HEART score data, we only used those patients having records for all 5 parameters, excluding patients without an ECG or troponin test.






