Cobblestonelike Papules on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Fibroelastolytic Papulosis
Histopathology demonstrated decreased density and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the superficial reticular and papillary dermis consistent with an elastolytic disease process (Figure). Of note, elastolysis typically is visualized with Verhoeff-van Gieson stain but cannot be visualized well with standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Additional staining with Congo red was negative for amyloid, and colloidal iron did not show any increase in dermal mucin, ruling out amyloidosis and scleromyxedema, respectively. Based on the histopathologic findings and the clinical history, a diagnosis of fibroelastolytic papulosis (FP) was made. Given the benign nature of the condition, the patient was prescribed a topical steroid (clobetasol 0.05%) for symptomatic relief.
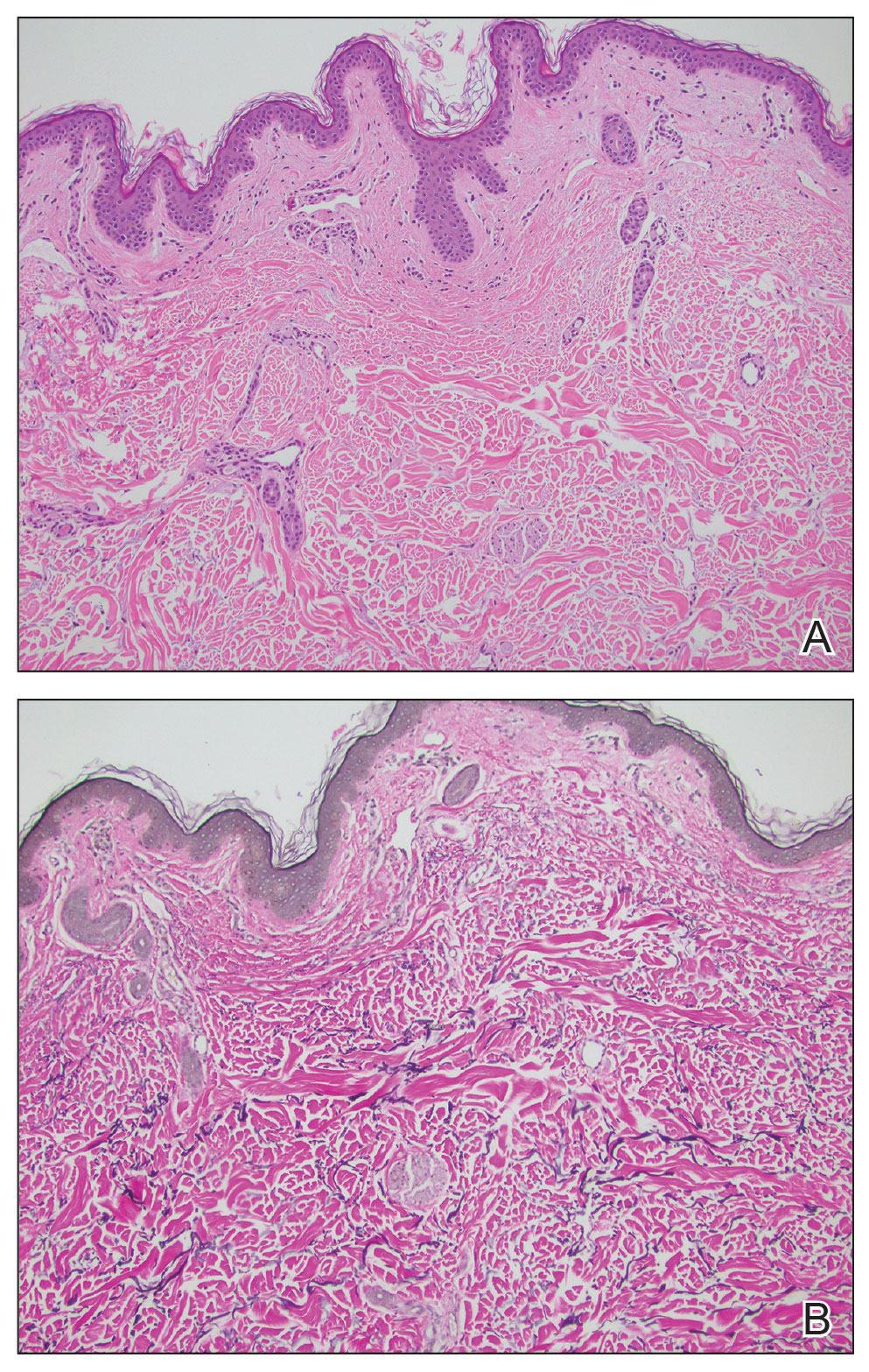
Cutaneous conditions can arise from abnormalities in the elastin composition of connective tissue due to abnormal elastin formation or degradation (elastolysis).1 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is a distinct elastolytic disorder diagnosed histologically by a notable loss of elastic fibers localized to the papillary dermis.2 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is an acquired condition linked to exposure to UV radiation, abnormal elastogenesis, and hormonal factors that commonly involves the neck, supraclavicular area, and upper back.1-3 Predominantly affecting elderly women, FP is characterized by soft white papules that often coalesce into a cobblestonelike plaque.2 Because the condition rarely is seen in men, there is speculation that it may involve genetic, hereditary, and hormonal factors that have yet to be identified.1
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be classified as either pseudoxanthoma elasticum–like papillary dermal elastolysis or white fibrous papulosis.2,3 White fibrous papulosis manifests with haphazardly arranged collagen fibers in the reticular and deep dermis with papillary dermal elastolysis and most commonly develops on the neck.3 Although our patient’s lesion was on the neck, the absence of thickened collagen bands on histology supported classification as the pseudoxanthoma elasticum– like papillary dermal elastolysis subtype.
