The Role of Bedside Intestinal Ultrasound in IBD Management





Bincy Abraham, MD, MS
Professor, Department of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology;
Director, Fondren IBD Program;
Director, Gastroenterology Fellowship;
Department of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, Houston Methodist Academic Gastroenterology Associates
Houston, Texas
Bincy Abraham, MD, MS, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a consultant for: Abbvie; BMS; Janssen; Pfizer; Takeda; Celltrion; Lilly; Prometheus Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbvie; BMS; Janssen; Pfizer; Takeda; Lilly; Prometheus





Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) need accessible, timely, and noninvasive monitoring strategies. Bedside intraabdominal ultrasound (IUS) is a beneficial tool for diagnosing and monitoring patients with IBD, including both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.1,2 Integrating IUS can have a significant impact on decision-making and endoscopy use in a standardized care pathway for these patients, given that the benefits outweigh the risks and costs of other imaging modalities.
IUS is radiation free, and provides accurate point-of-care detection of bowel wall thickening and inflammation in individuals with IBD.3 This imaging is effective for monitoring treatment response and guiding early interventions and is suitable for special populations (e.g., pediatrics and patients who are pregnant or obese).1,2 IUS allows for medication adjustments without requiring urgent endoscopies or special preparations.1 The small and large intestine can be visually monitored for IBD activity with IUS, with occasional exception regarding the rectum because of its deep location; however, a transperineal or transrectal ultrasound approach may be needed to view the rectum and perianal areas.2,3
Further, in 2024, AGA reviewed and provided guidance on the use of IUS in IBD care,1 underscoring its growing importance and utility. IUS provides a noninvasive, cost-effective, and accurate method for IBD evaluation and monitoring.
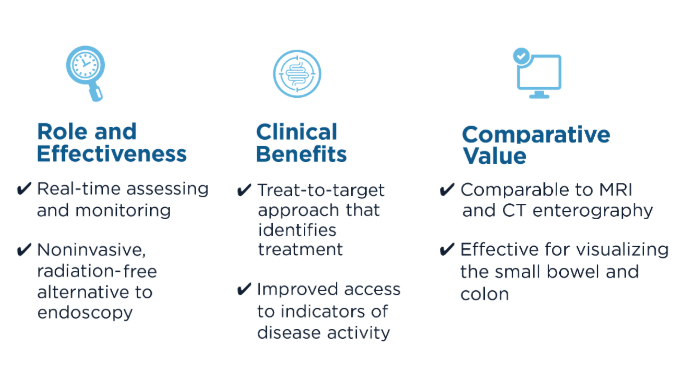 Benefits of IUS2,3
Benefits of IUS2,3
Current efforts focus on training gastroenterologists to increase the adoption of IUS in clinical practice.1 Future training of advanced practice providers, especially those primarily focused on IBD care, could further benefit patients.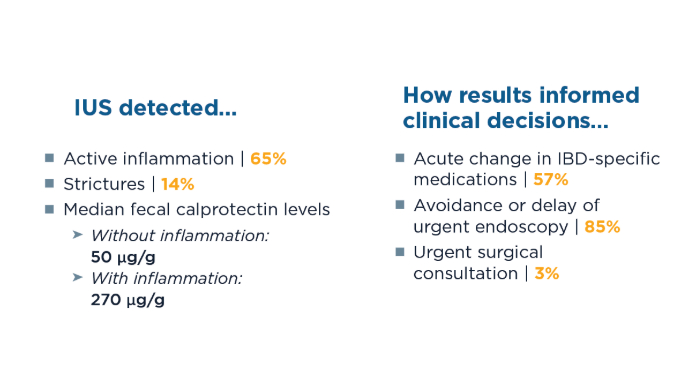 IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
To assess how IUS, alone or in combination with in-clinic sigmoidoscopy, affects clinical decision-making and reliance on endoscopy, 158 patients with Crohn's disease (78%), ulcerative colitis (11%), or new/suspected IBD (11%) were evaluated. Using point-of-care IUS during a clinical flare significantly enhances the management and delivery of care for patients with IBD, often reducing the need for urgent endoscopy by effectively informing therapeutic decisions.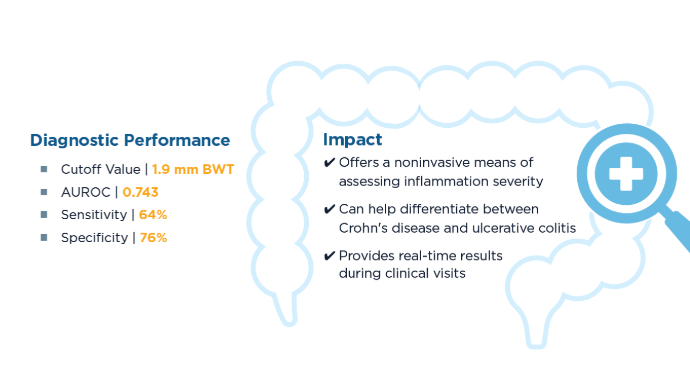 Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
A 2024 study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of bowel wall thickness (BWT) measured by IUS vs endoscopic disease activity in children suspected of having IBD. A total of 174 bowel segments from 33 children were examined. Bedside IUS was effective in visualizing more than 85% of bowel wall segments. Elevated median BWT was significantly associated with increased bowel-segment disease severity. AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.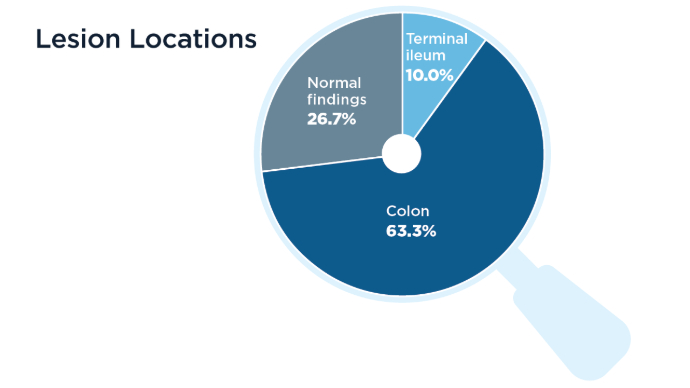 Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Lastly, a small study of patients with IBD (ulcerative colitis, n = 21; Crohn's disease, n = 9) sought to determine correlations between BWT and wall stratification, color Doppler signal, and inflammatory markers (i.e., hemoglobin, ferritin, C-reactive protein [CRP], and fecal calprotectin).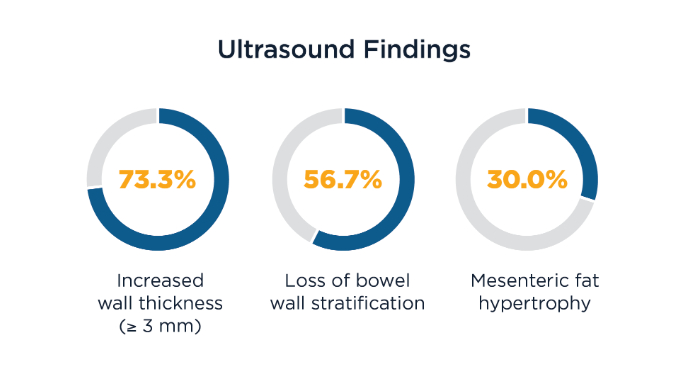 Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5 Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5 Benefits of IUS2,3
