“To Conserve Fighting Strength”: The Role of Military Culture in the Delivery of Care
Introduction: There are ongoing discussions about reorganizing the delivery of health care within the US Armed Forces. The military cultural context of care has beneficial qualities for patients with orthopedic and extremity trauma acquired during deployments to conflict zones.
Methods: The study included 35 participants with lower limb amputations who had been discharged from the Amputee Patient Care Program ≥ 12 months prior to the study. Participants were interviewed using a lightly structured schedule designed to elicit accounts of community integration, which attended to reports of belongingness supported by accounts of social engagement in work, school, family, and social events. Interviews were analyzed using a modified content analysis approach.
Results: Participants generally described their postcare lives as “successful” that had been built on “good outcomes.” For most former patients, remembering the social intensity of their rehabilitation program was an important element in their narratives of recovery. Weekly amputee clinics worked to alleviate stress and anxiety in participants’ minds around the complexities of their injuries and care.
Conclusions: Participants reported that features of their care were particularly valuable to their recovery and their current assessment of their injury related health. These features are present, in part because of the military cultural context that is part of the framework of care delivery.
Methods
Data were extracted from research conducted between 2012 and 2014 that investigated how former patients evaluated their posttreatment lives considering the care received in the MATC at WRNMMC. We used a lightly structured set of interview questions and categories in each interview that focused on 3 themes in the individual’s pathway to injury: education, joining their branch of service, injury experience. The focus was on developing an understanding of how events antecedent to the injury experience could influence the rehabilitation experience and postcare life. The second focus was on the experience of rehabilitation and to learn how the individual navigated community living after leaving care.
Results
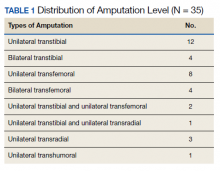
Thirty-five participants with lower extremity amputations were recruited who had been discharged from the Amputee Patient Care Program ≥ 12 months prior to the study (Table 1). Participants were interviewed either over the telephone, or when possible, in person. Interviews were based on a lightly structured schedule designed to elicit accounts of community integration, which attended to reports of belongingness supported by accounts of social engagement in work, school, family, and social events. Interviews were analyzed using a modified content analysis approach. The study did not rely on a structured interview, but as is the case with many qualitative and ethnographic interviews, each session shared themes in common, such as questions about injury experience, rehabilitation experience, life after care (work, school, relationships), and so forth. Interviews were conducted by the lead author who was a medical anthropologist with training in health services research.
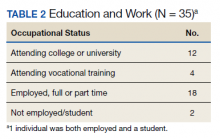
Participants generally described their post-care lives as “successful” that had been built on “good outcomes.” We left these concepts loosely defined to grant participants latitude in developing their own definitions for these ideas. That said, there is reason to view participants' lives as meeting specific criteria of success (Table 2). For example:
- 16 participants attended higher education postrehabilitation;
- 18 participants were working, or had worked, at the time of the interview;
- There was overlap between these groups and the total that had worked or attended school was 33 of 35; and
- 2 participants who had neither worked nor attended school were still recovering from injury complications at the time of the interview.
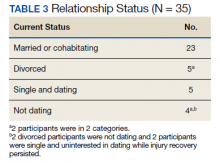
Family and relationships were other areas of success (Table 3). Twenty-three participants were currently in long-term relationships, including a mix of marriage and cohabitation households, while 3 were recently divorced and 2 were divorced for a longer term. Of the 5 participants who had been divorced, 3 were interested in pursuing new relationships. All 5 of these participants had children and were actively involved in their lives. Seven participants were not in relationships. Two participants did not have or seek relationships because of complications associated with their ongoing recovery.
Whether considering the claims of participants, or how the literature conceptualizes successful community living, the evidence of success is supported by the accounts of work, school, and relationships. The attribution of these successes, in part, to the MATC rehabilitation program is important to understand because of the implications that this has on program value. Three features of the program continually emerged in interviews: recovering alongside peers, routine access to the entire treatment team, and ongoing relationships with key health care providers (HCPs).