Hyperlipidemia management: A calibrated approach
Gauge the level of LDL cholesterol and assess risk-enhancing factors for ASCVD—thus setting the table for primary and secondary prevention with medical therapy.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Use an alternative to the Friedewald equation, such as the Martin–Hopkins equation, to estimate the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) value; order direct measurement of LDL-C; or calculate non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to assess the risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) in patients who have a low LDL-C or a high triglycerides level. C
› Consider the impact of ASCVD risk-enhancing factors and coronary artery calcium scoring in making a recommendation to begin lipid-lowering therapy in intermediate-risk patients. C
› Add ezetimibe if a statin does not sufficiently lower LDL-C or if a patient cannot tolerate an adequate dosage of the statin. C
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
How much does lifestyle modification actually matter?
The absolute impact of diet and exercise on lipid parameters is relatively modest. No studies have demonstrated a reduction in adverse cardiovascular outcomes with specific interventions regarding diet or activity.
Diet. Nevertheless, ACC/AHA recommends that at-risk patients follow a dietary pattern that (1) emphasizes vegetables, fruits, and whole grains and (2) limits sweets, sugar-sweetened beverages, and red meat.
Saturated fat should constitute no more than 5% or 6% of total calories. In controlled-feeding trials,10 for every 1% of calories from saturated fat that are replaced with carbohydrate or monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fat, the LDL-C level was found to decline by as much as 1.8 mg/dL. Evidence is insufficient to assert that lowering dietary cholesterol reduces LDL-C.11
Activity. Trials of aerobic physical activity, compared with a more sedentary activity pattern, have demonstrated a reduction in the LDL-C level of as much as 6 mg/dL. All adult patients should be counseled to engage in aerobic physical activity of moderate or vigorous intensity—averaging ≥ 40 minutes per session, 3 or 4 sessions per week.11
Primary prevention:Stratification by age
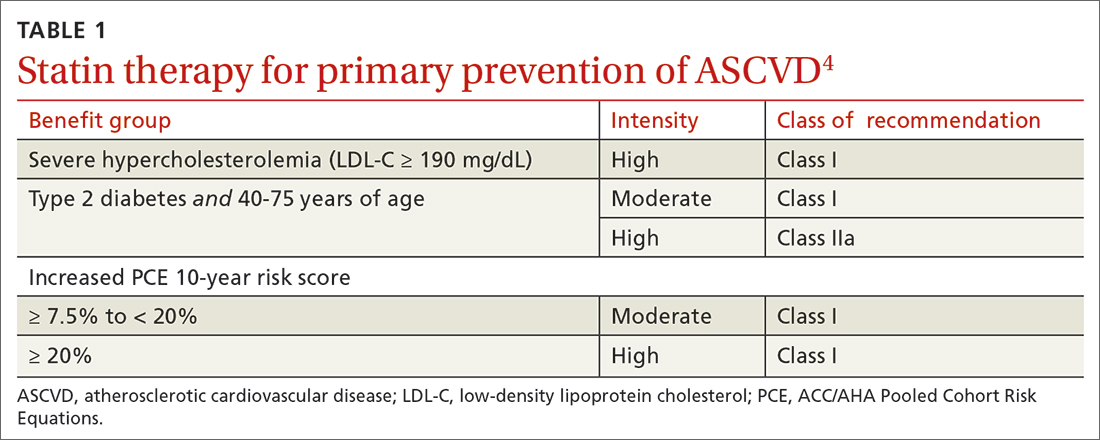
40 to 75 years. ACC/AHA recommends that you routinely assess traditional cardiovascular risk factors for these patients and calculate their 10-year risk for ASCVD using the PCE. Statin therapy as primary prevention is indicated for 3 major groups (TABLE 1).4 The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends a 10-year ASCVD risk ≥ 10%, in conjunction with 1 or more additional CVD risk factors (dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, smoking), as the threshold for initiating low- or moderate-intensity statin therapy in this age group.12
Continue to: In adults at borderline risk...






