Pediatric ENT Complaints: An Update
Treatment and Management
Streptococcal pharyngitis is treated mainly to prevent the poststreptococcal complications of rheumatic fever, though it will not prevent poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Treatment of SP also facilitates resolution of symptoms and return to baseline activities.
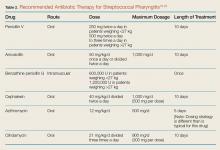
Antibiotic Therapy. Patients who have a positive RAT or a follow-up throat culture positive for group A streptococcus should be given antibiotics. The gold standard treatment is penicillin V orally for 10 days.
Corticosteroid Therapy. The use of corticosteroids for symptom control of SP in pediatric patients is controversial. Although the Infectious Disease Society of America does not recommend corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of SP, several studies show such therapy (namely dexamethasone), improves pain in children and adolescents diagnosed with SP, but without significant change to the overall disease course.21,23-26
Case 3 Resolution
The patient had a modified Centor criteria score of 4, as well as siblings with similar symptoms. In following current guidelines, the EP performed a RAT and back-up culture. The RAT was negative in the ED, but the back-up culture was subsequently positive, and the child was started on a 10-day course of oral amoxicillin.
Conclusion
When evaluating pediatric patients presenting with ENT signs and symptoms such as ear pain and erythema, fever, sore throat, nasal congestion and discharge, a thorough physical examination and history-taking—including recent illness of any siblings—along with testing when indicated, is essential to guide the diagnosis and determine appropriate treatment and management. In addition to administering antibiotic therapy when such is warranted, the EP should provide appropriate analgesia to manage the patient’s pain and assure relief prior to discharge.