Lean and clean: Minimally invasive endoscopic and pharmacologic approaches to obesity
Our clinical approach
In 2015, the first Veterans Affairs hospital-based endoscopic bariatric program was established at the VA New York Harbor Healthcare System utilizing IGBs and weight loss pharmacotherapy in conjunction with the VA MOVE! Program to treat obesity and metabolic comorbidities in veterans. Since then, EBMTs have expanded to include ESG and novel medications. Our treatment algorithm accounts for the chronic nature of obesity, the risk of weight regain after any intervention, and the need for longitudinal patient care.
Patients undergo work-up by a multidisciplinary team (MD team) with a nutritionist, psychologist, primary care physician, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist to determine the optimal treatment plan (Fig. 1).29
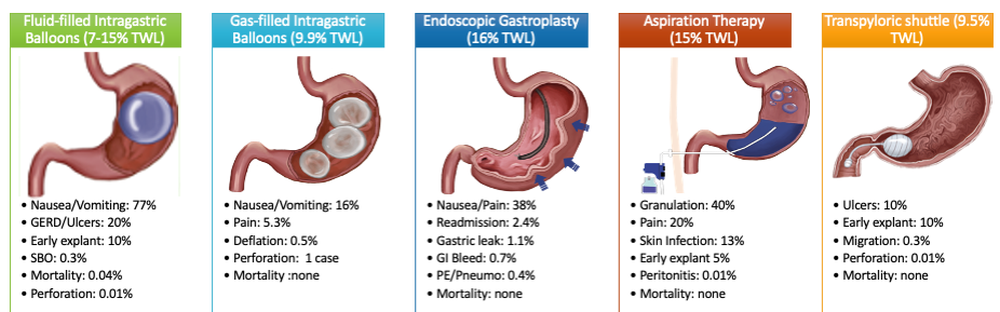
Patients are required to attend multiple information sessions, where all weight-loss methods are presented, including surgery, bariatric endoscopy, and pharmacotherapy. Other specialists also help manage comorbid conditions. Prior to selecting an initial intervention, patients undergo intensive lifestyle and behavioral therapy (Fig. 2 and 3). Depending on the selected therapy, initial treatment lasts between 3 and 12 months with ongoing support from the MD team.
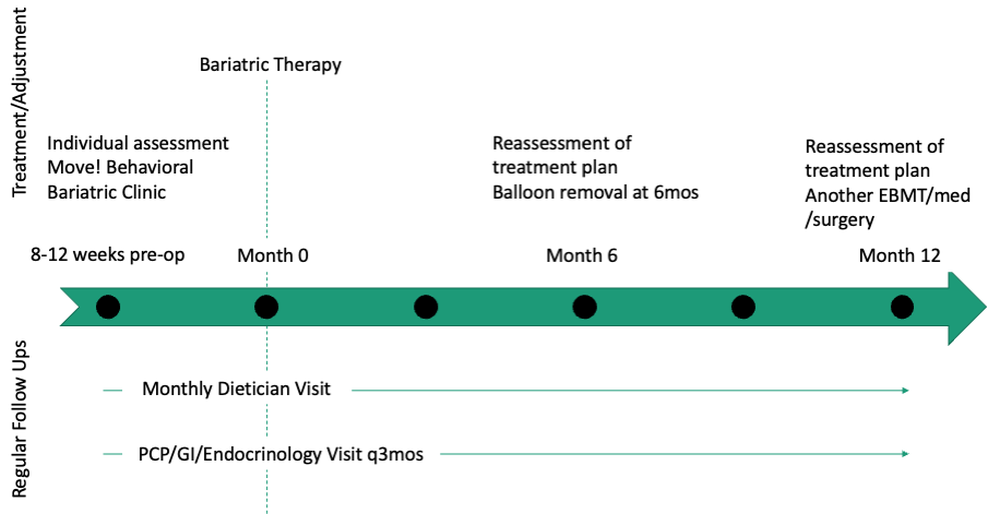
If patients do not achieve their targeted weight loss after initial treatment, a new strategy is selected. This includes a different EBMT such as ESG, alternate pharmacotherapy, or surgery until the weight and health goals of the patient are achieved and sustained (Fig. 3). From the start, patients are informed that our program is a long-term intervention and that active participation in the MOVE! Program, as well as follow-up with the MD team are keys to success. EBMTs and medications are presented as effective tools that only work to enhance the effects of lifestyle changes.
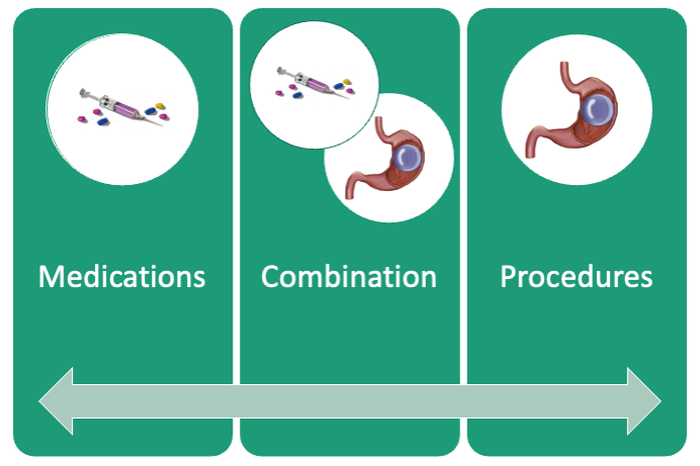
Our multidisciplinary approach provides flexibility for patients to trial different options depending on their progress. Research on long-term outcomes with weight loss and metabolic parameters is ongoing, though early results are promising. Thus far, we have observed that patients undergoing a combination therapy of EBMTs and AOMs have greater weight loss than patients on a single therapeutic approach with either EBMT or AOMs alone.34 Racial and socioeconomic disparities in referrals to bariatric surgery are yet another barrier for patients to access weight reduction and improvement in cardiovascular health.35 EBMTs and pharmacotherapy are no longer just on the horizon; they are here as accessible, effective, and long-term treatments for all patients with obesity. More expansive insurance coverage is needed for EBMTs and AOMs in order to prevent progression of obesity-related comorbidities, reduce high costs, and ensure more equitable access to these effective therapies.
Dr. Young and Dr. Zenger are resident physicians in the department of internal medicine at New York University. Dr. Holzwanger is an advanced endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Dr. Popov is director of bariatric endoscopy at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System, and assistant professor of medicine at New York University. Dr. Popov reported relationships with Obalon, Microtech, and Spatz, but the remaining authors reported no competing interests.







