Tolerability of Tretinoin Lotion 0.05% for Moderate to Severe Acne Vulgaris: A Post Hoc Analysis in a Black Population
Acne vulgaris (acne) is the most common dermatologic disorder seen in black patients. However, data are lacking on the effects of treatments, such as topical retinoids. Acne in black patients is frequently associated with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which can be of greater concern than the patient’s acne and often is the main reason these patients seek a dermatologist consultation. Retinoids can treat both acne and PIH. However, the potential for retinoids to induce an irritant contact dermatitis, which could lead to PIH, is a concern. A lotion formulation of tretinoin was developed to provide an important alternative option to treat acne in black patients who may be sensitive to the irritant effects of other tretinoin formulations or where PIH is a concern.
Practice Points
- Acne vulgaris is the most common dermatologic disorder seen in black patients, though data on treatment effects is lacking.
- Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) frequently coexists with acne, and retinoids are known to treat both.
- Tretinoin lotion 0.05% is effective in treating both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions in black patients with acne and reducing PIH without the irritant contact dermatitis seen with other retinoid formulations.
Study Population
Eligible patients for the post hoc analysis included male and female patients with black skin who were 9 years and older and presented with 20 to 40 inflammatory lesions (papules, pustules, and nodules), 20 to 100 noninflammatory lesions (open and closed comedones), and 2 or fewer nodules. A washout period of up to 1 month was required for patients who previously used prescription and over-the-counter acne treatments, and a washout period of 6 months was required for systemic retinoids.
Safety Evaluation
Cutaneous safety (erythema and scaling) and tolerability (itching, burning, and stinging) were evaluated on a 4-point scale (0=none; 3=severe). Severity of hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation also was assessed using this 4-point scale. The investigator assessed erythema and scaling at the time of each study visit. Reports of itching, burning, and stinging were solicited from participants and recorded as an average score of their symptoms during the period since the prior visit.
Adverse events were evaluated throughout and summarized by treatment group, severity, and relationship to study medication.
,Statistical Analysis
The safety analysis set comprised all randomized patients who were presumed to have used the study drug at least once and who provided at least 1 postbaseline evaluation. All AEs occurring during the studies were recorded and coded using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities version 18.0. Treatment group comparisons were made by tabulating the frequency of participants reporting 1 or more AEs during the study.
Cutaneous safety (scaling, erythema, hypopigmentation, and hyperpigmentation) and tolerability (itching, burning, and stinging) scores were presented by treatment group with descriptive statistics at baseline and weeks 4, 8, and 12. Frequencies and percentages for each outcome category were included in the statistics.
RESULTS
Baseline Characteristics
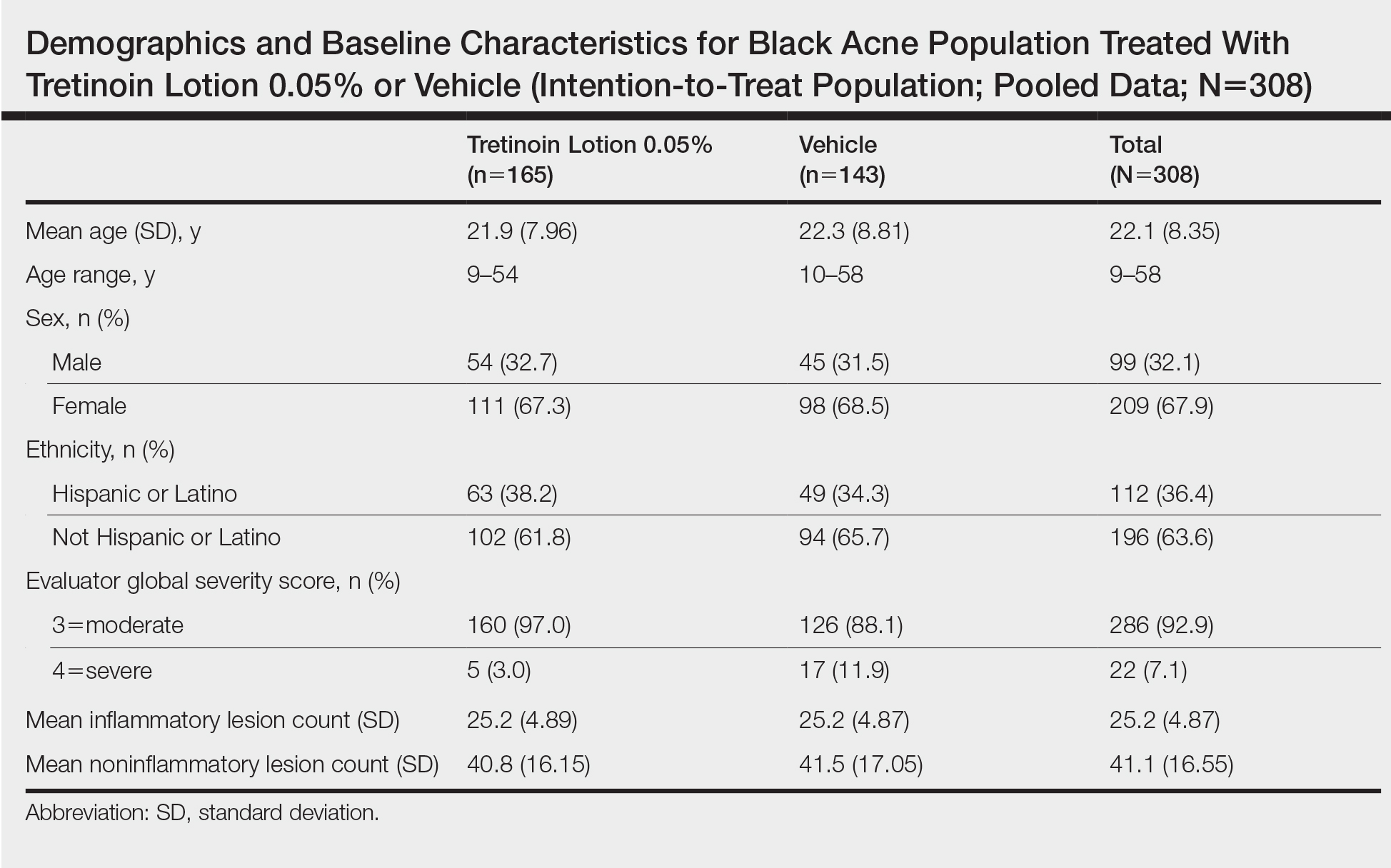
A total of 308 patients were included in the post hoc analysis. Overall, 257 (83.4%) patients completed the studies, including 138 (83.6%) patients receiving tretinoin lotion 0.05% and 119 (83.2%) receiving vehicle (Figure 1). Completion rates were similar in the female and male subgroups (83.3% and 83.8%, respectively). The most common reasons for study discontinuations were lost to follow-up (n=32; 10.4%) or participant request (n=13; 4.2%) and were similar irrespective of treatment or sex. There were no study discontinuations due to AEs.

Demographic data (Table) were similar across the 2 treatment arms. The mean age (standard deviation [SD]) of the participants was 22.1 (8.35) years (range, 9–58 years). Participants were predominantly female (209/308 [67.9%]) and tended to be a little older than the males (mean age, 23.6 vs 18.8 years).