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be distinguished from other elastic abnormalities by its characteristic clinical appearance, demographic distribution, and associated histopathologic findings. The differential diagnosis of FP includes pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), anetoderma, scleromyxedema, and lichen amyloidosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a hereditary or acquired multisystem disease characterized by fragmentation and calcification of elastic fibers in the mid dermis.1,4 Its clinical presentation resembles that of FP, appearing as small, asymptomatic, yellowish or flesh-colored papules in a reticular pattern that progressively coalesce into larger plaques with a cobblestonelike appearance.1 Like FP, PXE commonly affects the flexural creases in women but in contrast may manifest earlier (ie, second or third decades of life). Additionally, the pathogenesis of PXE is not related to UV radiation exposure. The hereditary form develops due to a gene variation, whereas the acquired form may be due to conditions associated with physiologic and/or mechanical stress.1
Anetoderma, also known as macular atrophy, is another condition that demonstrates elastic tissue loss in the dermis on histopathology.1 Anetoderma commonly is seen in younger patients and can be differentiated from FP by the antecedent presence of an inflammatory process. Anetoderma is classified as primary or secondary. Primary anetoderma is associated with prothrombotic abnormalities, while secondary anetoderma is associated with systemic disease including but not limited to sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematous, and Graves disease.1
Neither lichen myxedematosus (LM) nor lichen amyloidosis (LA) are true elastolytic conditions. Lichen myxedematosus is considered in the differential diagnosis of FP due to the associated loss of elastin observed with disease progression. An idiopathic cutaneous mucinosis, LM is a localized form of scleromyxedema, which is characterized by small, firm, waxy papules; mucin deposition in the skin; fibroblast proliferation; and fibrosis. On histologic analysis, typical findings of LM include irregularly arranged fibroblasts, diffuse mucin deposition within the upper and mid reticular dermis, increased collagen deposition, and a decrease in elastin fibers.5
Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, a rare condition characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin and a lack of systemic involvement. Although it is not an elastolytic condition, LA is clinically similar to FP, often manifesting as multiple localized, pruritic, hyperpigmented papules that can coalesce into larger plaques; it tends to develop on the shins, calves, ankles, and thighs.6,7 The condition commonly manifests in the fifth and sixth decades of life; however, in contrast to FP, LA is more prevalent in men and individuals from Central and South American as well as Middle Eastern and non-Chinese Asian populations.8 Lichen amyloidosis is a keratin-derived amyloidosis with cytokeratin-based amyloid precursors that only deposit in the dermis.6 Histopathology reveals colloid bodies due to the presence of apoptotic basal keratinocytes. The etiology of LA is unknown, but on rare occasions it has been associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A rearranged during transfection mutations.6
In summary, FP is an uncommonly diagnosed elastolytic condition that often is asymptomatic or associated with mild pruritus. Biopsy is warranted to help differentiate it from mimicker conditions that may be associated with systemic disease. Currently, there is no established therapy that provides successful treatment. Research suggests unsatisfactory results with the use of topical tretinoin or topical antioxidants.3 More recently, nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers have been evaluated as a possible therapeutic strategy of promise for elastic disorders.9




