New and Emerging Treatments for MASLD/MASH





Naim Alkhouri, MD
Chief Medical Officer, Department of Hepatology
Arizona Liver Health
Phoenix, Arizona
Naim Alkhouri, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; AstraZeneca; Echosens; Gilead Sciences; Intercept Pharmaceuticals; Ipsen; Madrigal Pharmaceuticals; Perspectum Served as a speaker or a member of a speaker’s bureau for: 89bio; Akero; Boehringer Ingelheim; Echosens; Fibronostics; Gilead Sciences; Intercept Pharmaceuticals; Ipsen; Madrigal Pharmaceuticals; NorthSea Therapeutics; Novo Nordisk; Perspectum; Pfizer; Regeneron Received research grant from: 89bio; Akero; Arbutus; AstraZeneca; BioAge; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol Myers Squibb; Corcept Therapeutics; CymaBay Therapeutics; DSM; Galectin Therapeutics; Genentech; Genfit; Gilead; Healio; Hepagene; Intercept; Inventiva; Ionis Pharmaceuticals; Ipsen; Lilly; Madrigal Pharmaceuticals; Merck; NGM; Novo Nordisk; Perspectum; Pfizer; PharmaIN; Poxel; Viking Therapeutics; Zydus





With the global rise in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), the lack of approved medications is striking.1,2 Fortunately, during the past year, significant advancements have been made in the US treatment landscape for MASLD. Recent insights into the heterogeneous nature of MASLD have spurred the discovery of novel therapeutic agents and the repurposing of drugs (e.g., semaglutide) available for type 2 diabetes and obesity.1,3
Although lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise remain the cornerstones of treatment,1,2,4 effective pharmacologic options have been elusive. Numerous phase 3 trials are underway, and more promising therapies will likely become available within the next few years. In 2024, the FDA conditionally approved resmetirom, a