New frontline treatments needed for Hodgkin lymphoma
In this editorial, Anna Sureda, MD, PhD, details the need for new frontline treatments for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma, including those with advanced stage disease.
Dr Sureda is head of the Hematology Department and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Programme at the Institut Català d'Oncologia, Hospital Duran i Reynals, in Barcelona, Spain. She has received consultancy fees from Takeda/Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Hodgkin lymphoma has traditionally been known as a cancer with generally favorable outcomes. Yet, as with any cancer treatment, there is always room for improvement. For Hodgkin lymphoma specifically, there remains a significant unmet need in the frontline setting for patients with advanced disease (Stage III or Stage IV).
Hodgkin lymphoma most commonly affects young adults as well as adults over the age of 55.1 Both age at diagnosis and stage of the disease are significant factors that must be considered when determining treatment plans, as they can affect a patient’s success in achieving long-term remission.
Though early stage patients have demonstrated 5-year survival rates of approximately 90%, this number drops to 70% in patients with advanced stage disease,2-4 underlining the challenges of treating later stage Hodgkin lymphoma.
Additionally, only 50% of patients with relapsed or refractory disease will experience long-term remission with high-dose chemotherapy and an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT)5-6— a historically and frequently used treatment regimen.
These facts support the importance of successful frontline treatment and highlight a gap with current treatment regimens.7-10
With current frontline Hodgkin lymphoma treatments, it can be a challenge for physicians to balance efficacy with safety. While allowing the patient to achieve long-term remission remains the goal, physicians are also considering the impact of treatment-related side effects including endocrine dysfunction, cardiac dysfunction, lung toxicity, infertility, and an increased risk of secondary cancers when determining the best possible treatment.8-15
Advanced stage vs early stage Hodgkin lymphoma
Stage of disease at diagnosis has a large influence on outcomes, with advanced stage patients having poorer outcomes than earlier stage patients.7,15-16 Advanced Hodgkin lymphoma patients are more likely to progress or relapse,7,15-16 with nearly one third remaining uncured following standard frontline therapy.7-10
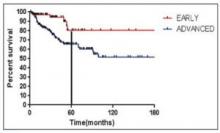
As seen in Figure 1 below, there is a clear difference in progression-free survival for early versus advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma.16
The difference between early stage and advanced stage patients treated with doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine (ABVD) demonstrates the heightened importance of successful frontline treatment for those with advanced stage disease.16
Unmet needs with current frontline Hodgkin lymphoma treatment
Though current treatments for frontline Hodgkin lymphoma, including ABVD and bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone (BEACOPP), have improved outcomes for patients, these standard regimens are more than 20 years old.
ABVD is generally regarded as the treatment of choice based on its efficacy, relative ease of administration, and side effect profile.17
Escalated BEACOPP, on the other hand, was developed to improve outcomes for advanced stage patients but is associated with increased toxicity.8-10,13,18
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans have also been identified as a pathway to help guide further treatment, but patients with advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma may relapse more often, despite a negative interim PET scan, compared to stage II patients.19
Among current treatments, side effects including lung and cardiotoxicity as well as an increased risk of secondary cancers are a concern for both physicians and their patients.8-10,13-15
Similarly, radiation therapy, often used in conjunction with chemotherapy for patients who have a large tumor burden in one part of the body, usually the chest,20 is also associated with an increased risk of secondary cancers and cardiotoxicity.8-10,21