Digital cohorts within the social mediome to circumvent conventional research challenges?
Social media in rare disease research
Rare diseases (conditions with a prevalence of less than 200,000 patients in North America), in particular, are prime for high-yield results and community impact using novel SM approaches. This is the result of established digital support groups, publications with historically low study numbers, and few focused investigators. Several studies of rare diseases have shown considerable advantages of using SM as a study tool. For instance, an existing neuroendocrine cervical cancer Facebook support group recently was used to recruit a geographically widespread cohort of patients with this rare cancer. Through an online survey posted in the Facebook group, patients were able to provide specific information on their treatment, disease, and symptom history, current disease status, and quality of life, including various psychological factors. Without the use of SM, collecting this information would have been virtually impossible because the patients were treated at 51 cancer centers across the country.14
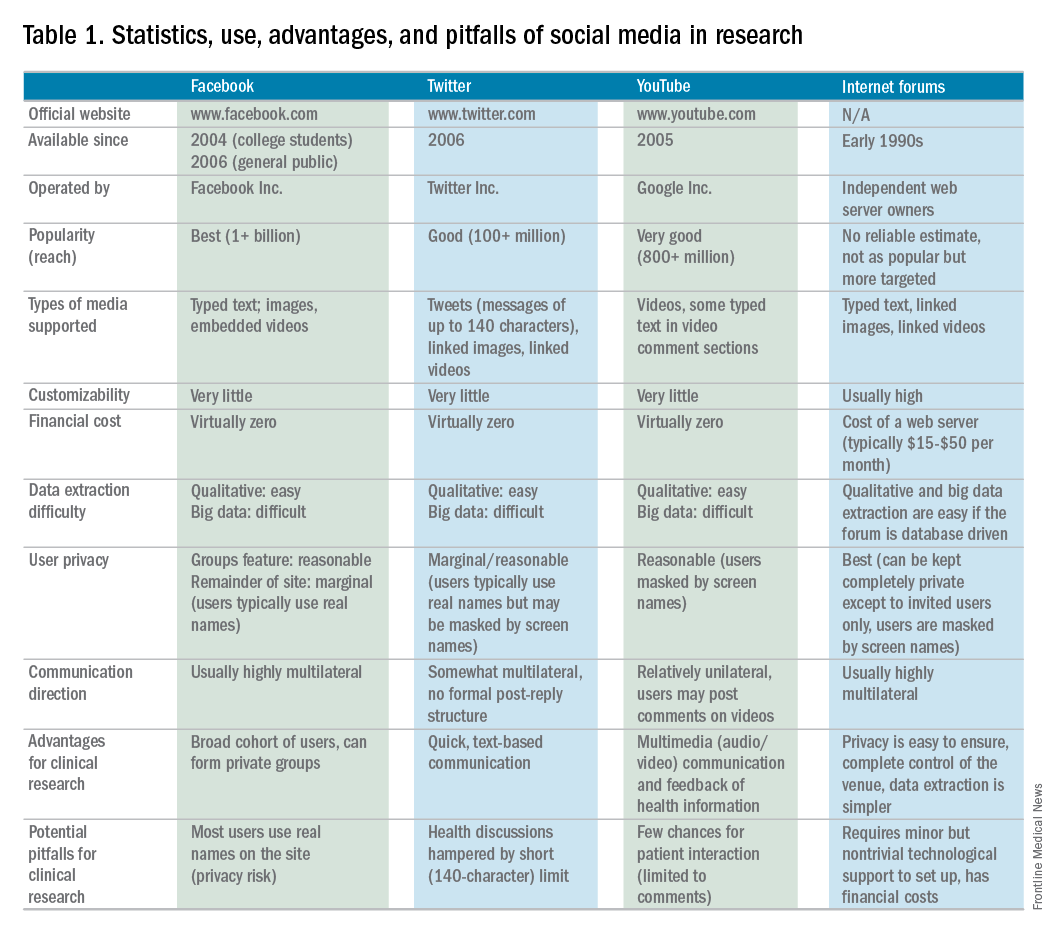
Currently, the use of SM in hepatology research, focused specifically on autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), is under exploration at Indiana University. AIH is a rare autoimmune liver disease that results in immune-mediated destruction of liver cells, possibly resulting in fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver failure if treatment is unsuccessful. One of the authors (C.L.) used both Facebook and Twitter to construct a large study group of individuals affected with AIH called the Autoimmune Hepatitis Research Network (AHRN; 1,500 members) during the past 2 years.4 Interested individuals have joined this research group after searching for AIH online support groups or reading shared AHRN posts on other media platforms. Between April 2015 and April 2016, there were posts by more than 750 unique active members (more than 50% of the group contributes to discussions), most of whom appear to be either caregivers of AIH patients or AIH patients themselves.