thyroid hormone receptor-β selective drug, for treating non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with moderate to advanced fibrosis.4 Although this condition is highly underdiagnosed,5 combination therapy may improve outcomes,1,3,6 with greater efficacy for metabolic treatments initiated in the early stages and for liver-targeting drugs initiated in the advanced stages.3
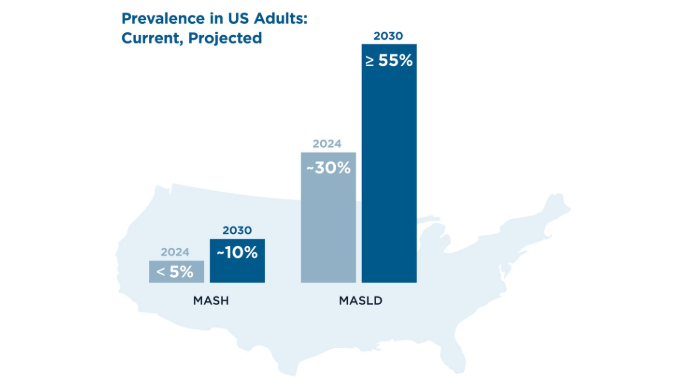 MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
The economic burden of MASLD/MASH in the United States is projected to grow substantially, to over $1 trillion by 2034, highlighting the growing need for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies (and for encouragement of patient lifestyle changes) to effectively manage MASLD and MASH.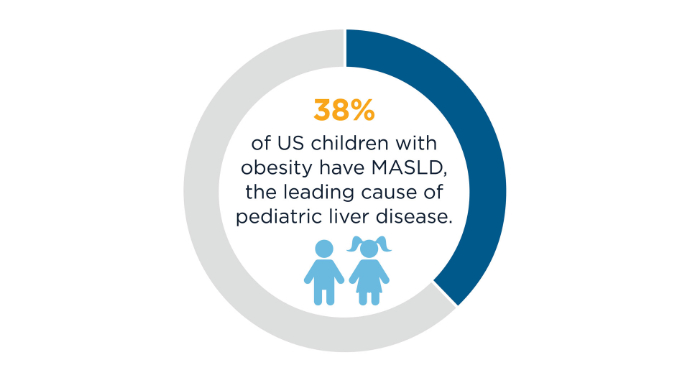 MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.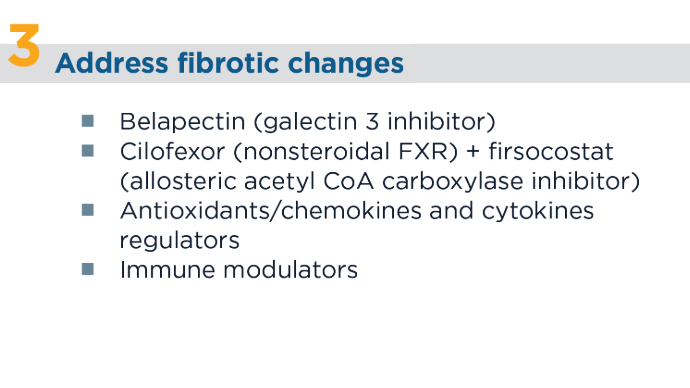 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15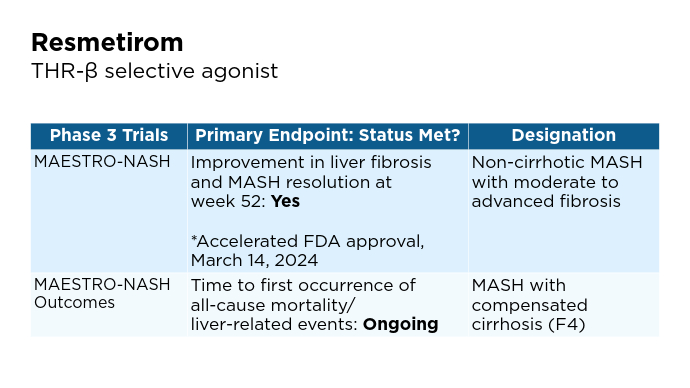 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
BMI, body mass index; BTD, Breakthrough Therapy Designation; CV, cardiovascular; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; pan-PPAR, pan-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RA, receptor agonist; THR, thyroid hormone receptor.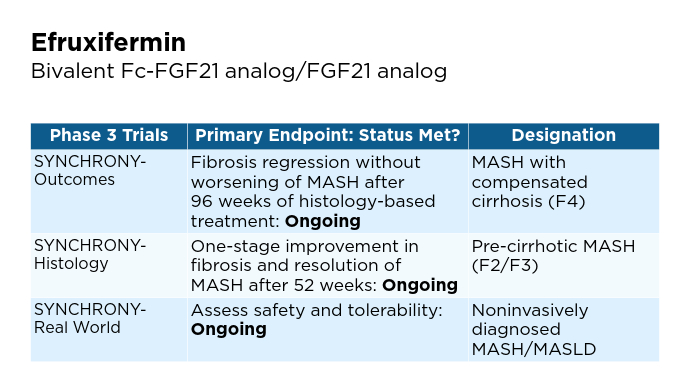 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20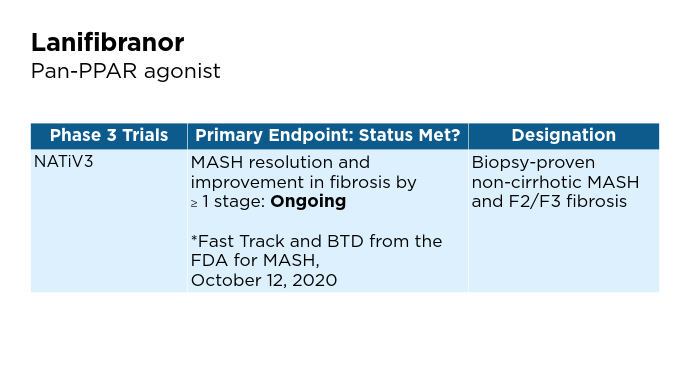 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20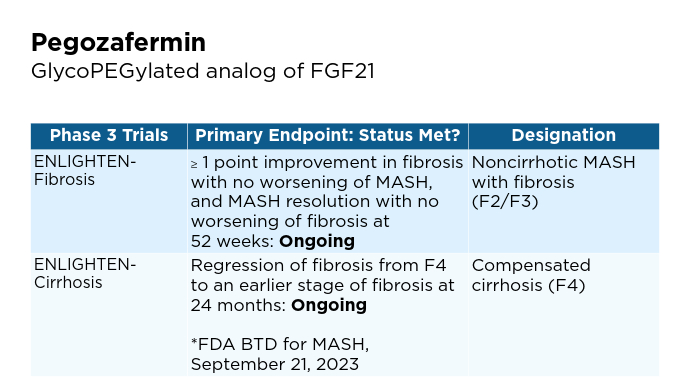 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20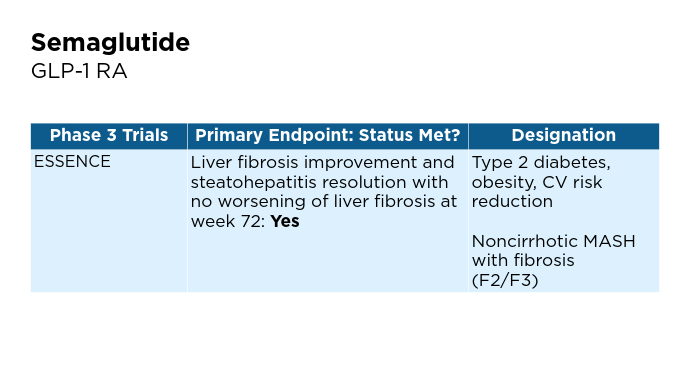 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20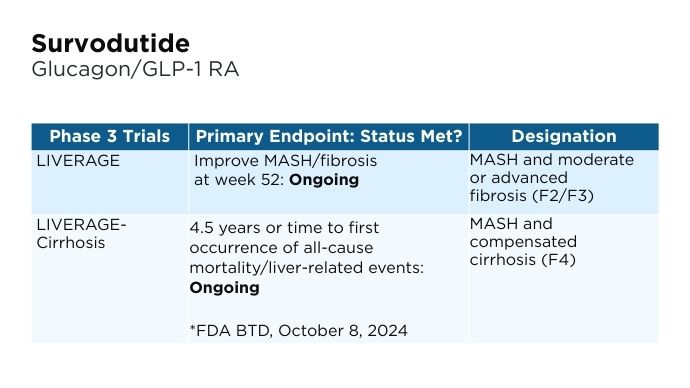 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
The economic burden of MASLD/MASH in the United States is projected to grow substantially, to over $1 trillion by 2034, highlighting the growing need for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies (and for encouragement of patient lifestyle changes) to effectively manage MASLD and MASH. MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
BMI, body mass index; BTD, Breakthrough Therapy Designation; CV, cardiovascular; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; pan-PPAR, pan-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RA, receptor agonist; THR, thyroid hormone receptor. Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
The economic burden of MASLD/MASH in the United States is projected to grow substantially, to over $1 trillion by 2034, highlighting the growing need for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies (and for encouragement of patient lifestyle changes) to effectively manage MASLD and MASH. MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12
MASLD/MASH Burden5,7-12 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 CoA, coenzyme A; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IMM-124e, hyperimmune bovine colostrum enriched with IgG anti-LPS; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated agonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15
4 Main Pathways of MASLD Therapies1,13-15 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
BMI, body mass index; BTD, Breakthrough Therapy Designation; CV, cardiovascular; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; pan-PPAR, pan-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RA, receptor agonist; THR, thyroid hormone receptor. Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20 Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20
Promising Phase 3 Trials2,6,16-20

