Hypotrichosis and Hair Loss on the Occipital Scalp
The Diagnosis: Monilethrix
A diagnosis of monilethrix was rendered based on the clinical and trichoscopic findings. Simple surveillance of the patient’s condition and prevention of further hair trauma were proposed as management options.
Monilethrix is a hair shaft disorder that is inherited in a predominantly autosomal-dominant pattern with variable expressiveness and penetrance resulting from heterozygous mutations in hair keratin genes KRT81, KRT83, and KRT86 in a region of chromosome 12q13.13.1,2 An autosomalrecessive form has been described with mutation in desmoglein 4, but it differs from the classical form by the variable periodicity of the region between the nodules.3,4
The morphologic alteration consists of the formation of fusiform nodules of normal structure alternated with narrow and dystrophic constrictions (Figure). These internodes are fragile areas that cause breakage at constricted points.5 Clinically, monilethrix presents as areas of focal or diffuse alopecia with frequent involvement of the terminal follicles, mainly in areas of friction. The hair is normal at birth due to the predominance of lanugo in the neonatal period, but it subsequently is replaced by abnormal hairs in the first months of life.6 Initial clinical signs begin to appear when the terminal hairs begin to form.7 Although rarer, the eyebrows and eyelashes, as well as the axillary, pubic, and body hair, may be involved.5
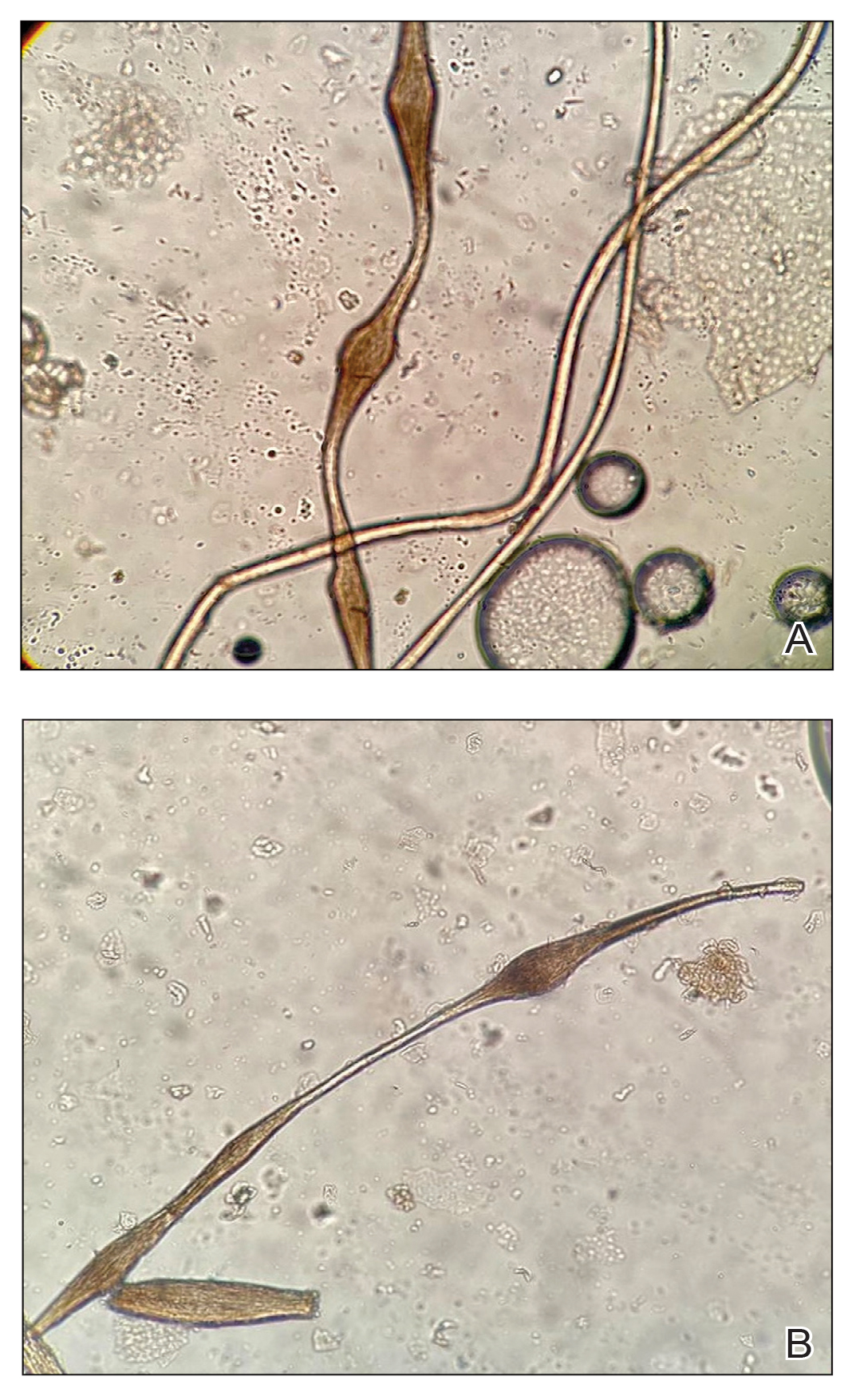
Other hair shaft anomalies merit consideration in the differential diagnosis of monilethrix, including pseudomonilethrix, pressure alopecia, trichorrhexis invaginata, ectodermal dysplasia, tinea capitis, and trichothiodystrophy.6 The diagnosis is reached by clinical history and physical examination. Trichoscopy and light microscopy are used to confirm the diagnosis. Trichoscopic examination shows markedly higher rates of anagen hair. The shafts examined in our patient revealed 0.7- to 1-mm intervals between nodes. Hair can be better visualized under a polarized microscope, and the condition can be distinguished from pseudomonilethrix using this approach.5,6 In our patient, the diagnosis was made based on light microscopy and trichoscopic findings with no genetic testing; however, genetic testing for the classic mutations of the keratin genes would be desirable to confirm the diagnosis but was not done in our patient.6 The prognosis of monilethrix is variable; most cases persist into adulthood, though spontaneous improvement may occur with advancing age, during summer, and during pregnancy.8
There is no definitive therapy for monilethrix. Although there have been reports of cases treated with systemic corticosteroids, oral retinoids, topical minoxidil, vitamins, and peeling ointments (desquamative oil), the cornerstone of management is protecting the hair against traumatic procedures such as excessive combing, brushing, and friction, as well as parent and patient education about the benign nature of the condition.9 Additionally, some cases have shown improvement with minoxidil solution at 2% and 5% concentrations, oral minoxidil, or acitretin.7-9