Benefits of IUS2,3
Current efforts focus on training gastroenterologists to increase the adoption of IUS in clinical practice.1 Future training of advanced practice providers, especially those primarily focused on IBD care, could further benefit patients. IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
To assess how IUS, alone or in combination with in-clinic sigmoidoscopy, affects clinical decision-making and reliance on endoscopy, 158 patients with Crohn's disease (78%), ulcerative colitis (11%), or new/suspected IBD (11%) were evaluated. Using point-of-care IUS during a clinical flare significantly enhances the management and delivery of care for patients with IBD, often reducing the need for urgent endoscopy by effectively informing therapeutic decisions. Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
A 2024 study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of bowel wall thickness (BWT) measured by IUS vs endoscopic disease activity in children suspected of having IBD. A total of 174 bowel segments from 33 children were examined. Bedside IUS was effective in visualizing more than 85% of bowel wall segments. Elevated median BWT was significantly associated with increased bowel-segment disease severity. AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Lastly, a small study of patients with IBD (ulcerative colitis, n = 21; Crohn's disease, n = 9) sought to determine correlations between BWT and wall stratification, color Doppler signal, and inflammatory markers (i.e., hemoglobin, ferritin, C-reactive protein [CRP], and fecal calprotectin). Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5 Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5 Benefits of IUS2,3
Benefits of IUS2,3
Current efforts focus on training gastroenterologists to increase the adoption of IUS in clinical practice.1 Future training of advanced practice providers, especially those primarily focused on IBD care, could further benefit patients. IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
IUS Enhances Care for Patients With IBD: Study4
To assess how IUS, alone or in combination with in-clinic sigmoidoscopy, affects clinical decision-making and reliance on endoscopy, 158 patients with Crohn's disease (78%), ulcerative colitis (11%), or new/suspected IBD (11%) were evaluated. Using point-of-care IUS during a clinical flare significantly enhances the management and delivery of care for patients with IBD, often reducing the need for urgent endoscopy by effectively informing therapeutic decisions. Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
Evaluating Bowel Wall Thickness, IBD Severity in Children3
A 2024 study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of bowel wall thickness (BWT) measured by IUS vs endoscopic disease activity in children suspected of having IBD. A total of 174 bowel segments from 33 children were examined. Bedside IUS was effective in visualizing more than 85% of bowel wall segments. Elevated median BWT was significantly associated with increased bowel-segment disease severity. AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Lastly, a small study of patients with IBD (ulcerative colitis, n = 21; Crohn's disease, n = 9) sought to determine correlations between BWT and wall stratification, color Doppler signal, and inflammatory markers (i.e., hemoglobin, ferritin, C-reactive protein [CRP], and fecal calprotectin). Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5 Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5
Correlations Between BWT and Inflammatory Markers5

