Yellow-Brown Ulcerated Papule in a Newborn
The Diagnosis: Congenital Self-healing Reticulohistiocytosis
Biopsy of a representative lesion from this patient was consistent with congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis, as shown in the Figure. Characteristic Langerhans cells were present in the dermis that stained CD1a positive, S-100 positive, and CD68 negative to confirm the diagnosis.
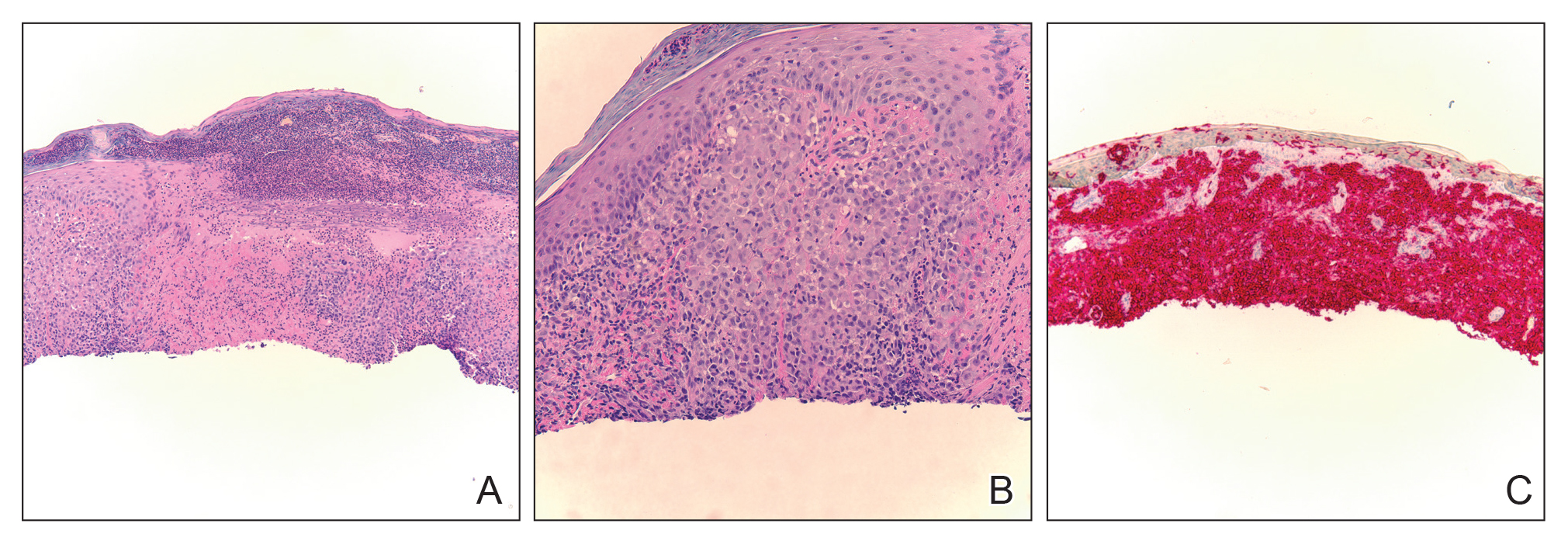
Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis, or Hashimoto-Pritzker syndrome, is a rare benign form of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. It is twice as common in males than females and typically noted at birth or early during the neonatal period. Lesions may present as pink, firm, asymptomatic papulonodular lesions that often ulcerate with possible residual hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation.1 The differential diagnosis includes congenital infectious and hematologic diseases typically associated with blueberry muffin baby. Thus, varicella, cytomegalovirus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella, neuroblastoma, leukemia cutis, and extramedullary hematopoiesis, among others, may be considered. Juvenile xanthogranuloma or urticaria pigmentosa also enter the differential diagnosis given the yellow-brown appearance. As a clonal proliferation of Langerhans cells, pathology reveals lesions that stain positive for CD1a and S-100.2
Although typically absent, evaluation for systemic involvement is warranted, which may be an early presentation of multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Continued monitoring is recommended given the risk of relapse and associated mortality. Our patient continues to do well. He will continue to be followed by our team and hematology/oncology during early childhood.
,The treatment of congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis may include conservative monitoring, topical steroids, topical nitrogen mustard, tacrolimus, or psoralen plus UVA.3 Surgical excision may be considered for large lesions.




