Top Qualifications Hospitalist Leaders Seek in Candidates: Results from a National Survey
Despite rapidly growing interest in Hospital Medicine (HM), no prior research has examined the factors that may be most beneficial or detrimental to candidates during the HM hiring process. We developed a survey instrument to assess how those involved in the HM hiring process assess HM candidate attributes, skills and behaviors. The survey was distributed electronically to nontrainee physician Society of Hospital Medicine members. Respondents ranked the top five qualifications of HM candidates and the top five qualities an HM candidate should demonstrate on interview day to be considered for hiring. In thematic analysis of free-response questions, several themes emerged relating to interview techniques and recruitment strategies, including heterogeneous approaches to long-term versus short-term applicants. These findings represent the first published assessment in the area of HM hiring and should inform HM candidates and their mentors.
© 2019 Society of Hospital Medicine
Data Analysis
Multiple-choice responses were analyzed descriptively. For ranking-type questions, answers were weighted based on ranking order.
Responses to all open-ended survey questions were analyzed using thematic analysis. We used an iterative process to develop and refine codes identifying key concepts that emerged from the data. Three authors independently coded survey responses. As a group, research team members established the coding framework and resolved discrepancies via discussion to achieve consensus.
RESULTS
Survey links were sent to 8,398 e-mail addresses, of which 7,306 were undeliverable or unopened, leaving 1,092 total eligible respondents. Of these, 347 (31.8%) responded.
A total of 236 respondents reported having a formal role in HM hiring. Of these roles, 79.0% were one-on-one interviewers, 49.6% group interviewers, 45.5% telephone/videoconference interviewers, 41.5% participated on a selection committee, and 32.1% identified as the ultimate decision-maker. Regarding graduate medical education teaching status, 42.0% of respondents identified their primary workplace as a community/affiliated teaching hospital, 33.05% as a university-based teaching hospital, and 23.0% as a nonteaching hospital. Additional characteristics are reported in Appendix 2.
Quantitative Analysis
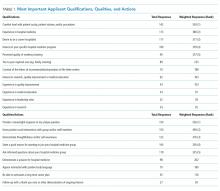
Respondents ranked the top five qualifications of HM candidates and the top five qualities a candidate should demonstrate on the interview day to be considered for hiring (Table 1).
When asked to rate agreement with the statement “I evaluate and consider all hospital medicine candidates similarly, regardless of whether they articulate an interest in hospital medicine as a long-term career or as a short-term position before fellowship,” 99 (57.23%) respondents disagreed.
Qualitative Analysis
Thematic analysis of responses to open-ended survey questions identified several “red flag” themes (Table 2). Negative interactions with current providers or staff were commonly noted. Additional red flags were a lack of knowledge or interest in the specific HM group, an inability to articulate career goals, or abnormalities in employment history or application materials. Respondents identified an overly strong focus on lifestyle or salary as factors that might limit a candidate’s chance of advancing in the hiring process.
Responses to free-text questions additionally highlighted preferred questioning techniques and approaches to HM candidate assessment (Appendix 3). Many interview questions addressed candidate interest in a particular HM program and candidate responses to challenging scenarios they had encountered. Other questions explored career development. Respondents wanted LT candidates to have specific HM career goals, while they expected ST candidates to demonstrate commitment to and appreciation of HM as a discipline.
Some respondents described their approach to candidate assessment in terms of investment and risk. LT candidates were often viewed as investments in stability and performance; they were evaluated on current abilities and future potential as related to group-specific goals. Some respondents viewed hiring ST candidates as more risky given concerns that they might be less engaged or integrated with the group. Others viewed the hiring of LT candidates as comparably more risky, relating the longer time commitment to the potential for higher impact on the group and patient care. Accordingly, these respondents viewed ST candidate hiring as less risky, estimating their shorter time commitment as having less of a positive or negative impact, with the benefit of addressing urgent staffing issues or unfilled less desirable positions. One respondent summarized: “If they plan to be a career candidate, I care more about them as people and future coworkers. Short term folks are great if we are in a pinch and can deal with personality issues for a short period of time.”
Respondents also described how valued candidate qualities could help mitigate the risk inherent in hiring, especially for ST hires. Strong interpersonal and teamwork skills were highlighted, as well as a demonstrated record of clinical excellence, evidenced by strong training backgrounds and superlative references. A key factor aiding in ST hiring decisions was prior knowledge of the candidate, such as residents or moonlighters previously working in the respondent’s institution. This allowed for familiarity with the candidate’s clinical acumen as well as perceived ease of onboarding and knowledge of the system.