A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: How to avoid drug interactions
Use these strategies to maximize efficacy and minimize adverse effects when prescribing an MAOI. Second of 2 parts.
Desipramine, a potent norepinephrine transporter (NET) inhibitor, blocks the entry of tyramine into cells by NET, thereby preventing hypertensive events in animal models of tyramine overexposure. However, in some assays, the affinity for the serotonin transporter is not insignificant, so at higher doses desipramine may pose the same theoretical risk for SS as seen with other tricyclics.3
Lastly
Astute clinicians will recognize that antidepressants that lack 5HT reuptake (eg, bupropion, mirtazapine) are not on this list of agents that may increase SS risk when taken with an MAOI. Older papers often list mirtazapine, but as a 5HT2A antagonist, it does not possess a plausible mechanism by which it can induce 5HT toxicity.9,10 Most atypical antipsychotics have significant 5HT2A antagonism and can be combined with MAOIs, but ziprasidone is an exception: as a moderate SNRI, it has been associated with SS when administered with an MAOI.11
Pressor reactions. The only theoretical sources of concern for pressor effects are medications that act as norepinephrine releasers through interactions at the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) (for more information on TAAR1, see
Starting a patient on an MAOI

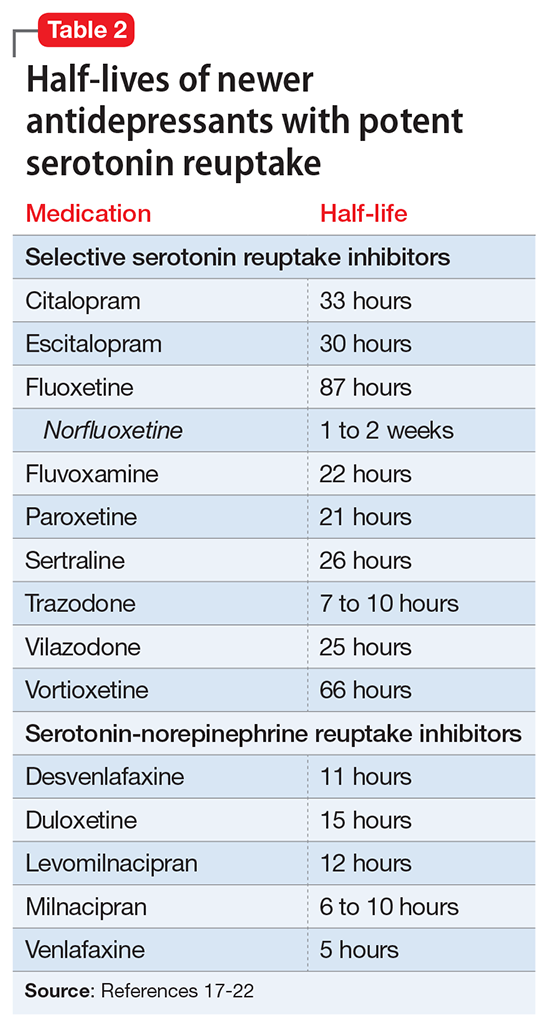
Contraindicated medications need to be tapered before beginning MAOI treatment. The duration of the washout period depends on the half-life of the medication and any active metabolites. Antidepressants with half-lives of approximately ≤24 hours should be tapered over 7 to 14 days (depending on the dose) to minimize the risk of withdrawal syndromes, while those with long half-lives (eg, fluoxetine,






