Natural History of HPV Infections
The Journal of Family Practice. 2009 September;58(9):S3-S7
Author and Disclosure Information
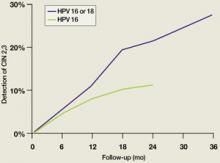
FIGURE 2
Cumulative detection of CIN 2,3 after incident HPV infections in two studies
HPV, human papillomavirus.
After incident HPV 16 infection (green line) and after incident HPV 16 or 18 infection (blue line).
Modified from Winer RL, et al. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:731-738 (blue line); Mao C, et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:18-27 (green line).
TABLE
Detection of CIN 2,3 or cancer
| HPV status | Percent with CIN 2+* |
|---|---|
| HPV negative | 0.4% |
| HPV 16 | 37% |
| HPV 18 | 26% |
| HPV 31 | 37% |
| HPV 33 | 48% |
| HPV 52 | 26% |
| HPV 58 | 30% |
| CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HPV, human papillomavirus. | |
| *Percentage of women diagnosed with CIN 2,3 or cancer during a 4-year follow-up period. | |
| Modified from Naucler P, et al. Br J Cancer. 2007;97:129-132. | |
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- HPV infections are common, and approximately half of young women become infected within 4 years of initiating sexual activity.
- The predominant mode of transmission of HPV is by sexual intercourse; consistent use of condoms reduces, but does not prevent, transmission.
- More than 80% of HPV infections spontaneously clear over a 3-year period.
- Less than 5% of women in the general population are high-risk HPV positive by the age of 45 years.
- HPV 16 and HPV 18 are quite oncogenic, and about 1 out of 4 infected individuals will develop CIN 2,3 over a 3-year period.