Preliminary informational analysis on this group has shown that C.L. and study collaborators have been able to uncover rich clinical and nonclinical information that otherwise would remain unknown. This research was performed by semi-automated download of the Facebook group’s content and subsequent semantic analysis. Qualitative analysis also was performed by direct reading of patient narratives. Collected clinical information has included histories of medication side effects, familial autoimmune diseases, and comorbid conditions. The most common factors that patients were unlikely to discuss with a provider (e.g., financial issues, employment, personal relationships, use of supplements, and alcohol use) frequently were discussed in the AHRN group, allowing a more transparent view of the complete disease experience.
Beyond research conducted in the current paradigm, the AHRN has provided a rich community construct in which patients offer each other social support. The patient impression of AHRN on Facebook has been overwhelmingly positive, and patients often wonder why such a model has not been used with other diseases. The close digital interaction the author (C.L.) has had with numerous patients and families has promoted other benefits of this methodology: more than 40 new AIH patients from outside Indiana have traveled to Indiana University for medical consultation despite no advertisement.
Conclusions
SM has the potential to transform health care research as a supplement to traditional research methods. Compared with a conventional research model, this methodology has proven to be cost and time effective, wide reaching, and similarly capable of data collection. Use of SM in research has tremendous potential to direct patient-centered research because invested patient collaborators can take an active role in their own disease and may hone investigatory focus on stakeholder priorities. Limitations to this method are known, however; if implemented cautiously, these can be mitigated. Investment in and application of the social mediome by investigators and patients has the potential to support and transform research that otherwise would be impossible.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to extend their gratitude to the members of the Autoimmune Hepatitis Research Network for their continued proactivity and engagement in autoimmune hepatitis research. Furthermore, the authors are grateful to Dr. Naga Chalasani for his continued mentorship and extensive contributions to the development of social media approaches in clinical investigation.
References
1. Asch, D.A., Rader, D.J., Merchant, R.M. Mining the social mediome. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21:528-9.
2. Brotherton, C.S., Martin, C.A., Long, M.D. et al. Avoidance of fiber is associated with greater risk of Crohn’s disease flare in a 6-month period. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:1130-6.
3. Fenner, Y., Garland, S.M., Moore, E.E., et al. Web-based recruiting for health research using a social networking site: an exploratory study. J Med Internet Res. 2012;14:e20.
4. Lammert, C., Comerford, M., Love, J., et al. Investigation gone viral: application of the social mediasphere in research. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:839-43.
5. Wicks, P., Massagli, M., Frost, J., et al. Sharing health data for better outcomes on PatientsLikeMe. J Med Internet Res. 2010;12:e19.
6. Admon, L., Haefner, J.K., Kolenic, G.E., et al. Recruiting pregnant patients for survey research: a head to head comparison of social media-based versus clinic-based approaches. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18:e326.
7. Farnan, J.M., Sulmasy, L.S., Chaudhry, H. Online medical professionalism. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:158-9.
8. Massachusetts Medical Society: Social Media Guidelines for Physicians. Available from: https://www.massmed.org/Physicians/Legal-and-Regulatory/Social-Media-Guidelines-for-Physicians/#. Accessed: January 3, 2017.
9. Pirraglia, P.A. Kravitz, R.L. Social media: new opportunities, new ethical concerns. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28:165-6.
10. Duggan, M., Ellison, N.B., Lampe, C. et al. Demographics of key social networking platforms. (Available from:) (Accessed: January 4, 2017) Pew Res Cent Internet Sci Tech. 2015; https://www.pewinternet.org/2015/01/09/demographics-of-key-social-networking-platforms-2
11. Kang, X., Zhao, L., Leung, F., et al. Delivery of Instructions via mobile social media app increases quality of bowel preparation. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:429-35.
12. Bajaj, J.S., Heuman, D.M., Sterling, R.K., et al. Validation of EncephalApp, Smartphone-based Stroop test, for the diagnosis of covert hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1828-35.
13. Riaz, M.S. Atreja, A. Personalized technologies in chronic gastrointestinal disorders: self-monitoring and remote sensor technologies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:1697-705.
14. Zaid, T., Burzawa, J., Basen-Engquist, K., et al. Use of social media to conduct a cross-sectional epidemiologic and quality of life survey of patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix: a feasibility study. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;132:149-53.
15. Schumacher, K.R., Stringer, K.A., Donohue, J.E., et al. Social media methods for studying rare diseases. Pediatrics. 2014;133:e1345–53.







