Focal hair loss
A 23-year-old, otherwise healthy, woman was referred to Dermatology for acute and worsening hair loss at the central and frontal scalp. She said her hair loss had begun 2 months earlier. On exam, there were smooth, round patches of hair loss without other associated scalp lesions.
What’s your diagnosis?
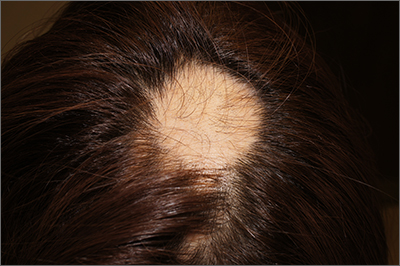
The findings of smooth, round alopecia occurring rapidly without associated scarring, pain, or itching, is consistent with the diagnosis of alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease caused by T lymphocytes targeting hair follicles and resulting in rapid and nonscarring hair loss. It is usually self-resolving and about 2% of all individuals are affected at some point during their lifetime, with an average age of onset of 33 years.1 Some patients may progress to loss of all scalp hair (alopecia totalis) or all hair on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis).1
,It is important to inspect a patient’s scalp, face, and body for more subtle areas of loss that could signal other disorders, such as lichen planopilaris, discoid lupus, or telogen effluvium. It is worth noting that alopecia areata is not associated with scalp lesions, crusting, or scars without follicles. Such findings should be further investigated with a 4-mm punch biopsy of affected and adjacent follicular units. Carefully labeling biopsy specimens as scalp specimens for hair loss will aid in a correct histopathologic diagnosis.
Systematic data comparing treatments for alopecia areata are lacking. For localized disease, topical or intradermal triamcinolone injections at a concentration of 5 to 10 mg/mL, with about 0.1 mL to 0.05 mL injected every square centimeter of affected area (up to 40 mg per visit), can provide rapid regrowth.1 Within 4 months of the monthly injections, 63% of patients experience complete regrowth.1 Despite this favorable outcome, there is also a high rate of recurrence.
For more widespread disease, contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or diphencyprone can provoke a low-grade contact allergy and induce antigenic completion. This therapy is painless but can be itchy; medications must be compounded and titrated to activity.
The patient in this case opted to receive monthly triamcinolone injections in an undiluted concentration of 10 mg/mL for 3 months, at which point she experienced excellent hair regrowth. A small patch of recurrence was noted a year later and treated twice with monthly triamcinolone injections.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).




