Hearing loss
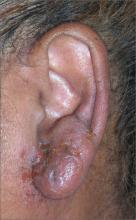
A 40-year-old woman complained to her family physician (FP) that she’d had bilateral otalgia, otorrhea, and hearing loss for the past 2 days. Her symptoms started in the right ear and then rapidly spread to the left. She had a low-grade fever and was systemically ill. The external ear was swollen with honey-crusts. The external auditory canal (EAC) was narrowed and contained purulent discharge.
What’s your diagnosis?
The FP consulted an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) colleague and the patient was admitted to the hospital with a presumptive diagnosis of malignant otitis externa. The patient’s diabetes was also out of control. The necrotizing or malignant form of otitis externa is defined by destruction of the temporal bone, usually in patients with diabetes or those who are immunocompromised. It is often life threatening.
In this case, a computed tomography scan showed some destruction of the temporal bone. The patient was started on IV ciprofloxacin and the ear culture grew out Pseudomonas aeruginosa sensitive to ciprofloxacin. The patient responded well to treatment for the otitis externa (and to treatment for her diabetes); she went home on oral ciprofloxacin 5 days later.
Text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. Photo courtesy of EJ Mayaeux, Jr, MD. This case was adapted from: Rayala B. Otitis externa. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:180-184.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/ref=dp_ob_title_bk
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app for mobile devices by clicking this link: https://usatinemedia.com/